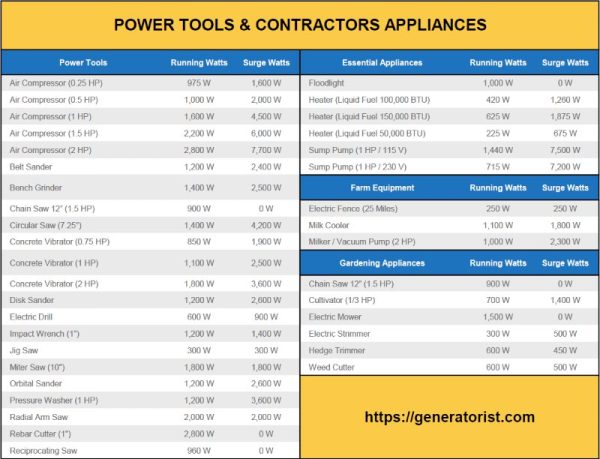
Have you ever wondered how many watts you need to run power tools? It’s an important question if you want to make sure you have enough power to get the job done. In this article, we’ll break it down for you in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
When it comes to power tools, having the right amount of wattage is crucial. Whether you’re using a drill, a saw, or any other tool, you need to provide it with enough power to operate efficiently. But how do you determine the wattage you need? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered!
In this guide, we’ll explain the factors that determine how many watts you need for different power tools. From drills to circular saws, we’ll help you understand the power requirements so you can choose the right tools for your projects. Let’s dive in and shed some light on this electrifying topic!
Step 1: Identify the power requirements of each tool.
Step 2: Add up the wattage for all the tools you plan to use simultaneously.
Step 3: Consider any additional power needs for starting or running devices.
Step 4: Account for voltage and amperage requirements.
Step 5: Choose a generator or power source with a wattage capacity that exceeds your total power needs.
Remember, proper wattage calculation ensures efficient and safe operation of your power tools.
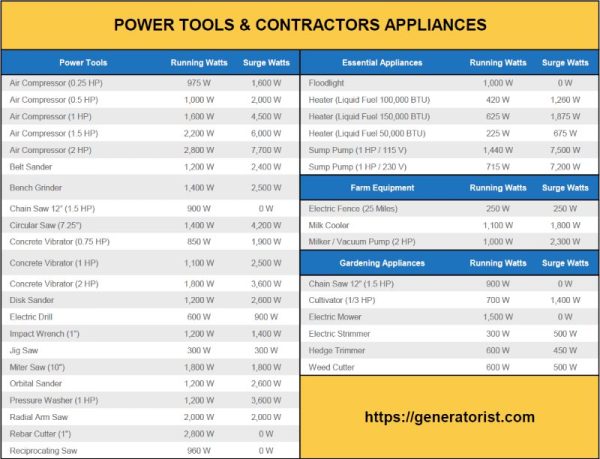
How Many Watts Do I Need to Run Power Tools?
Power tools are essential for any DIY enthusiast or professional handyman. From drills to saws, these tools require a certain amount of power to function effectively. But how many watts do you actually need to run power tools efficiently and safely? In this article, we will delve into the world of power tool wattage, explaining the factors that influence power consumption and offering guidance on selecting the right wattage for your tools.
Understanding Power Consumption: A Brief Overview
Before we dive into the specifics of wattage requirements for power tools, let’s first understand how power consumption works. Power tools draw electricity from an electrical outlet to operate. The amount of power a tool requires depends on various factors, including its motor size, voltage rating, and the type of work it is designed for.
The unit of measurement for power is known as a watt. A watt measures the rate of energy transfer or consumption. When it comes to power tools, the wattage indirectly indicates how much energy is required to operate the tool. Understanding the wattage requirements of your power tools is crucial to ensure they work efficiently and avoid potential electrical issues.
Key Factors Affecting Power Tool Wattage
Now that we have a basic understanding of power consumption, let’s explore the key factors that influence power tool wattage:
- Motor Size: The motor of a power tool is one of its most critical components. It generates the power needed to operate the tool. Generally, larger motors require more power to run efficiently. For example, a heavy-duty circular saw with a larger motor will typically require more watts compared to a smaller, handheld jigsaw.
- Voltage Rating: Power tools come with different voltage ratings, which can range from 110 volts to 240 volts or higher. The voltage rating indicates the electrical potential difference required for the tool to function correctly. Generally, tools with higher voltage ratings will require more wattage to operate efficiently.
- Tool Type: The type of power tool also plays a significant role in determining its wattage requirements. For example, a basic electric drill with simple functionality will require fewer watts compared to a high-powered rotary hammer used for drilling into concrete. The complexity and workload of the tool impact the power it needs.
Calculating Wattage for Power Tools: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you have an understanding of the factors influencing power tool wattage, let’s explore how to calculate the wattage required for your specific tools:
- Check the Tool’s Label: Most power tools will have a label or plate on them that details important specifications, including their wattage requirements. Look for this label to get an idea of the wattage needed to power the tool adequately.
- Multiply Voltage by Amperage: If the wattage information is not readily available, you can calculate it using a simple formula. Multiply the voltage rating of the tool by its amperage rating. For example, if a tool has a voltage rating of 120 volts and an amperage of 5 amps, the wattage requirement will be 600 watts (120V x 5A = 600W).
- Consider Safety Factors: It’s always a good idea to leave some room for safety margins when calculating wattage requirements. Adding an extra 10-20% to the calculated wattage will ensure your tool runs smoothly without putting excessive strain on your electrical system.
Selecting the Right Wattage: Tips and Recommendations
Now that you know how to calculate wattage requirements for your power tools, here are some additional tips and recommendations to help you select the right wattage:
- Research the Tool’s Wattage: Before purchasing a new power tool, research its wattage requirements to ensure it aligns with your available power supply.
- Consider Upgrade Possibilities: If you plan on expanding your collection of power tools or undertaking more demanding projects in the future, it’s wise to invest in a higher wattage generator or upgrade your electrical system to support the additional load.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unsure about the wattage requirements or concerned about your electrical system’s capacity, consult a professional electrician. They can assess your requirements and make recommendations based on your specific needs.
Power Tools and Their Wattage Demands: A Closer Look
Now that we have covered the basics of power tool wattage, let’s explore the wattage requirements for some common power tools:
Circular Saw
A circular saw is a versatile tool used for making straight cuts in various materials. These saws typically operate at a wattage ranging from 1200 watts for entry-level models to 2400 watts for heavy-duty professional-grade saws.
Drill
A drill is a staple tool in any toolbox, used for drilling holes and driving screws. The wattage requirements for drills vary depending on their size and functionality. Generally, a basic corded drill will require around 500 to 800 watts, while more powerful hammer drills can range from 800 to 1200 watts.
Angle Grinder
An angle grinder is a versatile tool used for grinding and polishing materials. These tools typically have a wattage requirement between 700 and 2500 watts, depending on their size, power, and intended usage.
Jigsaw
A jigsaw is a handheld power tool used for making curved cuts in various materials. These tools usually operate at a wattage ranging from 350 to 800 watts, depending on their power and cutting capacity.
Conclusion
When it comes to power tools, understanding their wattage requirements is essential for optimal performance and safety. By considering factors like motor size, voltage rating, and tool type, you can calculate the wattage needed and select the right tools for your projects. Remember to research tool wattages, consider potential upgrades, and consult professionals when necessary. Armed with this knowledge, you can power up your projects with confidence!
Key Takeaways: How Many Watts Do I Need to Run Power Tools?
- 1. Different power tools require different wattages to operate.
- 2. It’s important to check the power tool’s specifications for the required wattage.
- 3. For most power tools, a wattage between 500-1500 watts is sufficient.
- 4. Heavy-duty power tools may require higher wattages, such as 2000 watts or more.
- 5. Using a wattage calculator can help determine the exact wattage needed for specific power tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to power tools, determining the right wattage can be confusing. Here are some commonly asked questions to help you understand how many watts you need to run power tools effectively.
1. How do I calculate the wattage needed for power tools?
Calculating the wattage needed for power tools involves understanding the power requirements of each tool. Most power tools have their power consumption listed in watts or amps on the label or in the user manual. For example, if a circular saw uses 10 amps, you can multiply that by the voltage of your electrical system (usually 120 volts in the US) to get the wattage requirement. In this case, it would be 10 amps x 120 volts = 1200 watts.
It is crucial to factor in any additional electrical devices running on the same circuit. If multiple tools are used simultaneously, add up the wattage requirements of each tool to get the total power consumption.
2. Can I use a lower wattage than recommended for my power tools?
While it may be tempting to use a lower wattage than recommended for power tools, it is generally not advisable. Power tools are designed to operate at specific wattages to ensure efficient performance and prevent damage. Using a lower wattage can cause the tool to underperform or overheat, leading to premature failure or safety hazards.
It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for optimal performance and longevity of your power tools. If you’re unsure about the wattage requirements, you can consult the tool’s user manual or reach out to the manufacturer for guidance.
3. Can I use a higher wattage rating for my power tools?
Using a higher wattage rating for power tools generally does not pose a problem. Most power tools have built-in safety measures to handle higher wattages. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the electrical circuit can support the increased power consumption. Exceeding the circuit’s capacity can cause the breaker to trip or even lead to electrical fires.
Additionally, using a higher wattage tool may not necessarily translate to better performance unless it is specifically required for a particular job or application. It’s important to balance the tool’s wattage with the task at hand to ensure efficient and safe operation.
4. Are there any power tools that require a significantly higher wattage?
Yes, some power tools require a significantly higher wattage due to their demanding nature. Examples include table saws, air compressors, and welders. These tools require higher wattages to generate the power needed for their respective functions. It’s crucial to review the tool’s specifications or consult the manufacturer to determine the specific wattage requirements for such power tools.
When using power tools with higher wattage requirements, it is essential to ensure the electrical circuit can handle the load. Upgrading the circuit or using a dedicated circuit for these tools may be necessary to avoid electrical issues.
5. Can I use power tools with different wattage requirements on the same circuit?
Using power tools with different wattage requirements on the same circuit is generally acceptable as long as the circuit can handle the combined power consumption. However, it’s important to be mindful of the total wattage and not exceed the circuit’s capacity.
Before connecting multiple power tools to a single circuit, add up their wattage requirements to ensure it stays below the circuit’s rating. If the total wattage exceeds the circuit’s capacity, consider redistributing the load across multiple circuits or using separate circuits for different tools to ensure safe and optimal operation.
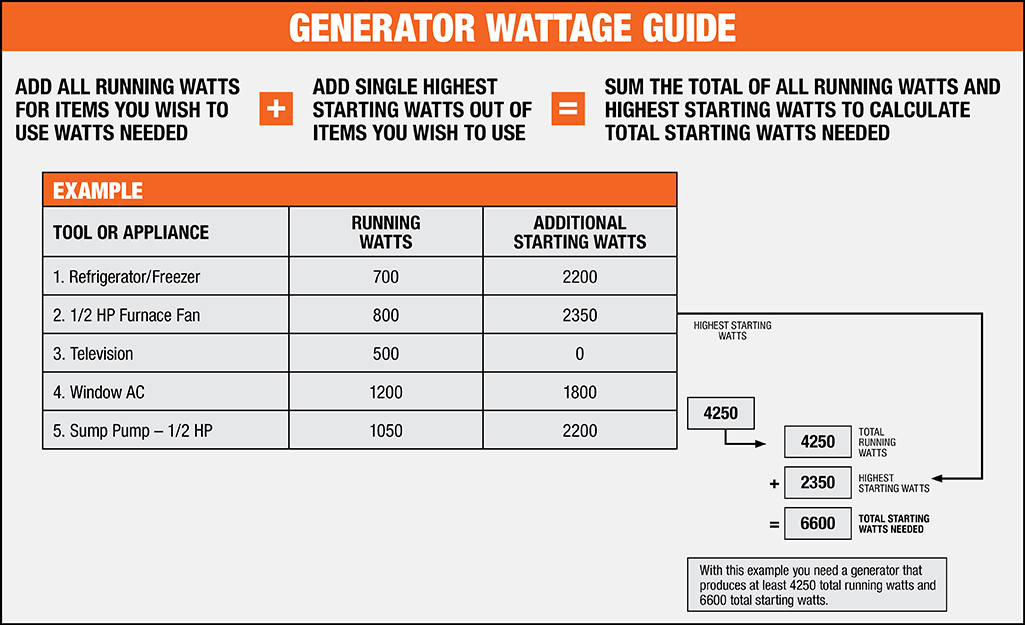
What size generator do I need for power tools compressor & more. Using volts x amps = watts formula.
Summary
When deciding how many watts you need to run power tools, it’s important to consider a few key factors. First, you should check the power requirements specified on each tool’s label or manual. Second, add up the wattage of all the tools you plan to use simultaneously. Finally, choose a generator or power source that can handle the total wattage needed. It’s better to have a generator that can handle more watts than you need to ensure smooth operation of your power tools. Remember, safety always comes first, so make sure to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and use the appropriate cables and circuit breakers for your tools and power source.