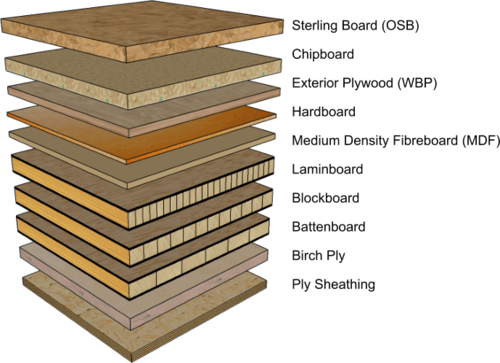
If you’ve ever wondered whether plywood is a manufactured board, you’re in the right place! Plywood is indeed a type of manufactured board, and in this article, we’ll dive deeper into what exactly that means and why it’s important. So, let’s kick things off by exploring the fascinating world of plywood!
Now, you might be thinking, “But isn’t plywood just a regular type of wood?” Well, not quite! Plywood is made by layering thin sheets of wood veneer together, using glue and heat to create a strong and versatile material. It’s like the lasagna of the woodworking world – multiple layers working together to create a sturdy and reliable product.
So why is plywood considered a manufactured board? Unlike solid wood, which comes directly from trees, plywood is crafted by humans. Each layer of wood veneer is carefully selected, bonded together, and processed to create a finished product that’s ready for a variety of applications. From construction projects to furniture making, plywood is a popular choice thanks to its strength, stability, and affordability.
So, whether you’re planning a DIY project or simply curious about the different types of wood materials out there, understanding that plywood is a manufactured board opens up a whole new world of possibilities. Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s dig deeper into the fascinating process behind creating this incredible material!
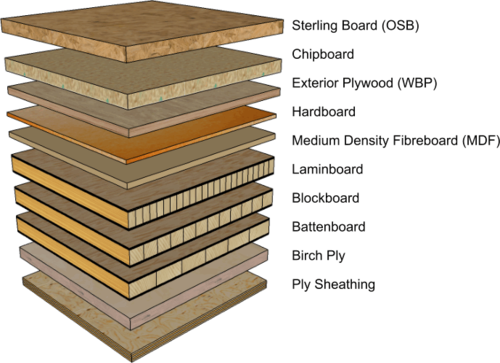
Is Plywood a Manufactured Board?
What is Plywood?
Plywood is a type of engineered wood made from thin layers of wood veneer that are glued together. It is incredibly versatile and used in a wide range of applications, including construction, furniture making, and packaging. Plywood is known for its strength, durability, and dimensional stability. It offers several advantages over solid wood, which makes it a popular choice in many industries.
The process of manufacturing plywood involves cutting logs into thin veneers, which are then dried and layered with their grains running perpendicular to one another. This cross-grain construction gives plywood its strength and resistance to warping or cracking. The layers are bonded together using an adhesive, such as phenol formaldehyde or melamine urea formaldehyde. The final product is pressed under high heat and pressure to create a strong and stable panel of plywood.
While plywood is a manufactured product, it still retains the natural qualities of wood, such as its appearance and ability to be shaped or carved. This makes it a versatile material that combines the best features of solid wood with the enhanced strength and stability provided by its manufacturing process.
Advantages of Plywood
Plywood offers several advantages over other types of wood products, which has contributed to its widespread use in various industries:
- Strength and Durability: Plywood is known for its strength and can withstand heavy loads and impacts better than solid wood. It is also resistant to warping, cracking, and shrinking, making it suitable for applications that require stability and durability.
- Dimensional Stability: The cross-grain construction of plywood gives it excellent dimensional stability, meaning it is less prone to expansion or contraction due to changes in temperature and humidity. This stability makes it ideal for use in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
- Versatility: Plywood can be easily cut, shaped, and drilled, allowing for intricate designs and complex structures. It can also be bent to a certain extent, making it suitable for curved applications. Additionally, plywood can be painted, stained, or veneered to achieve the desired aesthetic.
- Cost-Effective: Plywood is generally more affordable than solid wood, making it a cost-effective option for large-scale projects. It also offers better utilization of timber resources, as the manufacturing process allows for the production of larger panels from smaller logs.
- Environmental Sustainability: Plywood is a sustainable choice as it can be made from fast-growing tree species and the manufacturing process minimizes waste. Additionally, the use of wood products helps reduce carbon dioxide emissions by storing the carbon absorbed during tree growth.
The combination of these advantages makes plywood a preferred choice for a wide range of applications, from construction and interior design to packaging and furniture making.
Plywood vs. Solid Wood
One of the common comparisons made is between plywood and solid wood. While both materials have their own merits, there are distinct differences that make plywood a favorable option in many cases.
Strength: Plywood is generally stronger and more stable than solid wood, thanks to its layered construction. This makes it suitable for demanding applications where strength and durability are essential.
Cost: Plywood is often more cost-effective than solid wood. Its manufacturing process allows for better utilization of timber resources and creates fewer defects compared to solid wood.
Size: Plywood is available in larger sizes than solid wood, making it suitable for projects that require larger panels or sheets. It offers versatility in design and reduces the need for joinery work.
Stability: The cross-grain construction of plywood gives it excellent dimensional stability. It is less prone to warping, shrinking, or expanding due to changes in moisture content or temperature, making it ideal for areas with high humidity or fluctuating conditions.
Aesthetics: While solid wood is often favored for its natural beauty, plywood can also be visually pleasing. It can be veneered or overlaid with decorative finishes to achieve a desired look and can mimic the appearance of various wood species.
Ultimately, the choice between plywood and solid wood depends on the specific requirements of the project and the factors that are given priority, such as cost, strength, stability, or aesthetic preferences.
Tips for Choosing and Using Plywood
When selecting plywood for a project, there are a few factors to consider:
- Grade: Plywood is available in different grades, which indicate the quality and appearance of the panels. Choose a grade that is suitable for the intended application, taking into account factors like strength, visual appeal, and budget.
- Thickness: Plywood is available in various thicknesses, and the right thickness should be selected based on the structural requirements of the project. Thicker plywood panels generally offer greater strength and durability.
- Moisture Resistance: If the plywood will be exposed to moisture or used in wet areas, consider choosing a type that is specifically designed for moisture resistance. This will help prevent delamination and damage caused by water absorption.
- Quality of Bonding: Inspect the plywood for any signs of delamination or weak bonding. Ensure that the layers are securely glued together and that there are no visible gaps between them.
- Finish: If the plywood will be visible in the final project, consider the desired finish or appearance. Plywood can be left natural, painted, stained, or veneered to match the aesthetic requirements of the project.
When using plywood in a project, it is important to follow best practices to ensure optimal results:
- Use appropriate tools and techniques for cutting and shaping plywood, taking into consideration its cross-grain construction.
- Store plywood in a flat and dry area to prevent warping or damage. Avoid exposing it to extreme temperature or moisture conditions.
- Ensure proper sealing or finishing of the plywood to protect it from moisture and prolong its lifespan.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for installation and fastening methods to ensure the structural integrity of the project.
By considering these tips and guidelines, you can make the most out of plywood and harness its many benefits in your projects.
Using Plywood Wisely
Plywood is undoubtedly a manufactured board, but its unique construction and properties make it a standout in the world of wood products. Its strength, durability, and versatility have made it a popular choice among professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike. By understanding its manufacturing process, advantages, and best practices for use, you can confidently incorporate plywood into your projects, knowing that you are utilizing a reliable and high-quality material.
Additional Information:
What Makes Plywood Different from Other Manufactured Boards?
Plywood stands out from other manufactured boards due to its layered construction and the use of whole wood veneers. Unlike particleboard or MDF, which are made from wood fibers or particles held together with resin or adhesive, plywood retains the natural qualities of wood while offering enhanced strength and stability.
Additionally, plywood has a higher density than other manufactured boards, making it more suitable for structural and load-bearing applications. Its cross-grain construction also contributes to its superior strength and resistance to warping.
Applications of Plywood in Different Industries
Plywood finds wide-ranging applications across various industries:
- Construction: Plywood is extensively used in construction for wall sheathing, flooring, roofing, formwork, and concrete reinforcement.
- Furniture and Cabinetry: Plywood is a popular choice in furniture making for its strength, durability, and ability to withstand screws and fasteners. It is utilized in making cabinets, shelves, tables, and chairs.
- Interior Design: Plywood is used for wall cladding, ceiling panels, decorative elements, and furniture in interior design projects.
- Packaging and Shipping: Plywood is commonly used to create crates, pallets, and other packaging materials due to its strength and ability to protect goods during transport.
- Automotive and Aircraft: Plywood is utilized in the construction of vehicle and aircraft interiors, such as panels, partitions, flooring, and storage compartments.
These are just a few examples of the many industries that rely on the versatility and performance of plywood.
The Future of Plywood
Plywood has a bright future ahead, driven by its sustainability, versatility, and economic advantages. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the demand for sustainable materials like plywood is on the rise. Plywood’s ability to store carbon, its efficient use of timber resources, and its recycled content contribute to its eco-friendly reputation.
With advancements in technology, the manufacturing process for plywood continues to improve, resulting in higher quality products that meet the demands of modern-day applications. Additionally, innovations in veneer processing and adhesive technology are further enhancing the performance and durability of plywood.
As design trends lean towards nature-inspired aesthetics, plywood’s natural beauty and the ability to showcase the uniqueness of wood grains are becoming increasingly desirable. This, coupled with its strength and versatility, makes plywood a material of choice for architects, designers, and DIY enthusiasts.
Overall, plywood’s future is positioned for growth and innovation, cementing its place as a reliable and highly sought-after manufactured board.
Key Takeaways: Is Plywood a Manufactured Board?
- Plywood is a type of manufactured board made from layers of wood veneer.
- The layers are glued together, alternating the grain direction for added strength and stability.
- Plywood is commonly used in furniture, construction, and other applications where strength and durability are essential.
- It is a cost-effective alternative to solid wood and offers a more consistent and uniform material.
- Due to its construction, plywood has good resistance to warping, shrinking, and cracking.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about plywood as a manufactured board:
What is plywood made of?
Plywood is made from thin layers of wood called veneers. These veneers are obtained by peeling or slicing logs. The veneers are then glued together with the grain of each layer alternating in a perpendicular direction, creating a strong and stable panel.
The type of wood used for plywood can vary, but commonly used species include pine, fir, and spruce. Additionally, manufacturers often use different grades of plywood, which can affect its appearance and strength.
Is plywood considered a manufactured board?
Yes, plywood is classified as a manufactured board. It is created by combining wood veneers with adhesive to form a composite material. Unlike solid wood boards, plywood is made by artificially laminating layers of wood together rather than cutting from a single piece of timber.
This manufacturing process allows plywood to have improved strength and durability, making it a popular choice in various construction and woodworking applications.
What are the advantages of using plywood over solid wood?
Plywood offers several advantages over solid wood. Firstly, it is generally more cost-effective, as it can be produced from lower-grade or less expensive wood species. Additionally, plywood is less prone to warping and shrinking, making it more stable in different environmental conditions.
Furthermore, plywood can be manufactured in larger sizes compared to solid wood boards, allowing for seamless installations and reducing the need for joints. Its cross-laminated structure also provides improved strength, making it suitable for structural applications.
Are there different types or grades of plywood available?
Yes, there are various types and grades of plywood available. The type of plywood is determined by factors such as the type of wood veneers used, the bonding agent, and any special treatments applied to the surface.
The grading of plywood refers to its appearance and structural quality. Common grades include A, B, C, and D, with A being the highest quality and D being the lowest. These grades may also have additional symbols to denote specific characteristics or uses. It is important to choose the right type and grade of plywood based on the intended application.
What are the common uses of plywood?
Plywood is a versatile material used in various applications. It is commonly used in construction for sheathing, subfloors, and roofs. In furniture making, plywood is often used for shelves, cabinets, and tabletops due to its stability and strength.
Additionally, plywood is used in the manufacturing of doors, paneling, packaging crates, and even boat building. Its wide availability, affordability, and durability make it a popular choice across different industries and DIY projects.
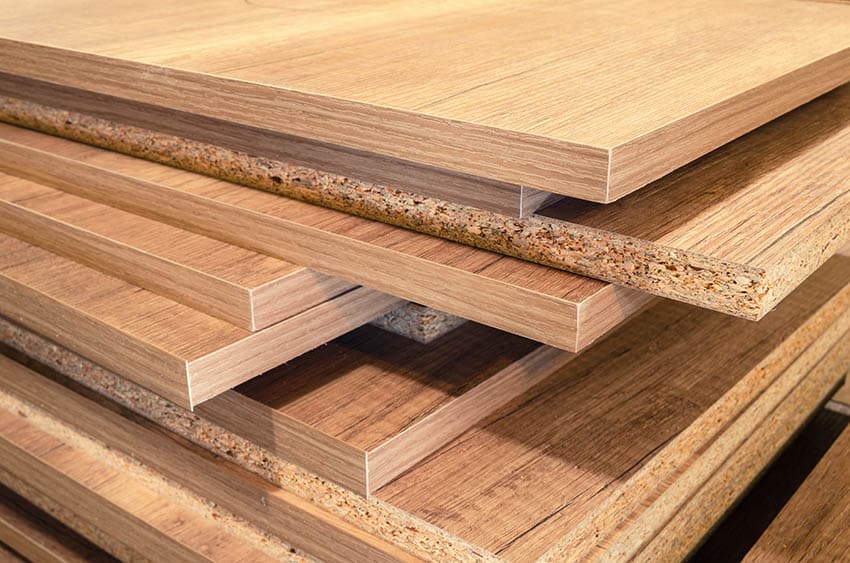

Summary
So, is plywood a manufactured board? Yes, it is! Plywood is made by gluing thin layers of wood together, which makes it a type of engineered wood. It is strong, durable, and used for various applications like furniture and construction.
Plywood is versatile and cost-effective, making it a popular choice in many industries. It is important to note that while plywood is a manufactured board, it still retains some of the qualities of natural wood. So, next time you see plywood, you’ll know that it’s a manufactured board that brings together the best of both worlds!