Have you ever wondered how a lathe cross feed works? Well, let me break it down for you in a simple and fun way! Imagine you have a lathe machine, which is like a super-powered spinning tool that shapes and cuts metal. Now, picture this – the lathe cross feed is like a magical sidekick that helps move the cutting tool horizontally along the metal to create precise and smooth cuts. Cool, right?
But how does it actually work? Let’s dive in! When you turn on the lathe and set it in motion, the cross feed mechanism kicks into action. It consists of a lead screw, which is like a long threaded rod, and a carriage, which holds the cutting tool. As the lead screw rotates, it engages with the carriage, causing it to move sideways. This movement allows the cutting tool to evenly remove material from the metal workpiece, resulting in a beautifully shaped object.
So, the lathe cross feed is like a trusty assistant that ensures the cutting tool moves just right, giving you precision and control over your work. It’s a fascinating mechanism that makes the magic happen on a lathe machine. Now that you know the basics, let’s explore more about the inner workings and advantages of this incredible feature. Let’s dive deeper into the world of lathe cross feed and unlock its secrets together!
How Does a Lathe Cross Feed Work?
When it comes to understanding how a lathe cross feed works, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the different components and mechanisms involved. The cross feed is an essential function in a lathe machine that allows the cutting tool to move perpendicular to the axis of rotation, enabling precise and controlled machining operations. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the lathe cross feed, exploring its components, operation, and benefits.
Understanding the Components of the Lathe Cross Feed
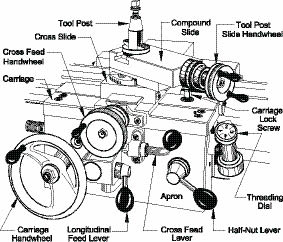
The lathe cross feed is comprised of various components that work together to enable the smooth movement of the cutting tool. One of the main components is the cross slide, which is responsible for carrying the tool holder and allowing it to move transversely. A lead screw, connected to the cross slide, plays a crucial role in converting the rotational movement of the feed rod into the linear movement of the cross slide. Additionally, the feed rod, which is powered by an electric motor or hand-driven mechanism, drives the lead screw, resulting in the desired cross feed motion.
Another important component of the lathe cross feed system is the compound rest, which provides additional support and stability to the cutting tool. It is usually located on top of the cross slide and can be adjusted to achieve different cutting angles. The compound rest works in conjunction with the cross slide to ensure accurate and precise machining operations.
Moreover, the lathe cross feed is controlled by various mechanisms, such as handwheels, micrometer dials, or digital readouts (DRO). These mechanisms allow the operator to determine the desired cross feed rate and make adjustments as needed. Overall, the combination of these components and mechanisms facilitates the smooth and controlled movement of the cutting tool during a lathe operation.
The Operation of the Lathe Cross Feed
Now that we have a basic understanding of the components, let’s explore how the lathe cross feed actually operates. When the operator engages the cross feed, whether manually or through an electric motor, the feed rod begins to rotate. This rotational motion is then transferred to the lead screw, which converts it into linear motion. As the lead screw rotates, it pushes or pulls the cross slide along the lathe’s axis, resulting in the desired cross feed.
The operator can adjust the cross feed rate by controlling the rotation speed of the feed rod or by manipulating the handwheel or micrometer dial attached to the system. This allows for precise control over the depth and width of the cut being made by the cutting tool. It’s important to note that the cross feed rate can vary depending on the requirements of the specific machining operation.
Furthermore, the combination of the cross feed and longitudinal feed, which controls the movement parallel to the lathe’s axis, allows for a wide range of machining operations to be performed, including facing, turning, threading, and tapering. The operator can adjust both the cross feed and longitudinal feed to achieve the desired cutting path and dimensions, resulting in accurate and high-quality machined parts.
The Benefits of Using the Lathe Cross Feed
The lathe cross feed offers several benefits that make it an essential feature in machining operations. Firstly, it allows for precise and controlled machining, ensuring accurate dimensions and surface finishes on the workpiece. The operator can make incremental adjustments to the cross feed rate, finely tuning the cutting tool’s movement to achieve the desired outcome.
Additionally, the cross feed enables efficient material removal, reducing the time and effort required to complete a machining operation. By controlling the depth and width of the cut, the operator can optimize the cutting process and prevent excessive material wastage.
Furthermore, the ability to perform both longitudinal and cross feed movements expands the capabilities of the lathe, allowing for a wide range of machining operations to be performed. From simple turning operations to complex thread cutting and tapering, the lathe cross feed provides the versatility needed in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace.
The Importance of Proper Maintenance for Optimal Lathe Cross Feed Performance
In order to ensure the optimal performance of the lathe cross feed, it is crucial to maintain the various components and mechanisms in good working condition. Regular cleaning and lubrication of the lead screw, cross slide, and compound rest are essential to prevent wear and tear and ensure smooth movement.
Additionally, regular inspection and adjustment of the feed rod’s tension and alignment are important to maintain accurate cross feed rates. Any misalignment or excessive play in the system can result in dimensional inaccuracies and poor surface finishes on the workpiece.
Furthermore, it is important to regularly check for any signs of damage or wear in the handwheels, micrometer dials, or digital readouts. Any faulty or malfunctioning components should be repaired or replaced immediately to avoid compromising the accuracy and functionality of the lathe cross feed.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for the Lathe Cross Feed
While the lathe cross feed is designed to provide smooth and accurate movement, there may be instances when issues arise during its operation. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
1. Sticking or Jerking Motion
If you experience a sticking or jerking motion in the lathe cross feed, it may be due to a lack of lubrication. Ensure that all moving parts are properly lubricated with appropriate lubricants. Clean any debris or dirt that may be causing friction and hindering the smooth movement of the cross feed components.
Additionally, check for any misalignment or damage in the lead screw or feed rod. Misalignment can cause uneven movement, leading to a jerking motion. Adjust or repair any misaligned or damaged components to restore the smooth operation of the lathe cross feed.
Lastly, inspect the handwheels, micrometer dials, or digital readouts for any faults or damage. Faulty mechanisms can cause uneven rotation, resulting in a sticking or jerking motion. Replace or repair any faulty components to ensure smooth and accurate cross feed operation.
2. Inconsistent Cross Feed Rate
If you notice inconsistent cross feed rates during machining operations, it may be due to an issue with the feed rod or lead screw. Check for any damage or wear in these components and replace them if necessary. Inconsistent cross feed rates can affect the accuracy and quality of the machined parts.
Another possible cause of inconsistent cross feed rates is a loose or worn-out handwheel or micrometer dial. Check for any play or damage in these mechanisms and tighten or replace them accordingly. Proper calibration and adjustment of these components are crucial to achieving consistent and accurate cross feed rates.
Lastly, ensure that the cross slide and compound rest are properly aligned and adjusted. Misalignment can result in an uneven cross feed rate. Make the necessary adjustments to align these components and ensure smooth and consistent cross feed movement.
3. Excessive Play in the Cross Feed
If you encounter excessive play or looseness in the cross feed, it may be due to worn-out or damaged components. Check for any signs of wear or damage in the lead screw, cross slide, or compound rest. Replace any worn-out or damaged parts to eliminate excessive play and ensure precise and controlled cross feed movement.
Additionally, inspect the feed rod for any misalignment or damage. Misaligned or damaged feed rod can result in excessive play and inconsistent cross feed. Adjust or replace the feed rod as needed to restore proper cross feed performance.
Lastly, check the tension of the lead screw. Excessive tension can cause binding and restrict the smooth movement of the cross feed. Conversely, insufficient tension can result in excessive play. Adjust the tension of the lead screw accordingly to achieve optimal cross feed performance.
Key Takeaways: How Does a Lathe Cross Feed Work?
- A lathe cross feed refers to the movement of the cutting tool perpendicular to the lathe’s axis.
- This movement allows the cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece, shaping it according to desired specifications.
- The cross feed mechanism consists of a lead screw and a feed nut that work together to control the tool’s lateral movement.
- By turning the lead screw, the feed nut translates the rotational motion into linear movement, adjusting the cross feed rate.
- The operator can adjust the cross feed manually or automatically, depending on the lathe’s capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
The cross feed on a lathe is an essential part of its functionality. It allows for the movement of the cutting tool perpendicular to the workpiece’s axis. Understanding how the cross feed works is crucial for those operating a lathe. Here are some common questions and answers related to the operation of a lathe’s cross feed.
1. How does the cross feed on a lathe work?
The cross feed on a lathe operates through the use of a lead screw and a gear mechanism. The lead screw is connected to the cross slide, which moves the cutting tool. When the lead screw rotates, it engages with the gear mechanism, causing the cross slide to move along the lathe’s bed. This movement enables the cutting tool to make precise cuts on the workpiece.
This mechanism allows for both automatic and manual control of the cross feed. In automatic mode, the lathe’s power feed mechanism moves the cross slide at a consistent rate. In manual mode, the operator manually adjusts the cross feed using the handwheel.
2. What is the purpose of the cross feed on a lathe?
The cross feed is responsible for moving the cutting tool perpendicular to the axis of the workpiece. This movement is essential for various lathe operations, such as facing, grooving, and threading. By adjusting the cross feed, the operator can control the depth and width of the cuts made by the cutting tool.
Without the cross feed, a lathe would only be able to make cuts along the length of the workpiece, limiting its versatility. The ability to move the cutting tool across the workpiece’s diameter opens up a wide range of machining possibilities.
3. How can I adjust the cross feed on a lathe?
To adjust the cross feed on a lathe, you can use the handwheel located on the lathe’s cross slide. Turning the handwheel clockwise or counterclockwise will move the cross slide along the lathe’s bed, adjusting the position of the cutting tool. The handwheel is usually graduated to provide a reference for the amount of movement and precision required.
If your lathe is equipped with an automatic power feed mechanism, you can also engage it to control the cross feed. The power feed mechanism allows for a consistent and controlled rate of movement, ensuring precise cuts. However, it’s important to note that the speed at which the cross slide moves may need to be adjusted based on the requirements of the specific machining operation.
4. Can the cross feed speed be adjusted on a lathe?
Yes, the speed of the cross feed on a lathe can be adjusted. The exact method of adjustment may vary depending on the lathe model, but generally, it involves changing the settings of the power feed mechanism. By adjusting the speed, you can control how quickly or slowly the cross slide moves along the lathe’s bed.
The optimal speed for the cross feed will depend on various factors, such as the material being machined, the desired finish, and the type of cutting tool being used. It’s important to consider these factors and make adjustments accordingly to achieve the best results.
5. What are some safety precautions to keep in mind when using the cross feed on a lathe?
When using the cross feed on a lathe, it’s important to prioritize safety. Here are some key precautions to keep in mind:
First, ensure that the cutting tool is properly secured and aligned. Any loose or misaligned tools can be hazardous and may cause accidents or damage to the lathe or workpiece. Always double-check the tool’s positioning and tighten any fasteners as needed.
Additionally, wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety goggles and gloves, to protect yourself from potential flying debris or contact with sharp edges. Finally, familiarize yourself with the specific safety guidelines and operational procedures outlined in the lathe’s user manual to ensure safe and effective use of the cross feed and other lathe components.
how lathe cross slide feed mechanism works animation
Summary
So, to summarize, a lathe cross feed is a mechanism that moves the cutting tool horizontally. It helps in shaping and finishing workpieces on a lathe machine. The process involves a lead screw that connects to a carriage and enables the movement of the tool with precision. By turning the handle or engaging the power feed, the cross feed controls the depth of the cut and allows for smooth and accurate machining.
In conclusion, the lathe cross feed is an essential part of a lathe machine that enables precise cutting and shaping of workpieces. It is operated through a lead screw and carriage mechanism, providing control over the horizontal movement of the cutting tool. Understanding how the cross feed works is fundamental for anyone looking to operate a lathe machine effectively.