Are you wondering how many watts you need to run your power tools? Well, you’ve come to the right place! If you’ve ever found yourself scratching your head over this question, don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of power tools and break down the wattage requirements for different types of tools.
Picture this: you’re in your workshop, ready to tackle your latest DIY project. You reach for your trusty power tools, only to wonder, “Do I have enough power to get the job done?” Understanding the wattage needed to run your power tools is crucial to ensure they operate efficiently and don’t overload your electrical system.
So, whether you’re a novice DIY enthusiast or a seasoned pro, join us as we demystify the world of power tool wattage and equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. Let’s dive in and discover how many watts it takes to run power tools effectively!
Running power tools requires different wattage depending on the specific tool. To calculate the wattage, multiply the voltage (V) by the amperage (A) requirement of the tool. For example, a 110V drill with 5A would require 550 watts. Refer to the tool’s manual or the label for the amperage rating, then use this formula to determine the wattage needed to run your power tools efficiently.
How Many Watts Do You Need to Run Power Tools?
Power tools are essential for any DIY enthusiast or professional contractor. However, knowing how many watts you need to power these tools efficiently can be a bit confusing. In this article, we will break down the power requirements of common power tools and guide you on selecting the right wattage for your needs. Whether you’re working on a small home project or a large construction site, understanding power tool wattage is crucial for safety and performance.
Understanding Wattage: What Does It Mean?
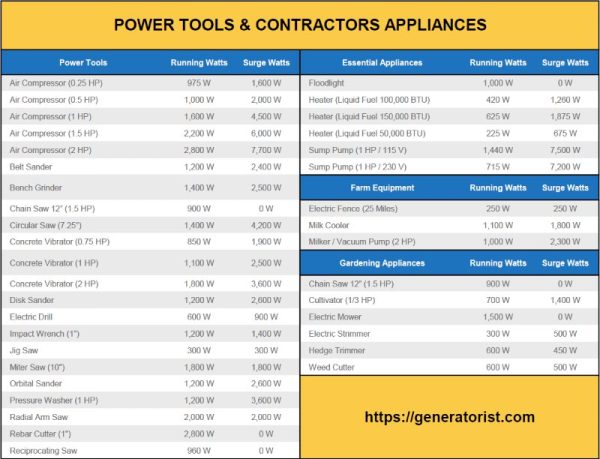
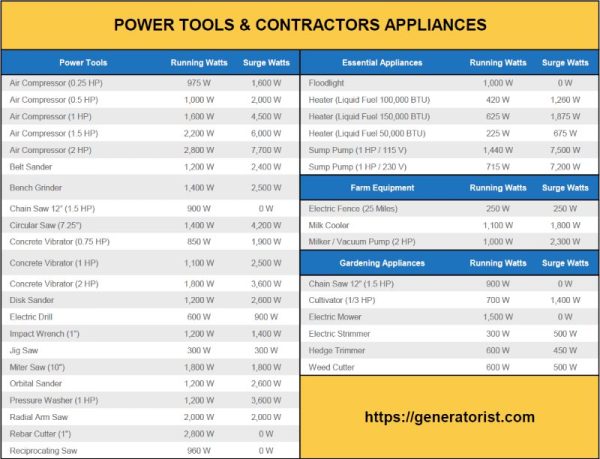
Wattage refers to the amount of power a device or appliance consumes. In the context of power tools, wattage indicates the power needed to run the tool effectively. It is important to note that different power tools have varying power requirements, ranging from as low as 500 watts to as high as 3000 watts or more.
When considering wattage, it’s essential to understand that a power tool’s efficiency and performance can be impacted by the power supply. Insufficient wattage can result in decreased power output, slower operation, and even potential damage to the tool. On the other hand, excessive wattage may lead to unnecessary energy consumption and increased costs. Finding the right balance is key.
Determining the Wattage for Common Power Tools
Let’s take a closer look at the power requirements for some common power tools:
1. Drills: Most electric drills operate with a power range of 500 to 1000 watts. However, heavy-duty drills used in construction or metalwork may require up to 1500 watts for optimal performance.
2. Circular Saws: Circular saws typically range from 1200 to 2400 watts. The power requirement will depend on the size and type of material you are cutting. Thicker or denser materials may require a higher wattage.
3. Jigsaws: Jigsaws typically have a wattage between 500 and 800 watts. These versatile tools are suitable for various cutting applications and have relatively lower power requirements compared to other saws.
4. Angle Grinders: Angle grinders can have a wide wattage range, from 500 watts for small models to over 2500 watts for heavy-duty versions. The power needed will depend on the size of the grinding disc and the intensity of the work.
5. Sanders: Sanders generally require around 200 to 500 watts, depending on the type and size. Belt sanders and random orbital sanders tend to have higher power requirements compared to detail sanders.
6. Routers: Routers fall within the range of 1000 to 2400 watts. These tools are commonly used for woodworking and require a sufficient power supply for precise cutting.
7. Welders: Welding machines often have high power demands, with welders ranging from 1000 watts for small projects to 3000 watts or more for industrial-scale welding.
Tips for Selecting the Right Wattage
Now that we’ve discussed the wattage requirements for common power tools, here are some tips to help you select the right wattage for your specific needs:
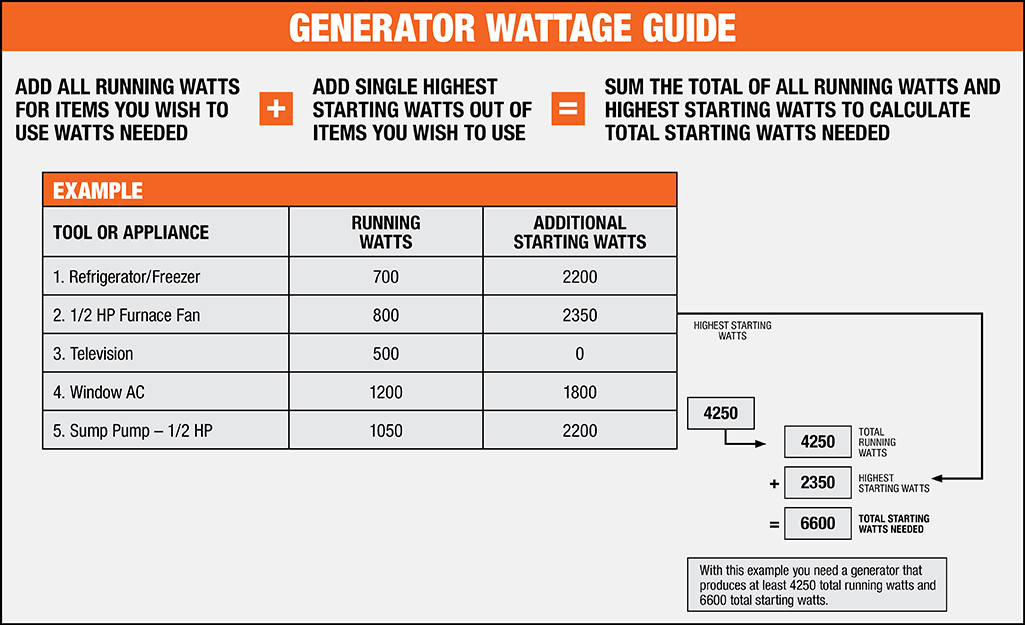
1. Identify Your Power Tools: Make a list of the power tools you plan to use and their wattage ratings. This will give you a better understanding of the overall power requirements.
2. Consider Simultaneous Use: If you’re likely to use multiple power tools simultaneously, calculate the total wattage needed. Ensure that your power source can handle the combined load.
3. Check Circuit Capacity: Before connecting your power tools, ensure that your electrical circuit can accommodate the wattage requirements. Consult an electrician if necessary.
4. Opt for Higher Wattage: If you’re unsure about the specific power requirements, it’s generally safer to choose a power source with a slightly higher wattage. This will prevent overloading and potential damage to your tools.
5. Use Surge Protectors: Investing in surge protectors can safeguard your power tools from voltage fluctuations and electrical spikes. This extra layer of protection can increase the longevity of your tools.
6. Energy Efficiency: Consider energy-efficient power tools that can deliver the same performance with lower wattage. This not only saves electricity but also reduces operating costs in the long run.
7. Safety First: Always prioritize safety when working with power tools. Ensure that your work environment has proper grounding, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions while operating the tools.
In conclusion, understanding the wattage requirements for power tools is essential for achieving optimal performance and safety. By identifying the wattage needs of your specific tools and considering factors like simultaneous use and circuit capacity, you can select the right wattage and enjoy efficient and reliable operation. Remember to prioritize safety and consult professionals when in doubt. Happy tooling!
Key Takeaways: How Many Watts to Run Power Tools?
- Power tools typically require different wattages depending on their type and size.
- Smaller power tools like drills and sanders usually require around 500-1000 watts.
- Larger power tools like table saws and miter saws may need between 1500-2500 watts.
- Always check the manufacturer’s instructions or labels on the power tool for the recommended wattage.
- Using a wattage calculator can help determine the exact power requirements for your specific power tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about determining the power requirements for running power tools:
Question 1: What factors should I consider to determine the power requirements for my power tools?
Answer: When determining the power requirements for your power tools, you need to consider two main factors: the rated power (watts) of each tool and the total power you’ll be using simultaneously. Refer to the label or user manual of each tool to find its power rating. Consider the maximum number of tools you’ll be using at the same time and add up their power ratings. Make sure your power source (generator, circuit, etc.) can handle the total power.
It’s important to note that certain power tools, such as high-powered saws or air compressors, may have peak power requirements that are higher than their rated power. In such cases, you may need to account for the peak power when determining your power needs.
Question 2: Can I use a regular household power outlet to run power tools?
Answer: It depends on the power requirements of your power tools. Most household power outlets in the US provide 120 volts of alternating current (VAC) at 15 or 20 amps. To determine if a regular household power outlet can handle your power tools, you need to calculate the wattage. For example, a 15-amp outlet can handle up to approximately 1800 watts (P = V x I), and a 20-amp outlet can handle up to approximately 2400 watts.
If your power tools’ total power requirements exceed these limits, you’ll likely need a dedicated circuit or a higher-capacity power source, such as a generator. It’s always best to consult a qualified electrician if you’re unsure about the electrical requirements of your power tools.
Question 3: How many watts do common power tools typically require?
Answer: The power requirements for common power tools can vary significantly. Some tools, like small drills or sanders, may require around 500 to 800 watts. However, larger tools, such as circular saws or table saws, can require anywhere from 1200 to 1800 watts or more.
It’s important to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications or the tool’s label for the exact power requirements. Keep in mind that different models or brands of the same type of power tool may have varying power requirements.
Question 4: Can I use an inverter generator to power my tools?
Answer: Yes, you can use an inverter generator to power your tools. Inverter generators provide clean and stable power, which is essential for the smooth operation of electronic devices and sensitive power tools. They are also typically more fuel-efficient and quieter compared to conventional generators.
When choosing an inverter generator for your power tools, calculate the total power requirements of your tools and ensure that the generator’s rated power output can handle the load. Additionally, check for features like overload protection and multiple power outlets to accommodate your tools.
Question 5: Is it better to have a power source with higher wattage than what my tools require?
Answer: Having a power source with a higher wattage rating than what your tools require can be beneficial. It provides a safety margin and prevents overloading the power source. If your tools require 1500 watts, for example, using a power source capable of delivering 1800 watts ensures that you have some headroom for unexpected power spikes or high-demand tasks.
However, it’s important not to use a power source with excessively higher wattage, as this can lead to inefficiency and unnecessary costs. It’s generally recommended to have a power source that can comfortably handle your power tools’ requirements without being too excessive.
Can a Power Station Run Power Tools? EcoFlow Delta Max
Summary
So, how many watts do you need to run power tools? Well, it depends on the tool. Different tools require different amounts of power. A simple handheld drill may only need around 500 watts, while a circular saw could require 1200 watts or more. It’s important to check the tool’s manual or packaging for the recommended wattage to ensure you have a power source that can handle it. And remember, safety first – always use the right wattage and follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid any accidents.
In conclusion, understanding the wattage needed to run power tools is crucial for any DIY enthusiast. By checking the manual or packaging of your tools, you can determine the required wattage and ensure a safe and efficient power supply. So, next time you’re gearing up for a project, be sure to match the wattage and get those tools running smoothly!