Looking to power your tools with a generator? Wondering how many watts you need? Well, you’ve come to the right place! Whether you’re a budding DIY enthusiast or a seasoned pro, this article will break down the wattage requirements for running power tools. So, let’s dive in and unleash the power of knowledge!
When it comes to running power tools, the wattage requirements can vary depending on the specific tool. It’s like a puzzle, trying to match the right generator to your power needs. But fear not, we’ll guide you through it step by step, so you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any project with ease.
From drills to saws, each power tool has its own power demands. But that’s where our friendly guide comes in. We’ll crunch the numbers and provide you with the essential information to ensure you have the right wattage generator for your power tools. So, let’s get started and uncover the secret to powering up your projects efficiently!
1. Small drills and sanders: 600-800 watts
2. Circular saws and jigsaws: 1,200-1,400 watts
3. Table saws and miter saws: 1,800-2,200 watts
4. Air compressors: 1,800-2,400 watts
5. Welders: 4,000-6,000 watts
These wattages are approximate and can vary. Always check your tool’s manual for the exact wattage needed and select a generator with slightly higher capacity to ensure smooth power delivery.
How Many Watts Generator Do You Need to Run Power Tools?
Power tools have revolutionized the way we work on various projects, from construction to DIY tasks. However, these tools require a reliable and efficient power source to function optimally. This is where generators come into play. If you’re wondering how many watt generator you need to run power tools, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of generators and explore their wattage requirements for powering different types of power tools.
Understanding Power Tools Wattage
Before we delve into the wattage requirements for generators, let’s first understand power tools’ wattage. Each power tool has a specific wattage rating, which indicates how much power it consumes to operate effectively. This wattage rating can usually be found on the tool’s label or in the user manual. Typically, power tools range from 500 to 2500 watts, depending on their size and functionality.
Some common examples of power tool wattages include:
- Drill: 500-1000 watts
- Circular Saw: 1200-1800 watts
- Air Compressor: 1200-2400 watts
- Angle Grinder: 1000-2000 watts
Knowing the wattage requirement of your power tools is crucial for selecting the right generator. Let’s move on to the next section to learn how to determine the wattage output for your generator.
Calculating Generator Wattage for Power Tools
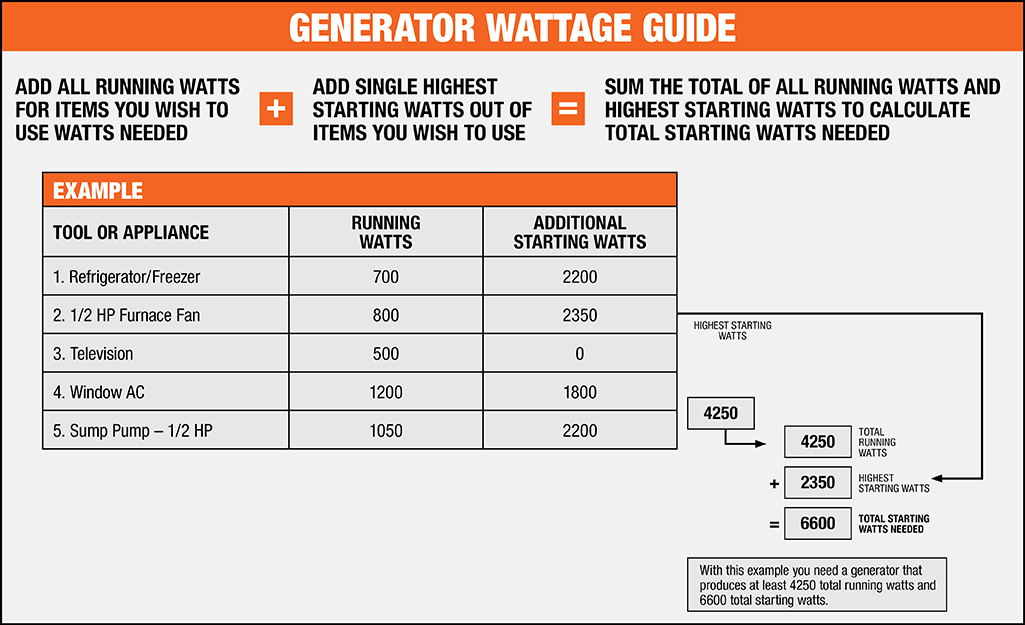
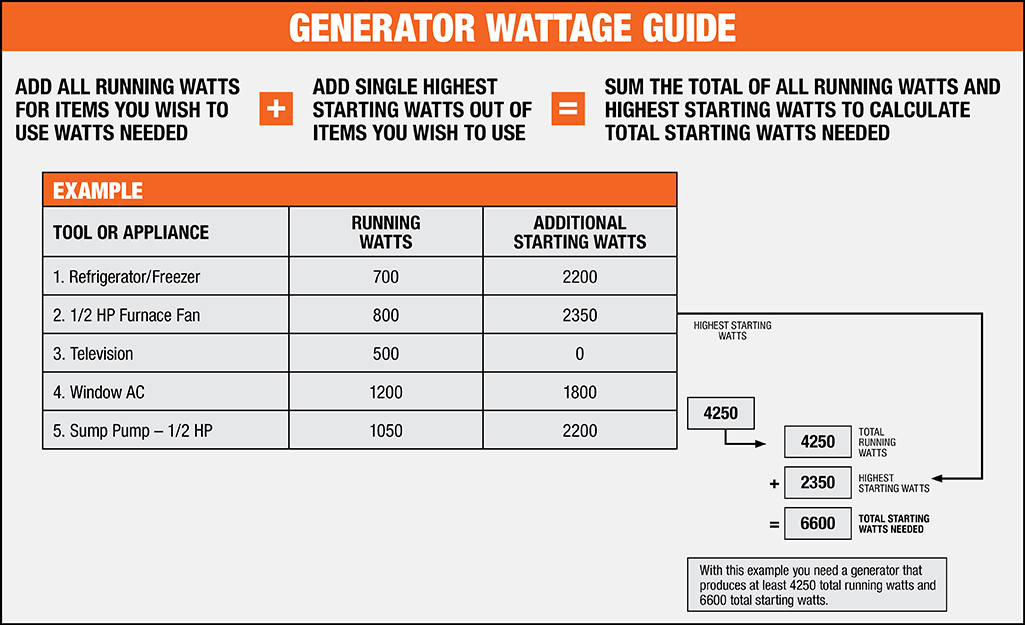
Calculating the necessary wattage output for your generator involves a simple addition of the wattage requirements of the power tools you intend to run simultaneously. To ensure the generator can handle the load, it’s advisable to add a 20-30% buffer to account for power surges and prevent overloading. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you determine the appropriate wattage for your generator:
- Make a list of the power tools you’ll be using simultaneously.
- Find the wattage rating for each power tool.
- Add up the wattages of all the power tools.
- Multiply the total wattage by 1.2 or 1.3 to incorporate the buffer.
For example, if you plan to run a circular saw (1800 watts), a drill (800 watts), and an air compressor (2200 watts) concurrently, the total wattage requirement would be 4800 watts. Adding a 20% buffer, the generator should have a minimum wattage output of 5760 watts to accommodate the load and prevent issues.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Power Tools
Now that you know how to calculate the wattage needed to power your tools, it’s time to select the right generator. Generators come in various wattage capacities, ranging from portable models (1000-5000 watts) to heavy-duty generators (5000+ watts). Consider the following factors when choosing a generator:
- Wattage Output: Ensure the generator’s wattage output matches or exceeds the total wattage requirement of your power tools.
- Portability: If you’re frequently working on different job sites, opt for a portable generator that is easy to transport.
- Fuel Type: Generators can run on gasoline, diesel, propane, or natural gas. Choose a fuel type that suits your needs and availability.
- Runtime and Fuel Efficiency: Look for generators with longer runtime capabilities and better fuel efficiency to avoid frequent refueling.
By considering these factors and using the wattage calculations, you’ll be able to select a generator that provides ample power for your power tool needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Generator
While understanding how to calculate generator wattage is crucial, it’s also important to avoid common mistakes when choosing a generator. Here are a few missteps to steer clear of:
1) Underestimating Power Needs
One common mistake is underestimating the total power needed for your tools. Failing to account for power surges and additional tools can lead to an overloaded generator, resulting in poor performance or even damage to your power tools.
2) Ignoring Portability Requirements
If you frequently work in different locations, opting for a bulky, less portable generator can become a hindrance. Consider your portability needs and select a generator that is easy to transport without compromising functionality.
3) Disregarding Fuel Type
Each fuel type has its advantages and disadvantages. Failing to consider the availability and cost of the chosen fuel type can lead to inconvenience and increased expenses. Choose a fuel type that matches your requirements and accessibility.
4) Neglecting Runtime and Fuel Efficiency
Longer runtime and better fuel efficiency are essential for uninterrupted work and cost-effectiveness. Ignoring these factors could mean frequent refueling breaks and increased fuel consumption.
Additional Considerations for Power Tools and Generators
In addition to calculating wattage and selecting a generator, here are a few extra considerations to optimize the use of power tools with generators:
1) Power Tool Compatibility
Ensure that your power tools are compatible with generators. Some sensitive electronic tools may require a generator with a pure sine wave inverter to prevent damage or poor performance.
2) Maintain and Service Your Generator
Regular maintenance and servicing of your generator are crucial for its optimal performance and longevity. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance schedules and necessary precautions.
3) Safety Measures
Follow all safety precautions and guidelines when using generators and power tools. These safety measures include proper grounding, avoiding wet conditions, using appropriate cords and outlets, and wearing appropriate protective gear.
In conclusion, determining the wattage requirement for your power tools and selecting the right generator is vital for efficient and smooth operation. By understanding power tool wattage, calculating generator wattage, and considering important factors, you can ensure a reliable power source for your tools. Remember to avoid common mistakes and prioritize safety to make the most of your power tools and generator setup.
Key Takeaways: How Many Watt Generator to Run Power Tools?
2. A general guideline is to have a generator with a minimum capacity of 2,000-3,000 watts for small power tools.
3. Larger power tools like table saws or air compressors may require a generator with a capacity of 5,000-8,000 watts.
4. It’s crucial to consider starting watts, as some power tools have a higher initial power surge upon startup.
5. Always consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and consider the total wattage of the tools you plan to use simultaneously.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here’s a list of commonly asked questions regarding wattage requirements for running power tools:
1. What factors should I consider when determining the wattage of a generator for power tools?
When determining the wattage of a generator for power tools, there are a few factors to consider. First, you need to know the wattage rating of each power tool you’ll be using. This information can usually be found on the tool itself or in the tool’s manual. Next, consider if you’ll be using multiple power tools simultaneously, as this will require a higher wattage generator. Finally, take into account any additional devices you’ll need to power, such as lights or chargers, and factor their wattage requirements into your calculations.
By considering the wattage ratings of your power tools, the number of tools you plan to use simultaneously, and any additional devices you’ll be powering, you can determine the appropriate wattage generator for your power tool needs.
2. What is the minimum wattage generator required to run basic power tools?
To power basic power tools, such as drills, circular saws, or sanders, you’ll generally need a generator with a minimum wattage of 3000-4000 watts. These tools typically have wattage ratings ranging from 500 to 1500 watts, so a generator in this range should provide sufficient power for single tool operation.
However, it’s important to note that if you plan on using multiple power tools simultaneously, or if you need to power larger tools with higher wattage ratings, you may need to consider a generator with a higher wattage capacity.
3. How many watts does a generator need to run heavy-duty power tools?
Heavy-duty power tools, like table saws, air compressors, or welders, generally require a generator with a higher wattage capacity. Depending on the specific tools you plan to use, you may need a generator with a wattage rating of 5000 watts or more.
It’s crucial to check the wattage requirements of each heavy-duty tool you’ll be using and add them up to determine the minimum wattage capacity needed for your generator. Keep in mind that larger tools usually have higher wattage ratings, so a higher-capacity generator will be necessary to handle their power needs.
4. Can I use an inverter generator for power tools?
Yes, you can absolutely use an inverter generator for power tools. Inverter generators are known for their ability to produce clean and stable power, making them ideal for sensitive electronic devices. Many power tools fall into this category, as they are equipped with electronic controls or motors.
Inverter generators also have the added advantage of being more fuel-efficient and quieter compared to conventional generators. So, if you prioritize portability, fuel efficiency, and low noise levels, an inverter generator is a great option for running your power tools.
5. Are there any additional safety considerations when using a generator to power tools?
Yes, there are a few safety considerations to keep in mind when using a generator to power tools. First and foremost, always make sure to operate the generator in a well-ventilated area to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Secondly, be mindful of the generator’s fuel source and use it in a safe and appropriate manner to avoid accidents or fires.
Additionally, ensure that the generator and power tools are properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for connecting and disconnecting tools to the generator, and never overload the generator with more wattage than it can handle. Lastly, it’s crucial to use the correct type and size of extension cords to connect your power tools to the generator, as inadequate cords can pose a safety hazard.

What size generator do I need for power tools compressor & more. Using volts x amps = watts formula.
Summary
So, to sum it all up, when choosing a generator for power tools, you need to consider their wattage requirements. Check the wattage rating of each tool, add them up, and get a generator that can handle that total wattage. It’s better to have a generator with a higher wattage rating to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Don’t forget to factor in any other appliances or devices you might want to run at the same time.
Remember, safety is important! Make sure to use the correct extension cords, keep the generator outdoors, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. With the proper generator and precautions in place, you’ll be all set to power your tools and get the job done!