Have you ever wondered how a centre lathe works? Well, you’re in the right place! In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of centre lathes and unravel the mysteries behind their functioning. So, sit back, relax, and get ready to embark on an exciting journey into the world of machining!
When it comes to machining and shaping metal, the centre lathe is a true champion. But how does it actually work? Picture this: a cylindrical workpiece is fixed between two points, with one end supported by a stationary headstock and the other end rotating against a cutting tool. As the workpiece rotates, the cutting tool removes material, resulting in precise and smooth surfaces.
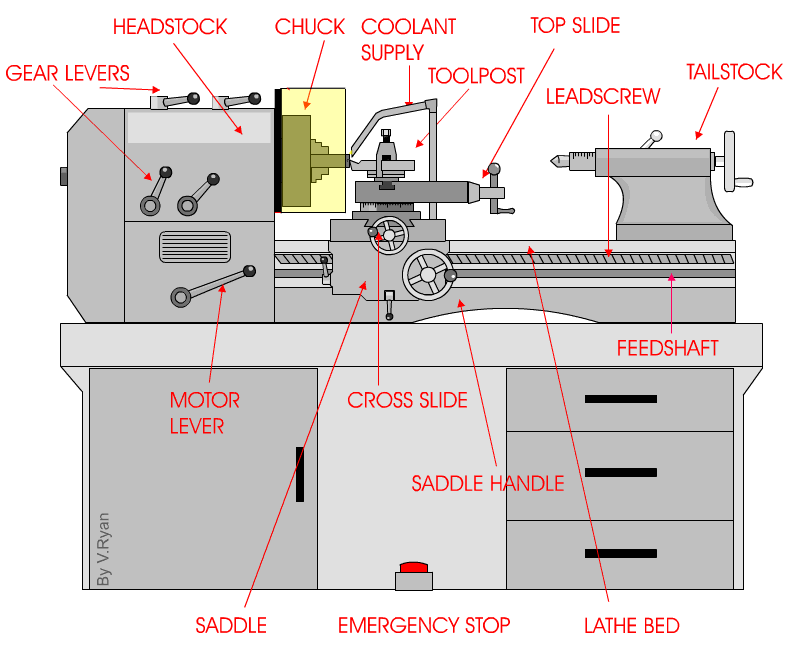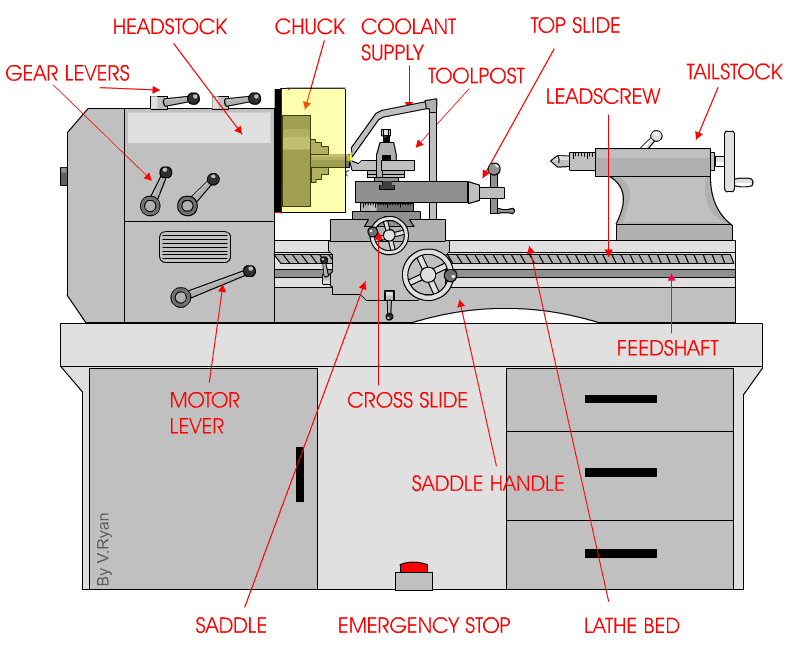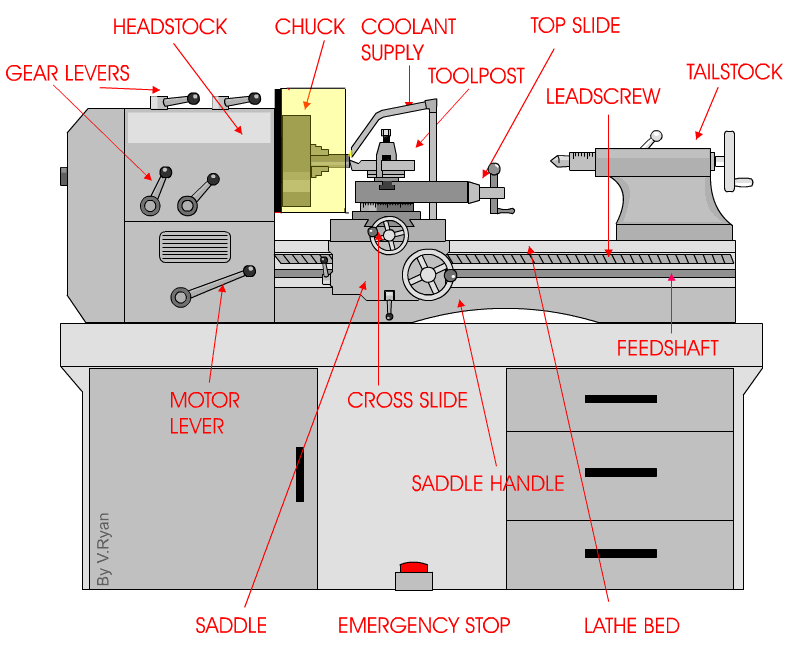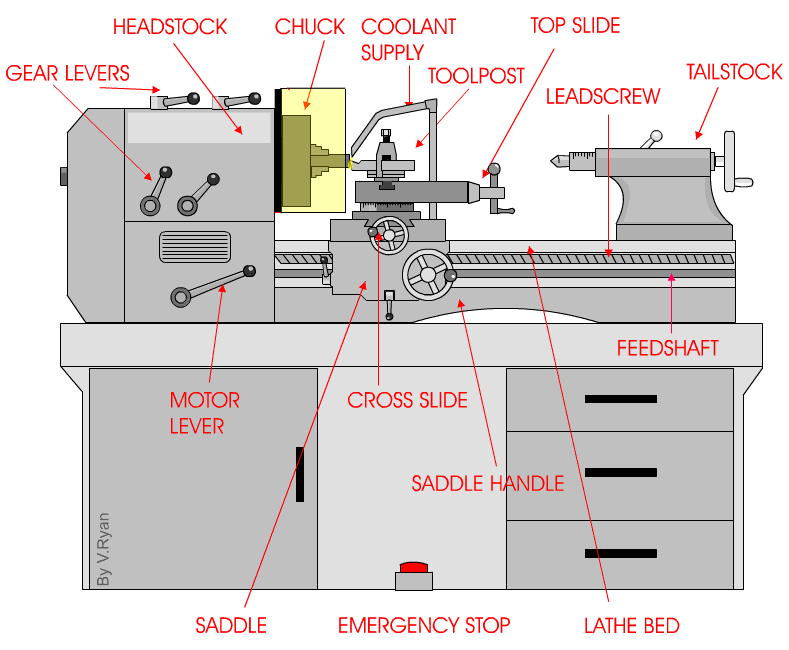
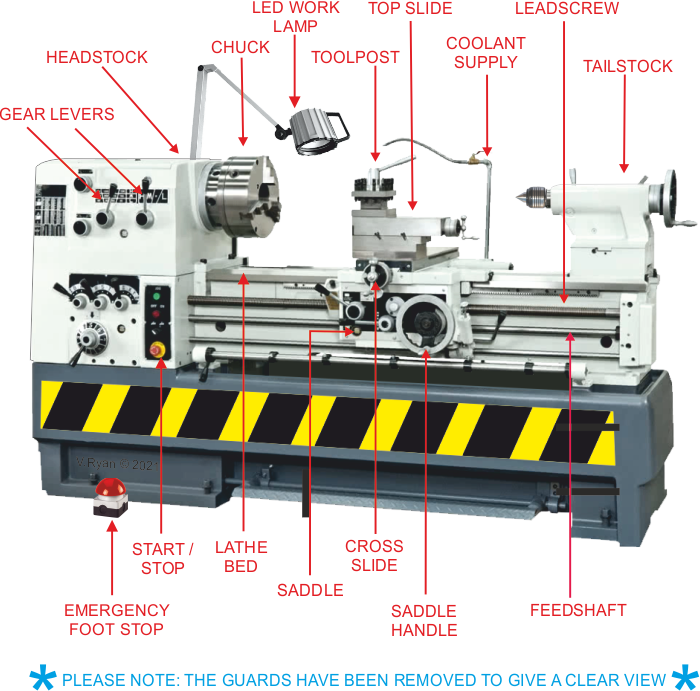
But wait, there’s more! Centre lathes are equipped with various components that work together to produce outstanding results. From the headstock that houses the main spindle to the tailstock that provides additional support, each part plays a crucial role in the machining process. It’s like a symphony of metalwork, creating intricate and functional pieces with skill and precision.
So, are you ready to dive deeper into the inner workings of a centre lathe? Let’s explore the different parts and functions to unravel the craftsmanship behind this powerful machine. Get ready to be amazed as we unlock the world of centre lathes and discover how they bring imagination to life through metalwork. Let’s get started!
How Does a Centre Lathe Work? An In-Depth Look into the Mechanics and Functions
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how a centre lathe works. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics and functions of this versatile machine. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced machinist, understanding the inner workings of a centre lathe is crucial to mastering its operation. So, let’s dive in and explore the intricacies of this essential tool in the manufacturing industry.
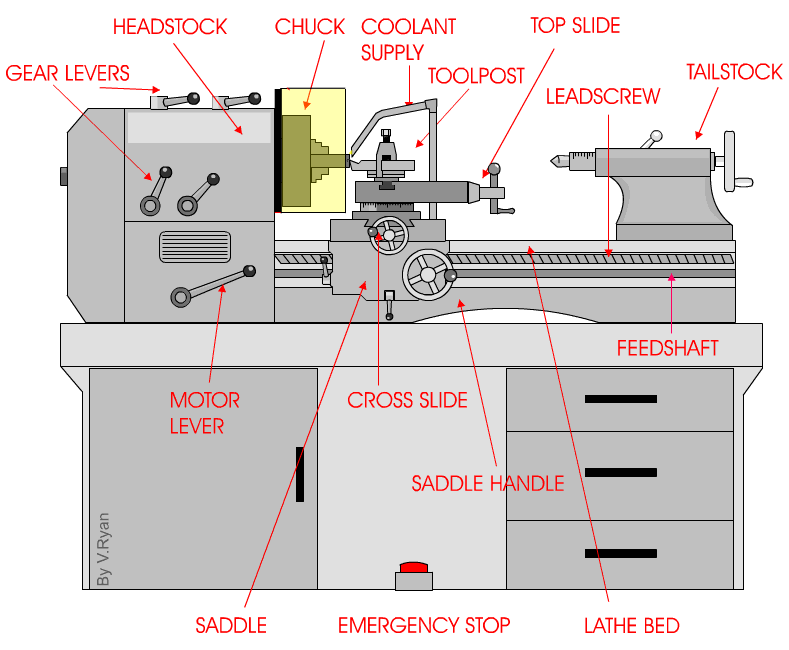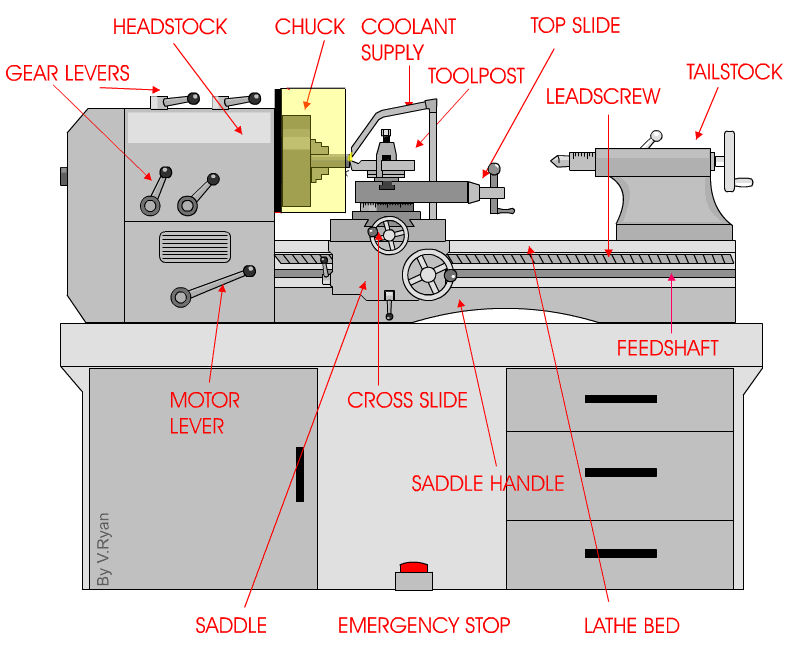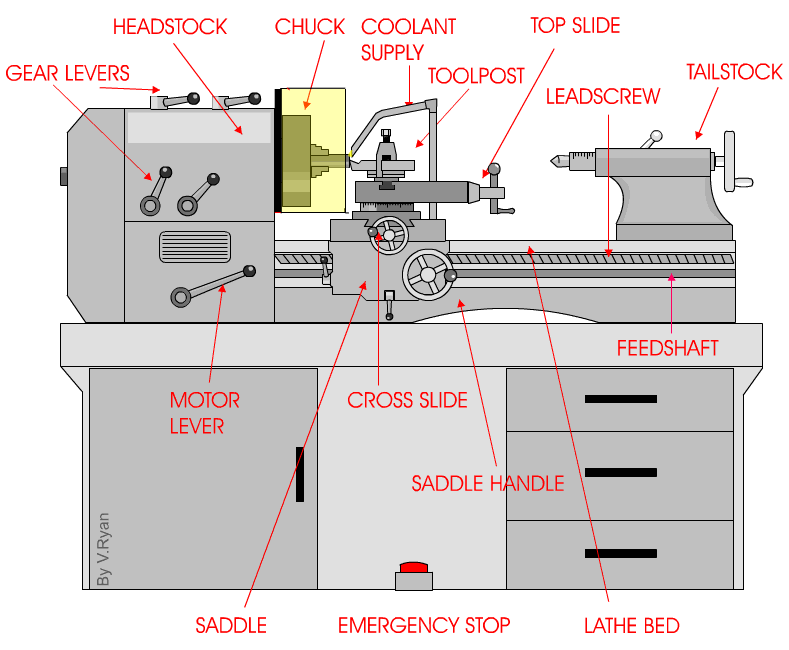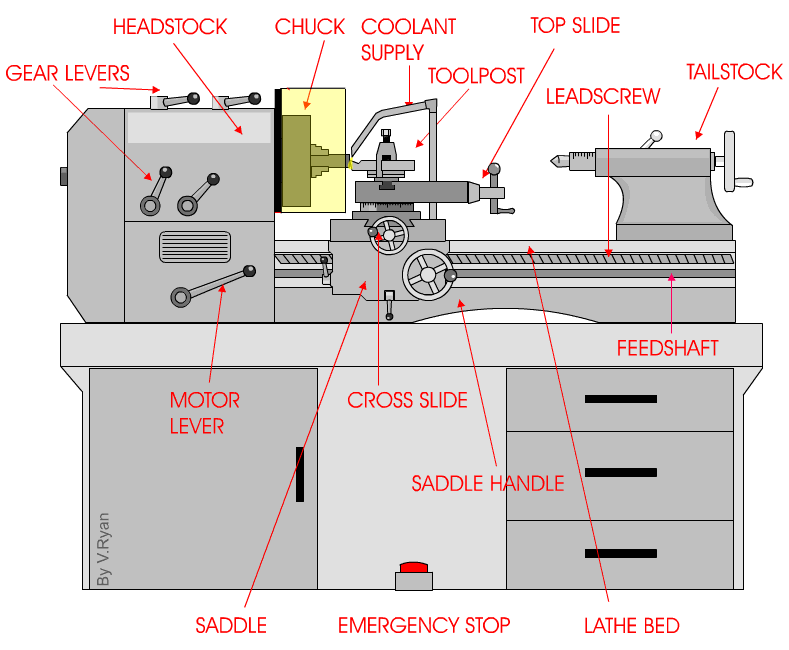
The Components of a Centre Lathe: From Headstock to Tailstock
At a glance, a centre lathe may seem like a complex piece of machinery, but when broken down into its components, it becomes much more manageable to understand. Let’s start from the headstock, which houses the main motor and spindle. The spindle is responsible for rotating the workpiece, allowing for the turning process to occur. Connected to the headstock is the gearbox, which provides multiple speed options for the spindle. Moving along, we have the bed, a sturdy and rigid base that supports the entire lathe. The carriage, saddle, and cross slide are mounted on the bed and allow for the movement of the cutting tool. Lastly, we have the tailstock, which can be used to support long workpieces and provide additional stability.
The Headstock: Powering the Rotation
The headstock of a centre lathe is the powerhouse. It houses the main motor that drives the rotation of the spindle. The spindle is driven by a series of belts or gears, depending on the lathe’s design. The motor can be adjusted to provide different speeds, allowing machinists to work with various materials and achieve desired cutting speeds. The spindle itself is precision-made and holds the workpiece securely in place during the turning process. It is also equipped with a chuck or faceplate, which grips the workpiece and rotates it.
The gearbox, located within the headstock, allows for the selection of different speeds. By engaging various gears, machinists can match the rotational speed of the spindle to the requirements of the material being worked on. This flexibility is essential when working with materials of different densities or when performing specific cutting operations that require varying speeds.
The Bed: A Solid Foundation for Precision Machining
The bed is a crucial component of a centre lathe and provides a sturdy and stable platform for machining operations. Typically made of cast iron, the bed is precisely machined and hardened to ensure rigidity and reduce vibrations. It serves as the foundation on which all other components of the lathe are mounted. The length of the bed determines the maximum length of the workpiece that can be accommodated.
On the bed, we find the carriage, saddle, and cross slide. The carriage is responsible for holding and moving the cutting tool and is mounted on the saddle. The saddle, in turn, moves along the bed’s length, allowing for longitudinal movements of the cutting tool. The cross slide is attached to the carriage and enables lateral movements of the cutting tool, allowing for precise shaping and finishing of the workpiece.
The Tailstock: Supporting Longer Workpieces
The tailstock is located on the opposite end of the lathe from the headstock and serves several essential purposes. First and foremost, it provides support for longer workpieces, ensuring stability during the machining process. It is equipped with a quill that can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments based on the length of the workpiece. The quill can be locked in place using a lever, securing the workpiece in position. Additionally, the tailstock may also feature a taper to accommodate different types of tooling, such as drill bits or live centers.
Furthermore, the tailstock can be used for drilling operations, as it can be aligned with the headstock spindle and locked into place. This allows the machinist to hold and drill into the workpiece accurately. The tailstock is an essential feature for turning long or thin workpieces where additional support is required.
The Operations and Capabilities of a Centre Lathe
Now that we have explored the key components of a centre lathe, let’s delve into the various operations and capabilities it offers. From turning and facing to taper turning and threading, a centre lathe allows for a wide range of machining operations. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key functions and techniques employed with this machine.
The Turning Process: A Fundamental Operation
One of the most fundamental operations performed on a centre lathe is turning. Turning involves removing material from the workpiece to create a desired shape, such as a cylinder. The cutting tool is secured in the toolpost, which is mounted on the carriage and can be adjusted to various angles and heights. As the workpiece rotates, the cutting tool is fed in, gradually removing material and shaping the workpiece according to the machinist’s specifications.
The Facing Technique: Creating Flat Surfaces
The facing technique is used to create flat surfaces on the workpiece. It involves positioning the cutting tool perpendicular to the axis of rotation and removing material from the end face of the workpiece. This process ensures that the end face is flat and parallel to the rotation axis, allowing for precise fits and finishes when assembling multiple components.
Taper Turning: Achieving Conical Shapes
Taper turning is a technique employed when a conical shape is required. By offsetting the tailstock quill or adjusting the angle of the cross slide, the cutting tool can be fed in at a gradual rate, creating a tapered surface. This technique is often used in applications such as pipe fittings, where a tight seal is necessary.
Threading: Creating Screw Threads
Threading is the process of creating screw threads on a workpiece. This technique is commonly employed when producing fasteners or components that require a threaded connection. The cutting tool is ground to match the desired thread profile, and the lathe’s lead screw is engaged to ensure the correct pitch and depth of the threads.
In Conclusion
A centre lathe is a versatile and essential tool in the world of machining. Understanding how it works and the various operations it can perform is crucial for anyone looking to delve into the world of metalworking. From the headstock to the tailstock, each component plays a vital role in the machining process. Whether you’re turning, facing, taper turning, or threading, the centre lathe offers a wide range of capabilities to shape and refine workpieces to precision. So, the next time you come across a centre lathe, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for its mechanics and functions.
Key Takeaways: How Does a Centre Lathe Work?
- A centre lathe is a machine used to shape and cut metal, wood, and other materials.
- It works by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool mounted on a spindle.
- The cutting tool continuously removes material from the workpiece to create the desired shape.
- The workpiece is secured between two points, called centres, which provide support and enable rotation.
- Centre lathes allow for precise cutting, turning, facing, and threading operations to be performed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Curious about how a centre lathe works? We’ve got you covered! Read on to find answers to common questions about this fascinating machine.
1. What is the purpose of a centre lathe?
A centre lathe is a machine tool used to shape and cut cylindrical metal or wood workpieces. It rotates the workpiece about its axis, allowing precise cutting, threading, and shaping operations. Essentially, it helps in turning raw materials into finished products by removing excess material and creating the desired shape.
The lathe’s versatility makes it a crucial tool in various industries, such as manufacturing, automotive, and construction. From creating intricate details to producing large-scale components, the centre lathe provides the precision and control needed for a wide range of applications.
2. How does a centre lathe work?
A centre lathe operates through a combination of movements facilitated by different components. The workpiece gets clamped onto the spindle, rotating it as the lathe’s power source drives the spindle. The cutting tool, positioned against the workpiece, then removes material as the workpiece rotates.
The operator can adjust the speed and depth of the cutting tool, enabling the creation of intricate designs and precise cuts. With various attachments and accessories, such as chucks and steady rests, the lathe can accommodate different workpiece sizes and shapes. The lathe’s precise control over the cutting operation ensures repeatable accuracy and high-quality finished products.
3. What are the main parts of a centre lathe?
A centre lathe consists of several essential parts, each playing a crucial role in its operation. The key components include the bed, headstock, tailstock, carriage, and cutting tool. The bed provides a sturdy base and support for the other parts. The headstock houses the motor and spindle, which rotates the workpiece. The tailstock supports the other end of the workpiece, ensuring stability during machining.
The carriage holds the cutting tool and moves along the bed, guiding the tool’s position relative to the workpiece. It helps control the depth, feed rate, and direction of the cutting operation. The cutting tool, often made of high-speed steel or carbide, removes material from the workpiece while creating the desired shape. These parts work cohesively to facilitate the lathe’s precise functioning.
4. What are the advantages of using a centre lathe?
Using a centre lathe offers numerous advantages in the machining process. Firstly, it allows for the creation of complex shapes and profiles with great precision. The operator has full control over the cutting tool’s speed, depth, and movement, making it possible to produce intricate designs and details.
Additionally, a centre lathe enables efficient material removal, reducing waste and saving costs. By precisely cutting away excess material, the lathe helps create finished products with minimal loss. Moreover, the lathe’s versatility allows for the machining of various types of materials, including metals and wood, catering to a wide range of industries and applications.
5. What safety precautions should be followed when operating a centre lathe?
When operating a centre lathe, it is essential to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Some important precautions include wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety glasses, gloves, and a face shield.
Furthermore, operators should be familiar with the machine’s controls, ensuring that they understand how to stop and start the lathe safely. Regular maintenance and inspection of the machine and its components are also vital to ensure its proper functioning and minimize risks. Lastly, operators should receive proper training and follow all safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer to use the centre lathe safely and efficiently.
Summary
So, here’s a quick summary of how a centre lathe works. It’s a machine that spins a workpiece while a cutting tool shapes it. The lathe has different parts like the chuck, spindle, and carriage that all work together to make it happen. You can use a lathe to make things like cylinders, cones, and even threads. It’s a cool machine that can create lots of different shapes! So, next time you see a lathe, you’ll know exactly what it’s doing. Pretty neat, huh?
In conclusion, a centre lathe is a machine that spins a workpiece while a cutting tool is used to shape it. It has different parts that work together in the process, and it can make various shapes like cylinders and cones. Now you know the basics of how a centre lathe works.