Do you ever wonder how things are made? Let’s talk about something fascinating: the lathe machine! Have you ever seen one? It’s a powerful tool that can shape materials with incredible precision.
So, how does the lathe machine work? Well, imagine a spinning wheel, kind of like a potter’s wheel. The material you want to shape, like wood or metal, is placed on this spinning wheel. As it rotates, a cutting tool is pressed against the material, removing layers until the desired shape is achieved. It’s like sculpting, but with a high-speed twist!
Now, you might be wondering why we need a lathe machine. Well, it’s versatile! From making intricate woodwork like table legs to creating precise metal parts for engines, the lathe machine can do it all. So next time you see a beautifully turned wooden bowl or a precisely shaped metal gear, you’ll know it was made with the magic of a lathe machine. So cool, right?
- Secure the material on the lathe.
- Select the desired speed and turn on the machine.
- Move the cutting tool towards the material to remove material and shape it.
- Adjust the cutting depth and repeat until the desired shape is achieved.
- Turn off the machine, remove the finished piece, and clean the lathe.
Learning how to operate a lathe machine opens up endless possibilities for creating intricate designs and functional objects.
How Does a Lathe Machine Work?
A lathe machine is a versatile tool used in machining and woodworking to shape, cut, drill, and mold materials. It is a key component in manufacturing processes and allows for precise and efficient customization of various workpieces. From creating intricate details on metal or wood to turning large cylindrical objects, the lathe machine plays a crucial role in modern industries and workshops. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of a lathe machine and understand how it operates to produce accurate and high-quality results.
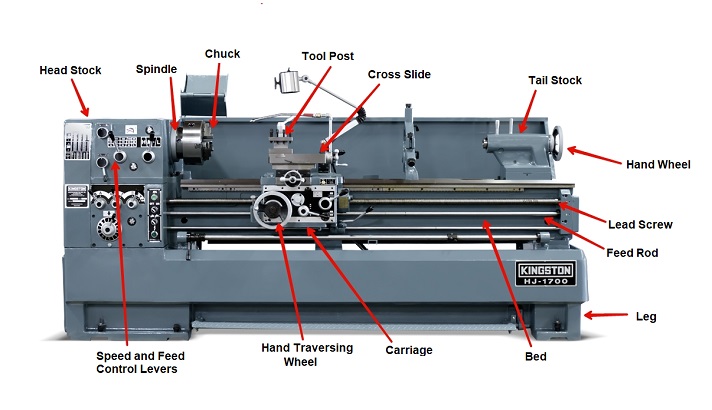
1. The Structure of a Lathe Machine
A lathe machine consists of several key components that work together to achieve different machining operations. The main parts of a lathe machine include:
- Bed: The bed is the base of the machine and provides support and stability.
- Headstock: The headstock houses the main motor, spindle, and gear mechanisms.
- Tailstock: The tailstock supports the opposite end of the workpiece and includes features like a quill and a turret for drilling operations.
- Carriage: The carriage moves along the bed and houses the cutting tools and tool holders.
- Apron: The apron contains the gears, clutches, and levers that control the movement of the carriage.
Understanding the structure of a lathe machine is crucial for comprehending how it functions and how different parts interact with each other to perform various tasks.
2. The Working Principle of a Lathe Machine
The working principle of a lathe machine is based on the rotation of a workpiece around its axis. The machine tool holds the workpiece securely while the cutting tool or tools remove the material to shape or finish it. Here are the main steps involved in the working principle of a lathe machine:
- Mounting the workpiece: The workpiece is securely mounted and centered on the lathe machine using methods such as collets, chucks, or centers.
- Selecting the cutting tool: Depending on the desired operation, the appropriate cutting tool is chosen and installed on the tool holder.
- Setting the desired feed rate: The feed rate is the speed at which the cutting tool moves along the workpiece. It must be adjusted based on the material and desired finish.
- Engaging the lathe machine: Once everything is set, the machine is turned on, and the cutting tool is brought into contact with the workpiece.
- Performing the machining operation: The cutting tool removes material from the workpiece by rotating around its axis or moving along its length, depending on the desired operation.
By controlling the movement of the cutting tool and adjusting various parameters, a lathe machine can perform tasks such as turning, drilling, facing, grooving, and threading with precision and accuracy.
3. Types of Lathe Machines
There are several types of lathe machines, each designed for specific applications. Here are some common types of lathe machines:
- Engine Lathe: This type of lathe machine is the most common and versatile. It is used for a wide range of tasks, including turning, facing, threading, and tapering.
- Turret Lathe: A turret lathe is known for its ability to perform multiple operations without manual intervention. It has a rotating turret that holds various cutting tools, allowing for quick tool changes and efficient machining.
- Speed Lathe: As the name suggests, a speed lathe is designed for high-speed operations. It is used for tasks like centering, polishing, and resizing small workpieces.
- Bench Lathe: A bench lathe is compact and suitable for workshops or hobbyists. It is used for small-scale projects and lighter materials.
4. Advantages of Using a Lathe Machine
Lathe machines offer several benefits that make them essential tools in various industries. Some advantages of using a lathe machine include:
- Precision: Lathe machines allow for highly precise and accurate machining, ensuring consistent quality in the final product.
- Versatility: With the ability to perform a wide range of operations, lathe machines can handle diverse projects and materials.
- Efficiency: Lathe machines enable efficient material removal and promote faster production rates, saving both time and costs.
- Versatility: With the ability to perform a wide range of operations, lathe machines can handle diverse projects and materials.
- Automation: Advanced lathe machines can be automated and integrated into computer numerical control (CNC) systems, allowing for increased productivity and reduced human errors.
Common Lathe Machine Operations
After understanding how a lathe machine works, let’s delve into some common operations it can perform.
1. Turning
Turning is the primary operation carried out on a lathe machine. It involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to create a desired shape, dimension, or finish. Turning is used to create cylindrical shapes, tapering, and smoothing surfaces.
2. Facing
Facing is the process of creating a flat surface on the end of a workpiece. It is commonly used to ensure precise alignment of two workpieces or for creating a smooth and even surface for joining or mating parts.
3. Drilling
Drilling is the operation of creating holes in a workpiece using a drill bit. Lathe machines equipped with a tailstock spindle and a drilling chuck can perform drilling operations with accuracy and precision.
4. Tapering
Tapering involves gradually reducing the diameter of a cylindrical workpiece along its length. This operation is often used to create conical shapes or to fit parts into tapered holes or sockets.
5. Threading
Threading is the process of cutting threads onto a workpiece to create a screw-like structure. This allows the workpiece to be screwed onto another component or to mate with a threaded hole.
6. Knurling
Knurling is a process used to create a pattern of ridges or grooves on the surface of a workpiece for improved grip or aesthetics.
7. Grooving
Grooving involves cutting a narrow groove or channel on the surface of a workpiece. It is often done to create space for retaining rings, O-rings, or other components.
8. Parting
Parting is the process of cutting a workpiece to separate it into two or more pieces. It is commonly used to create separate parts or to remove unwanted sections of a workpiece.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting a Lathe Machine
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential to keep a lathe machine in optimal condition. Here are some useful tips:
1. Lubrication:
Ensure proper lubrication of all moving parts to reduce friction and prevent excessive wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use the appropriate lubricants.
2. Cleanliness:
Keep the machine clean and free from dirt, dust, and metal chips. Regularly remove any debris that may accumulate in the nooks and crannies of the machine.
3. Calibration:
Periodically check and calibrate the machine to ensure accuracy and precision in the machining operations. This includes checking the alignment of the tool holder, tailstock, and workpiece centering.
4. Troubleshooting:
When issues arise, troubleshoot the machine systematically. Check for loose bolts or screws, abnormal noises, irregular movement, or any other signs of malfunction. Consult the machine’s manual or seek professional assistance if needed.
5. Safety:
Always follow safety protocols and wear appropriate protective equipment while operating a lathe machine. Treat sharp cutting tools with caution and be aware of potential hazards.
By following these maintenance tips and troubleshooting techniques, you can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your lathe machine.
Key Takeaways: How Does a Lathe Machine Work?
- A lathe machine is a tool used to shape and cut metal or wood.
- It works by rotating the material being worked on, while a cutting tool is used to shape or cut it.
- The material is held in place by a chuck or collet, and the cutting tool moves across the material to shape it.
- There are different types of lathes, such as engine lathes, turret lathes, and CNC lathes, each with its own specific purpose.
- Lathe machines are widely used in industries like manufacturing, carpentry, and metalworking.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on how a lathe machine works. Here, we will address common questions to help you better understand the inner workings of a lathe machine and its functions.
1. What is the main purpose of a lathe machine?
A lathe machine is primarily used for shaping and cutting materials, such as wood, metal, and even plastics. It rotates a workpiece against a cutting tool to create symmetrical objects, such as cylinders, cones, or intricate shapes. It is a versatile tool used in various industries, including woodworking, metalworking, and manufacturing.
The main objective of a lathe machine is to remove excess material and shape the workpiece according to the desired specifications, ensuring precision and accuracy in the final product.
2. How does a lathe machine work?
A lathe machine operates on the principle of rotating the workpiece while it is being cut by a cutting tool. The workpiece is mounted on the machine’s spindle, which rotates at various speeds. The cutting tool is then brought into contact with the workpiece, and as it rotates, it removes material by cutting or scraping.
The movements of a lathe machine are controlled using different mechanisms, including a carriage, apron, and tailstock. The carriage moves along the lathe bed, allowing the cutting tool to move horizontally or longitudinally. The apron houses the mechanism for controlling the feed rate and depth of cut. The tailstock supports the workpiece and provides stability.
3. What are the different types of lathe machines?
There are several types of lathe machines, each designed for specific purposes. Some common types include engine lathes, bench lathes, and turret lathes. Engine lathes are versatile and widely used for a variety of tasks. Bench lathes are smaller and portable, suitable for workshops or small-scale projects. Turret lathes have multiple cutting tools and can perform various operations without the need for manual tool changes.
Other specialized lathe machines include CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes, which are controlled by computer programs and can perform highly precise operations, and automatic lathes, which are fully automated and can handle repetitive tasks.
4. What safety precautions should be followed when operating a lathe machine?
Operating a lathe machine requires strict adherence to safety precautions to prevent accidents and injuries. Some important safety measures include wearing protective gear, such as safety glasses and gloves, to shield against flying chips or debris. Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped to prevent it from being dislodged during operation.
Always use appropriate cutting tools and ensure they are properly positioned and securely tightened. Avoid wearing loose clothing or jewelry that could get entangled in the machine. Familiarize yourself with the specific safety guidelines provided by the lathe machine manufacturer and follow them meticulously.
5. Can a lathe machine be used for both wood and metalworking?
Yes, a lathe machine can be used for both wood and metalworking. However, different cutting tools and techniques are required for working with each material. For woodturning, specialized tools, such as gouges and chisels, are used to shape the wood. Metalworking on a lathe machine involves using cutting tools specifically designed for metal, such as carbide inserts or high-speed steel tools.
It is important to know the limitations of the lathe machine and ensure the appropriate cutting tools and techniques are utilized for the specific material being worked on. Some lathe machines are specifically designed for either wood or metalworking, while others are more versatile and can handle both with the right adjustments and tooling.

Summary
So, to sum it up, a lathe machine is a tool used to shape and cut materials like wood or metal. It does this by rotating the material and using tools to shape it. By adjusting the speed and position of the tools, you can create different shapes and cuts. Lathe machines are versatile and can be used for many different projects, from making furniture to creating intricate designs. So, if you’re interested in woodworking or metalworking, learning how a lathe machine works can open up a world of possibilities for you!
