When it comes to work and power tools, there’s a question that many 16-year-olds may be wondering: can they use power tools at their job? Well, let’s uncover the answer together!
You might be eager to work with power tools and have the skills, but there are some regulations in place to ensure your safety. So, let’s dive into the world of power tools and find out if you can get your hands on them!
Whether you’re interested in construction, woodworking, or any other field that involves power tools, let’s explore the rules and guidelines that determine if a 16-year-old can use power tools at work. So, let’s get started and discover what’s in store for young workers like yourself!
Curious about the use of power tools in the workplace for 16-year-olds?
Although regulations may vary depending on the jurisdiction, in many places, 16-year-olds are allowed to use power tools at work. However, certain safety measures need to be followed. Employers should provide proper training, supervision, and personal protective equipment for young workers. It’s crucial to prioritize safety and ensure that young workers understand the risks and precautions associated with power tool use.
Can a 16 Year Old Use Power Tools at Work?: Exploring the Safety and Legal Considerations
When it comes to the use of power tools in the workplace, safety is of utmost importance, especially when it involves young workers. This article delves into the question of whether a 16-year-old can use power tools at work, examining the safety and legal considerations surrounding this issue. By understanding the guidelines and regulations in place, employers and young workers can make informed decisions to ensure a safe and productive work environment.
Safety Guidelines for Young Workers Using Power Tools
Employers have a duty to protect young workers and ensure their safety when using power tools. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) provides specific guidelines for businesses to follow when employing workers under the age of 18. These guidelines address several key areas:
- Training and Supervision: Before allowing a 16-year-old to use power tools, employers must provide comprehensive training on the safe use of these tools. Proper training should cover topics such as operation, maintenance, safety precautions, and emergency procedures. It is essential for employers to ensure that young workers possess the necessary knowledge and skills to use power tools safely.
- Age and Physical Capabilities: While there is no specific age restriction for using power tools, employers should consider the physical and emotional maturity of young workers. Factors such as strength, coordination, concentration, and ability to follow instructions play a significant role in determining if a 16-year-old is capable of safely operating power tools. Employers should assess these factors on an individual basis before allowing young workers to use power tools.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Adequate PPE is crucial for the safety of young workers using power tools. Employers must provide appropriate PPE, such as safety goggles, ear protection, gloves, and steel-toed boots, to mitigate the risk of injuries. Regular inspections and replacement of damaged PPE are necessary to ensure their effectiveness.
Proper Equipment Use and Maintenance
Employers must ensure that young workers understand how to properly use and maintain power tools to prevent accidents. This includes:
- Proper Operation: Young workers must be trained to use power tools correctly, following manufacturers’ instructions and guidelines. They should understand the limitations of each tool and avoid using tools for purposes they were not designed for. It is critical to emphasize the importance of caution and attentiveness throughout the entire operation process.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of power tools is essential to ensure their optimal performance and prevent malfunctions. Young workers should be taught how to inspect tools for damage, clean them properly, and report any issues to their supervisors. Understanding the importance of regular maintenance can help prevent accidents caused by faulty equipment.
- Emergency Procedures: Young workers should be educated on emergency procedures in the event of an accident or injury. This includes knowing how to safely shut off power tools, seeking immediate medical attention, and reporting incidents to supervisors. By preparing young workers for potential emergencies, employers can minimize the impact of accidents in the workplace.
Legal Considerations for Young Workers Using Power Tools
Alongside safety guidelines, there are legal considerations that employers and young workers should be aware of when it comes to using power tools in the workplace:
- Minimum Age Requirements: The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) sets the minimum age requirements for various occupations, including the use of power tools. According to federal law, a 16-year-old may operate most power tools, excluding those considered particularly hazardous, such as chainsaws or certain types of saws. State laws may impose additional restrictions, so it is essential to consult both federal and state regulations.
- Work Hour Restrictions: The FLSA also establishes work hour restrictions for young workers. These restrictions vary based on age and time of year, with stricter regulations in place during school hours or summertime. Employers should ensure that young workers using power tools comply with these work hour restrictions to protect their well-being and comply with the law.
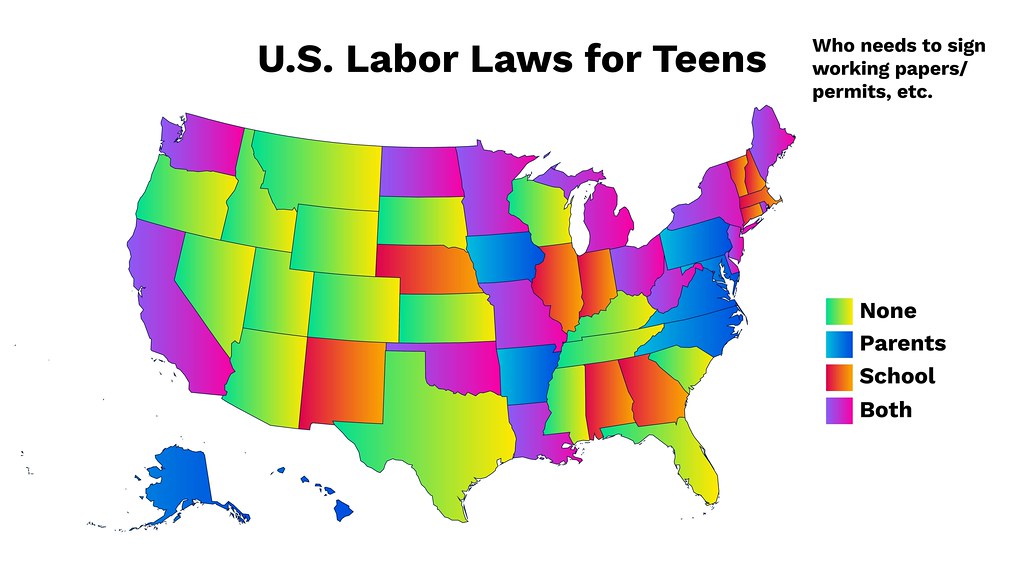
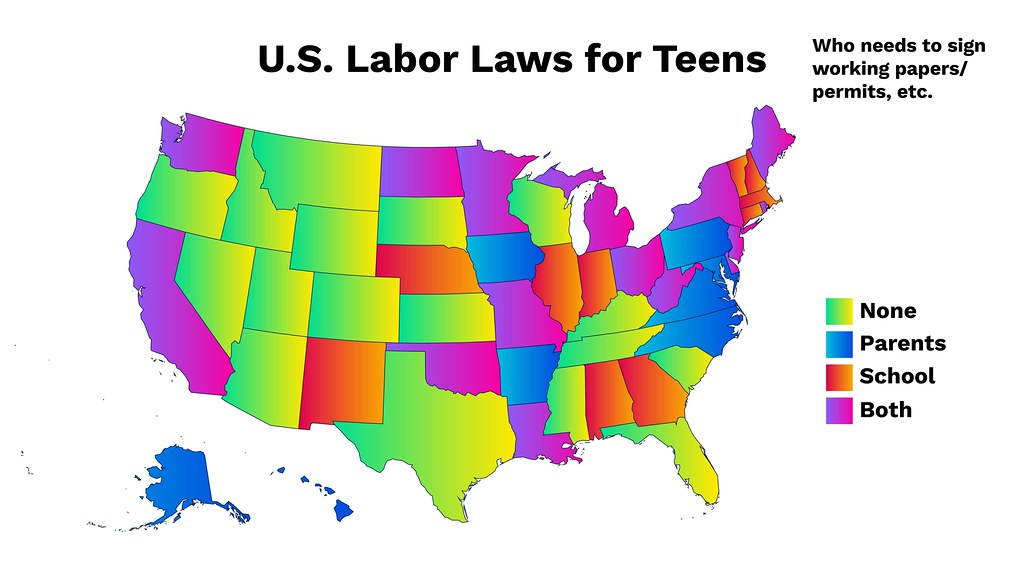
- Work Permit Requirements: Some states may require work permits or employment certificates for young workers, including those using power tools. These permits typically involve parental consent, proof of age, and verification of school enrollment. Employers must familiarize themselves with their state’s requirements and secure any necessary permits before allowing young workers to operate power tools.
Training and Supervision: Keys to Safe Power Tool Usage for Young Workers
Providing proper training and supervision is essential to ensure the safety of young workers using power tools. By doing so, employers can create a work environment where young workers can develop valuable skills while minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries. Here are three crucial aspects to focus on:
Comprehensive Training Programs
Employers should establish comprehensive training programs to equip young workers with the knowledge and skills necessary for safe power tool usage. These training programs should cover:
- Tool-Specific Training: Provide detailed training on how to safely operate each power tool commonly used in the workplace. This should include instruction on proper ergonomics, correct posture, and body mechanics to prevent strain or repetitive motion injuries.
- Hazard Awareness: Educate young workers on recognizing potential hazards associated with power tool usage, such as electrical shock, kickback, and flying debris. Teach them how to mitigate these risks through proper safety measures.
- Emergency Preparedness: Train young workers on emergency procedures, including first aid techniques and how to respond in the event of an accident or injury. This will ensure they can quickly and effectively respond to any unexpected situations.
Supervision and Mentorship
Appropriate supervision and mentorship play a crucial role in guiding young workers as they gain experience using power tools. Employers should:
- Assign Skilled Mentors: Pair young workers with experienced employees who can provide hands-on guidance and mentorship. These mentors can offer insights, answer questions, and correct any unsafe behaviors, ensuring the younger workers develop the skills needed for safe power tool usage.
- Regularly Assess Competency: Supervisors should regularly assess young workers’ competency in using power tools. This can be done through practical assessments or quizzes to evaluate their understanding of safety procedures and tool operation. Continuous feedback and support are essential for their growth and development.
- Encourage a Safety Culture: Foster a workplace culture that values safety above all else. Encourage all employees, including young workers, to report unsafe conditions or behaviors without fear of repercussions. By creating an open and supportive environment, employers can proactively address potential safety concerns and provide the necessary resources to ensure ongoing safety.
Benefits of Allowing 16-Year-Olds to Use Power Tools at Work
While there are safety considerations and legal restrictions surrounding 16-year-olds using power tools at work, there are also several benefits to allowing young workers this opportunity:
- Skills Development: The proper use of power tools can be an essential skill for many industries. Allowing 16-year-olds to gain firsthand experience with power tools provides them with valuable skills that can benefit their future careers.
- Increased Confidence and Responsibility: Taking on the responsibility of using power tools in a safe and controlled setting can help young workers develop confidence in their abilities. It also fosters a sense of responsibility and accountability as they learn to handle potentially dangerous equipment.
- Preparation for Higher Education: Many vocational programs and trade schools require proficiency in using power tools. By allowing 16-year-olds to gain experience early on, they can be better prepared for further education and future career opportunities.
Risk vs. Reward: Balancing Safety and Skill Development
The question of whether a 16-year-old can use power tools at work ultimately comes down to striking the right balance between safety and skill development. By following safety guidelines, providing comprehensive training, and ensuring adequate supervision, employers can create an environment where young workers can safely develop valuable skills. With the right support and guidance, 16-year-olds can gain valuable experience with power tools while minimizing the risk of accidents or injuries.
Key Takeaways: Can a 16-year-old use power tools at work?
– Safety regulations vary by country, but in many places, a 16-year-old can use power tools at work under certain conditions.
– Before using power tools, a 16-year-old should undergo proper training and receive supervision from a responsible adult.
– Employers must ensure that the tasks assigned to a 16-year-old with power tools are appropriate for their age and abilities.
– It is important for both employers and employees to understand local labor laws and comply with any age restrictions or requirements.
– Overall, while 16-year-olds can use power tools, their safety and well-being should always be prioritized.
Frequently Asked Questions:
At the age of 16, individuals may have questions about using power tools at work. Here are some common queries and their answers:
1. Are 16-year-olds allowed to use power tools at work?
Yes, 16-year-olds are generally allowed to use power tools at work, but there are some restrictions in place to ensure their safety. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) in the United States permits 16 and 17-year-olds to operate specific power tools, including electric drills, nail guns, and circular saws. However, more hazardous tools such as chainsaws, power-driven woodworking machines, and woodworking saws are generally prohibited for workers under 18. It’s always essential for employers to provide adequate training and supervision to ensure the safety of young workers.
It’s worth noting that laws and regulations regarding the use of power tools by minors may vary from country to country, so it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the specific laws in your region to ensure compliance.
2. Do 16-year-olds require any specific training to use power tools at work?
Yes, 16-year-olds must receive proper training to use power tools effectively and safely. Employers have the responsibility to provide comprehensive training programs that cover the correct operation, maintenance, and potential hazards associated with each specific power tool. This training should also include information about safety gear, such as goggles, gloves, and ear protection, which must be worn when using power tools.
Additionally, it’s important for employers to ensure ongoing supervision and guidance to ensure that young workers are using the tools correctly and adhering to proper safety procedures. By investing in proper training and supervision, employers can create a safer work environment for 16-year-olds using power tools.
3. Are there any time restrictions on when 16-year-olds can use power tools at work?
Yes, there are time restrictions on when 16-year-olds can use power tools at work. According to the FLSA, 16 and 17-year-olds are generally prohibited from operating power tools during school hours when they are required to attend vocational or technical training programs. However, outside of school hours, these individuals can operate power tools within the limits of the law and applicable regulations.
It’s important for employers to consult the specific regulations in their region to ensure compliance with both age and time restrictions on the use of power tools by 16-year-olds.
4. Can 16-year-olds work with power tools in all industries?
While 16-year-olds are generally allowed to work with power tools, the specific industries in which they can use these tools may vary. Some industries, such as construction and manufacturing, may have more opportunities for 16-year-olds to work with power tools, while others, such as healthcare or retail, may have fewer occasions for power tool usage. It’s crucial for young workers to be aware of the industries they are interested in and the associated regulations in their region.
Regardless of the industry, employers have a responsibility to ensure the safety of young workers using power tools. This includes providing necessary training, supervision, and safety equipment.
5. What safety precautions should 16-year-olds take when using power tools at work?
When using power tools at work, 16-year-olds should always prioritize safety. Here are some important precautions to take:
Firstly, it’s crucial to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety goggles, gloves, and hearing protection. These items can help prevent injuries from flying debris, loud noises, and potential hazards.
Secondly, 16-year-olds should ensure that they have received proper training on the correct operation and maintenance of each power tool they are using. They should also familiarize themselves with the specific safety features and precautions for each tool they work with. Additionally, it’s important to follow all safety guidelines and procedures outlined by the employer. If any concerns or uncertainties arise, workers should immediately consult a supervisor or experienced colleague for guidance.

Summary
So, can a 16-year-old use power tools at work? Well, it depends on the country and the specific job. In some places, there are laws that restrict young people from operating certain types of power tools. It’s important to check the rules and regulations in your area to know for sure.
If you’re interested in using power tools, it’s a good idea to start with proper training and supervision. Taking a class or shadowing an experienced worker can help you learn how to use power tools safely. Remember, safety should always come first when it comes to using any kind of tool, especially when you’re young and still gaining experience.
In conclusion, while the rules may vary, it’s essential to prioritize safety and follow the guidelines set out by your local laws and regulations.