Are you curious about how an engine lathe works? If so, you’ve come to the right place! Engine lathes are fascinating machines used to shape and cut various materials. In this article, we’ll delve into the inner workings of an engine lathe and explore how it operates.
So, let’s dive right in and discover the magic behind an engine lathe. Imagine a spinning wheel, like the ones you see on game shows or at carnivals. Now, picture that wheel being used to shape metal or wood instead of picking lucky contestants. That’s essentially what an engine lathe does – it spins the workpiece while a cutting tool shapes and cuts it.
With different settings and adjustments, an engine lathe can create a variety of shapes and cuts. By carefully controlling the rotation speed, feed rate, and positioning of the cutting tool, skilled operators can transform raw materials into precise and intricate designs. It’s like a master sculptor using a magical spinning wheel to bring their creations to life!

How Does an Engine Lathe Work?
Welcome to our guide on how engine lathes work. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of an engine lathe and provide you with a comprehensive understanding of its functions and uses. Whether you are a novice enthusiast or a seasoned machinist, this article will help you gain valuable insights into this essential tool in the world of metalworking.
The Basics of an Engine Lathe
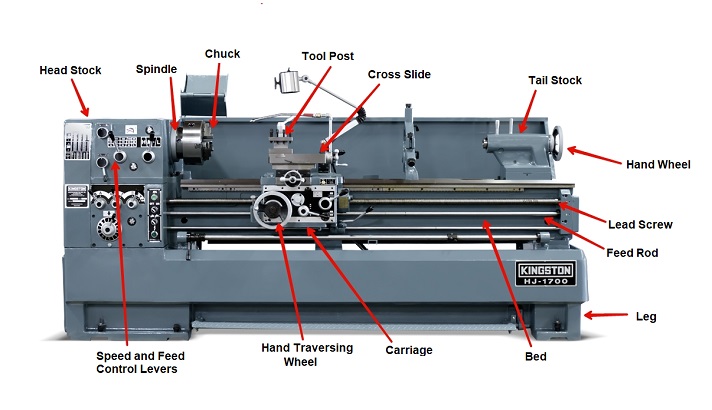
An engine lathe is a powerful machine used in metalworking to shape and cut cylindrical metal pieces with precision. It consists of various components, including a bed, headstock, tailstock, carriage, and tool post. Let’s dive into the details of how each of these parts operates to perform intricate turning and facing operations.
The Bed
The bed is the foundation of an engine lathe and provides a stable platform for the other components. It is typically made of cast iron and designed to withstand the heavy vibrations and forces generated during machining. The bed’s flat and rigid surface ensures accurate alignment of the lathe’s other components and helps maintain the cutting tool’s precise position.
It is important to note that the length of the bed determines the maximum size of the workpiece the lathe can accommodate. Engine lathes come in various sizes, with beds ranging from a few feet to several meters in length.
Furthermore, the bed is equipped with precision ways, which are accurately machined surfaces that guide the movement of the carriage and tailstock along the length of the bed. These ways, often lined with material like Turcite, reduce friction and ensure smooth and precise motion.
The Headstock
The headstock is located at the left end of the bed and houses the main spindle. The spindle serves as the primary rotating element in the engine lathe and is responsible for gripping and driving the workpiece. It is usually powered by an electric motor, which provides the necessary rotational power and speed control.
The spindle is mounted on precision bearings, allowing it to rotate smoothly and accurately. It also features a chuck or other types of workholding devices, such as collets or faceplates, which securely hold the workpiece in place during machining. The headstock often includes a gearbox to provide a range of spindle speeds and allow for the selection of the most appropriate speed for different materials and cutting operations.
Another crucial component within the headstock is the feed rod or lead screw. This mechanism allows for the automatic longitudinal movement of the carriage, enabling the cutting tool to traverse the length of the workpiece.
The Carriage and Tool Post
The carriage is responsible for moving the cutting tool along the length of the workpiece. It consists of several components, including the saddle, cross slide, compound rest, and tool post.
The saddle rides back and forth on the ways of the lathe bed and supports the cross slide. The cross slide, in turn, enables the cutting tool to move perpendicular to the workpiece’s rotational axis, allowing for facing and taper turning operations. The compound rest sits on top of the cross slide and provides additional tool positioning options. It allows for angular tool movements, facilitating chamfering, threading, and other complex machining tasks.
The tool post is attached to the compound rest and securely holds the cutting tool in place. It allows for quick and easy tool changes and adjustments, ensuring efficient operation and accurate machining. Engine lathes often have a variety of tool post designs, including quick-change tool post systems, enabling operators to swap tools rapidly without losing precious time.
How Does an Engine Lathe Work: The Machining Process
Now that we have covered the main components of an engine lathe, let’s explore the step-by-step process of how it operates to shape and cut metal:
Step 1: Workpiece Preparation
The first step is to select the appropriate workpiece and secure it in the lathe using the appropriate workholding device, such as a chuck or a collet. The workpiece should be centered and securely clamped to prevent any movement during machining.
Step 2: Tool Selection and Setup
Next, choose the correct cutting tool for the desired operation. Insert it into the tool post, ensuring it is securely tightened. Adjust the tool height and position as needed for precise machining.
Step 3: Setting the Speed and Feed Rates
Select the appropriate spindle speed based on the workpiece material and cutting operation. Adjust the feed rates to control the speed at which the cutting tool traverses the workpiece.
Step 4: Engaging the Spindle and Starting the Lathe
Engage the spindle, allowing it to rotate the workpiece. Start the lathe motor and gradually increase the speed to the desired setting.
Step 5: Feeding the Cutting Tool
Using the feed rod or lead screw, engage the carriage and begin feeding the cutting tool into the workpiece. Monitor the machining process closely, making any necessary adjustments to the tool position, speed, or feed rates as needed to achieve the desired shape and surface finish.
Step 6: Finalizing the Machining Operation
Once the desired dimensions and surface finish are achieved, disengage the spindle and stop the lathe. Remove the machined workpiece from the lathe, ensuring it is properly cooled if necessary, and inspect it for accuracy and quality.
Benefits of Using an Engine Lathe
Engine lathes offer a range of benefits that make them indispensable in metalworking operations:
- Precision: Engine lathes allow for precise shaping and cutting of metal workpieces, ensuring high-quality finished products.
- Versatility: Engine lathes can handle a wide variety of materials, sizes, and shapes, making them suitable for diverse machining projects.
- Customization: With an engine lathe, machinists have the flexibility to create unique and intricate designs by manipulating the cutting tool’s position and movement.
- Efficiency: Engine lathes enable efficient material removal, reducing production time and costs.
- Longevity: Well-maintained engine lathes have a long operational life, providing years of reliable service.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how an engine lathe works is essential for anyone involved in metalworking or those who simply have an interest in the field. We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the inner workings of an engine lathe and the machining processes it performs. Armed with this knowledge, you can now appreciate the precision and versatility of this indispensable tool in the world of metal fabrication.
Key Takeaways: How Does an Engine Lathe Work?
- An engine lathe is a machine tool used to shape and size metal objects.
- It works by spinning a workpiece on its axis while a cutting tool removes material to create the desired shape.
- The operator manually controls the lathe’s movement and adjusts settings to achieve precision and accuracy.
- Engine lathes can perform various operations, including turning, facing, threading, and drilling.
- The lathe’s motor provides power to rotate the workpiece at different speeds, allowing for versatility in machining tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our frequently asked questions section where we will address common queries about how an engine lathe works. Whether you’re a beginner or have some knowledge about lathe machines, we aim to provide simple answers to help you understand the basics of how these machines function.
1. What is the purpose of an engine lathe?
An engine lathe is a machine tool used to shape, cut, and turn various materials such as metal, wood, and plastic. It primarily serves the purpose of removing material to create a desired shape or surface finish. Engine lathes are versatile and can be used for a wide range of applications, including creating cylindrical shapes, threads, and chamfers.
With the use of different cutting tools and attachments, an engine lathe allows for the precise and accurate machining of complex parts, making it a vital tool in manufacturing and machining industries.
2. How does an engine lathe work?
At its core, an engine lathe rotates a workpiece while a cutting tool moves in a linear motion to remove material and shape the workpiece. The workpiece is held tightly in the lathe’s chuck or collet, which is connected to the lathe’s spindle. The spindle provides rotational motion to the workpiece.
The cutting tool, held in a tool post, moves perpendicular to the rotating workpiece, with the depth of the cut being controlled by the feed mechanism. As the workpiece and cutting tool interact, material is removed, allowing for precise machining and the creation of the desired shape or surface finish.
3. What are the main components of an engine lathe?
An engine lathe consists of several key components, including the bed, headstock, tailstock, carriage, and the feed and lead screw mechanisms. The bed is a horizontal base that provides support and rigidity to the lathe. The headstock houses the main spindle, while the tailstock supports longer workpieces and provides additional stability.
The carriage holds the cutting tool and moves along the bed’s length, enabling the tool to perform various machining operations. The movement of the carriage is controlled by the feed and lead screw mechanisms, allowing for precise and controlled tool movement. Other components include the chuck or collet, which holds the workpiece, and various controls for spindle speed, feed rate, and depth of cut.
4. What are the different operations performed on an engine lathe?
An engine lathe can perform a wide range of operations, including turning, facing, drilling, boring, threading, and taper turning. Turning involves rotating the workpiece to remove material and create cylindrical shapes. Facing is the process of cutting a flat surface perpendicular to the workpiece axis.
Drilling and boring are used to create holes of various sizes, while threading is the process of cutting external or internal threads. Taper turning allows for the gradual reduction or increase in the diameter of the workpiece. These operations, among others, make the engine lathe a versatile machine capable of performing intricate machining tasks.
5. What are the safety considerations when operating an engine lathe?
Operating an engine lathe requires strict adherence to safety precautions. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection. Ensure the lathe is properly grounded and that the workpiece is securely held in the chuck or collet.
Before starting the lathe, make sure the cutting tools and workpiece are properly aligned and positioned. Avoid loose clothing or jewelry that may become entangled in the lathe’s moving parts. And, most importantly, familiarize yourself with the lathe’s manual, including emergency shutdown procedures, to ensure safe and responsible operation.
Working principle of lathe
Summary
Here’s a quick summary of how an engine lathe works! An engine lathe is a machine used to shape materials like metal. It has a spinning spindle and different tools that help cut and shape the material. When you turn on the engine lathe, the spindle starts rotating, and you use different controls to move the tool and shape the material. It’s like a super precise carving machine!
In essence, an engine lathe works by spinning a spindle and using cutting tools to shape materials. It’s a cool machine that helps create all sorts of things!