Did you ever wonder how much electricity power tools use? Well, get ready to plug into the world of power tools and energy consumption! Whether you’re a handyperson or just curious about the inner workings of these devices, understanding their electricity usage can be enlightening.
Imagine this: you’re working on a DIY project, using your trusty power tools to bring your ideas to life. But have you ever stopped to think about how much electricity these tools actually gobble up? Let’s dive into the electrifying details and find out just how power-hungry these mighty tools can be.
In this article, we’ll explore the electrical appetite of different types of power tools, from cordless drills to table saws. So, tighten your tool belt and prepare to be shocked by the world of power tool electricity usage. Let’s get started!
How Much Electricity Does Power Tools Use?
Power tools have become essential tools for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. They provide efficiency, precision, and speed in various tasks. However, many users often wonder about the electricity consumption of these tools. Understanding how much electricity power tools use can help users make informed decisions about energy usage, cost, and environmental impact. In this article, we will explore the energy consumption of different power tools, factors affecting electricity usage, and tips for optimizing energy efficiency.
1. Energy Consumption of Power Tools
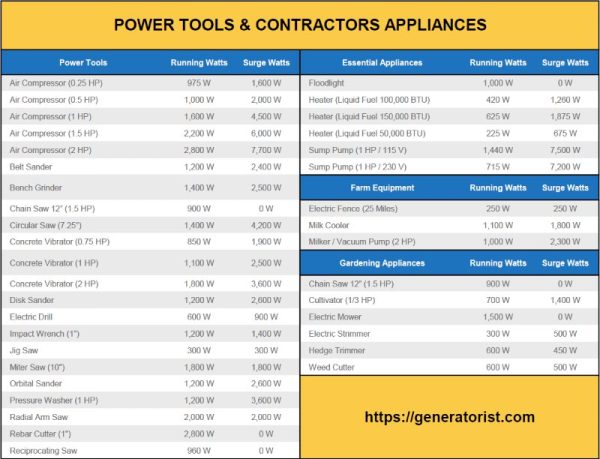
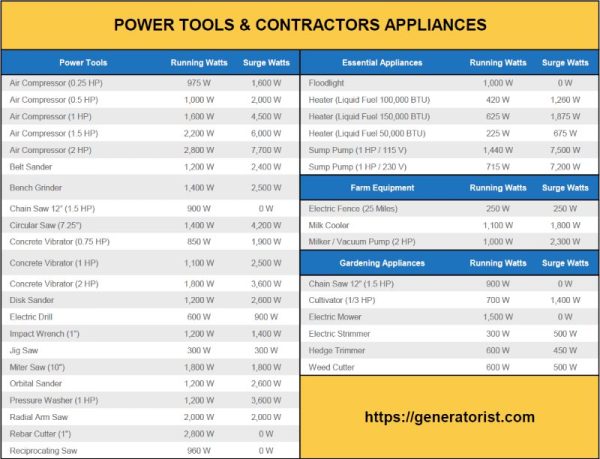
Power tools come in various types, sizes, and power ratings, resulting in different energy consumption levels. Small handheld power tools, such as drills and sanders, typically consume anywhere between 500 to 1500 watts per hour of continuous operation. Larger tools like circular saws or angle grinders can consume up to 2000 to 3000 watts per hour. It’s important to check the power specifications of each tool to get an accurate estimate of its energy consumption.
Furthermore, the intensity of power tool usage affects energy consumption. Tools that require continuous operation, like belt sanders or planers, consume more electricity compared to tools that are used intermittently, such as power drills. Additionally, the voltage of the power supply also influences energy usage. Tools operating at higher voltage tend to consume less electricity than those operating at lower voltage.
It’s important to note that energy consumption can also vary based on the brand, model, and efficiency of the power tool. Newer models often incorporate energy-saving features, resulting in lower electricity usage.
2. Factors Affecting Electricity Usage
Several factors contribute to the electricity usage of power tools. Firstly, the power setting or speed at which the tool operates significantly impacts energy consumption. Higher power or speed settings generally result in increased electricity usage. Users should adjust the power settings depending on the task requirements to optimize energy efficiency.
The duration of tool usage also affects electricity consumption. Extended periods of continuous operation will consume more energy compared to shorter durations. Users should consider taking breaks and turning off the tool when not in use to minimize unnecessary energy usage.
Another important factor is the type of task or material being worked on. Harder or denser materials may require more power and, consequently, increase electricity consumption. Users should choose the appropriate tool and power setting for each task to avoid wasteful energy usage.
3. Tips for Optimizing Energy Efficiency
To optimize energy efficiency while using power tools, here are some helpful tips:
- Choose tools with energy-saving features: Look for power tools that have energy-saving modes, variable speed settings, or automatic shut-off functions. These features can help reduce electricity consumption when the tool is not in active use.
- Proper tool selection: Select the right tool for the task at hand. Using a power tool that is too powerful for the task can result in unnecessary energy usage.
- Regular maintenance: Keep power tools in good condition by cleaning and maintaining them regularly. Properly maintained tools ensure optimal energy efficiency.
- Turn off when not in use: Always turn off the tool when taking a break or switching to a different task. Leaving power tools running when not in use wastes electricity.
- Consider cordless options: Cordless power tools often have lower energy consumption compared to corded ones. Invest in high-quality cordless tools if feasible for your tasks.
- Use the appropriate accessories or attachments: Using the correct accessories or attachments can improve efficiency and reduce the amount of energy required to complete a task.
Additional Information on Electricity Consumption
4. Comparison of Power Tool Energy Consumption
While the energy consumption of power tools can vary, it’s helpful to compare the energy usage of different tools. Here is a table showcasing approximate energy consumption for common power tools:
| Power Tool | Energy Consumption (Watts per Hour) |
|---|---|
| Drill | 500-1000 |
| Jigsaw | 500-1200 |
| Sander | 800-1500 |
| Circular Saw | 1500-2200 |
| Miter Saw | 1600-2500 |
5. Power Tools vs. Manual Tools: Energy Comparison
In comparison to manual tools, power tools generally consume more electricity. However, power tools offer faster and more efficient results, reducing overall task duration. This increased efficiency can offset the higher energy consumption. It’s important to carefully consider the specific task requirements and select the appropriate tool accordingly.
6. Safety Considerations with Power Tool Energy Usage
When using power tools, it’s crucial to prioritize safety alongside energy efficiency. Ensure that power tools are used in accordance with manufacturer guidelines, including proper usage techniques and safety precautions. Additionally, be mindful of electrical safety, such as using appropriate circuit breakers, grounding, and avoiding overload situations.
In conclusion, understanding the electricity usage of power tools is important for both cost considerations and environmental impact. By knowing the energy consumption levels of different power tools, factors affecting electricity usage, and implementing energy-saving practices, users can optimize efficiency and contribute to sustainable energy usage in their DIY or professional projects. Remember to choose the right tool for the task, adjust power settings accordingly, and maintain tools properly for optimal energy efficiency.
Key Takeaways: How Much Electricity Does Power Tools Use?
- Power tools vary in their electricity usage, but most operate on average between 500 and 1500 watts.
- Some power tools, like electric drills or sanders, use around 600-800 watts.
- More powerful tools, such as table saws or air compressors, can use up to 1500 watts.
- Using power tools for longer durations or with higher power settings will consume more electricity.
- It’s important to check the power tool’s specifications or user manual to determine its energy consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will address some common questions related to the amount of electricity power tools consume.
1. How much electricity do power tools typically use?
Power tools can vary in their electricity consumption depending on factors like the type of tool, its power rating, and how it is being used. Generally, power tools consume anywhere from a few hundred watts to a couple of thousand watts. For example, a small handheld drill may use around 500 watts, while a powerful circular saw might use 1500 watts.
It’s important to note that the actual electricity usage will also depend on how long the power tool is being used. If a tool is being used continuously for an extended period, it will consume more electricity compared to intermittent or short bursts of use.
2. Are cordless power tools more energy-efficient than corded ones?
Cordless power tools are generally more energy-efficient than their corded counterparts. Cordless tools are designed to be powered by rechargeable batteries, which provide the necessary electrical energy for operation. These batteries have limited capacity, which helps control and optimize the tool’s energy consumption.
Corded power tools, on the other hand, are directly connected to the electrical grid and draw power directly from it. While modern corded tools often have energy-saving features, such as variable speed controls or automatic shut-offs, they still draw a constant amount of electricity depending on their power rating, regardless of the actual workload.
3. Do power tools consume electricity even when they are not in use?
Most power tools consume negligible amounts of electricity when they are not in use and are fully switched off or unplugged. However, some power tools, especially those with standby modes, may still draw a small amount of “phantom” power even when not actively used. These power tools may have features like LED displays, clocks, or rechargeable batteries that require a minimal amount of electricity to maintain their functionality while in standby mode.
To minimize electricity usage when power tools are not in use, it is advisable to unplug them from the power source or use a power strip with an on/off switch to completely cut off the power supply.
4. Can using power tools efficiently help save on electricity costs?
Absolutely! There are several ways you can use power tools efficiently and reduce electricity costs. First, choose the right tool for the job. Using a tool with excessive power for a small task will waste energy. Additionally, maintaining your power tools properly, such as keeping them clean and well-lubricated, can ensure optimal performance and reduce energy consumption.
Furthermore, optimizing your work practices can also save electricity. For example, instead of leaving power tools running idle, turn them off when not in use. It’s also beneficial to plan your workflow to minimize unnecessary tool usage and avoid rework.
5. Are there any energy-saving alternatives to traditional power tools?
Yes, there are energy-saving alternatives to traditional power tools available in the market. One popular option is using manual tools, which rely on human power instead of electricity. Manual tools, like hand drills or hand saws, require physical effort but consume no electricity.
Another eco-friendly alternative is investing in electric power tools with energy-efficient ratings or certifications. These tools are designed to minimize energy consumption without compromising performance. Additionally, renewable energy-powered tools, such as solar-powered or wind-powered tools, are emerging as sustainable alternatives for certain applications.

Summary
Power tools use different amounts of electricity depending on their size and how they are used. Smaller tools like drills and sanders typically use around 500-800 watts, while larger tools like circular saws and table saws can use up to 1,500-2,500 watts. It’s important to check the power rating of your tools and use the appropriate circuit or power source to avoid overloading.
Using power tools efficiently can help conserve electricity. For example, not letting the tool run idle, using it at the lowest required speed, and making sure it is properly maintained can all help reduce energy consumption. By being mindful of how you use your power tools, you can both save electricity and extend the lifespan of your tools.