Do you ever wonder if there’s a standard for plywood? Well, you’re in luck because we’re here to answer that question! Plywood is a versatile and widely used material known for its strength and durability. But is there a specific standard that plywood must meet? Let’s dive in and find out!
When it comes to plywood, there are certain criteria that determine its quality and suitability for various applications. These criteria include factors like thickness, strength, and the types of wood used in its construction. Meeting a standard ensures that plywood meets specific requirements and performs as expected.
In this article, we’ll explore the different standards that exist for plywood and how they impact its quality and performance. So, if you’re curious about the standards for plywood, keep reading to discover all the essential information you need to know!
When it comes to plywood, understanding the standard specifications is crucial. Plywood standards define the quality, strength, and performance of the material. Different countries have their own set of standards, such as the British Standard (BS) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). These standards cover factors like veneer thickness, bonding types, and moisture resistance. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers ensure that the plywood meets the necessary requirements for various applications.
The Standard for Plywood: Exploring Quality and Specifications
Plywood is a versatile and widely used building material known for its strength and durability. As with any construction material, it is essential to understand the standard for plywood to ensure you select the right product for your project. In this article, we delve into the details of plywood standards, exploring the factors that determine quality and specifications. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional contractor, this article will provide you with valuable insights to make informed decisions when it comes to plywood.
Understanding Plywood Grading: Quality at a Glance
Plywood grading is an essential aspect of determining the quality of the material. Plywood sheets are categorized into different grades based on the appearance of the face and back veneers, as well as the number of defects present. The grading systems used may vary from country to country, but the most common one is the American Plywood Association (APA) grading system.
In the APA grading system, plywood is classified into four main grades: A, B, C, and D. Grade A plywood is the highest quality, with a smooth and consistent appearance, minimal voids, and few, if any, surface defects. On the other end of the spectrum, Grade D plywood may have noticeable defects, including knot holes and splits, making it more suitable for non-structural applications.
Benefits of Graded Plywood
Using graded plywood offers several advantages:
1. Quality Assurance: Graded plywood provides a standard measure of quality, ensuring you get a reliable and consistent product for your project.
2. Appearance: Choosing a higher grade of plywood guarantees a visually appealing finish for visible applications.
3. Structural Integrity: Higher-grade plywood offers better strength and stability, making it suitable for load-bearing applications.
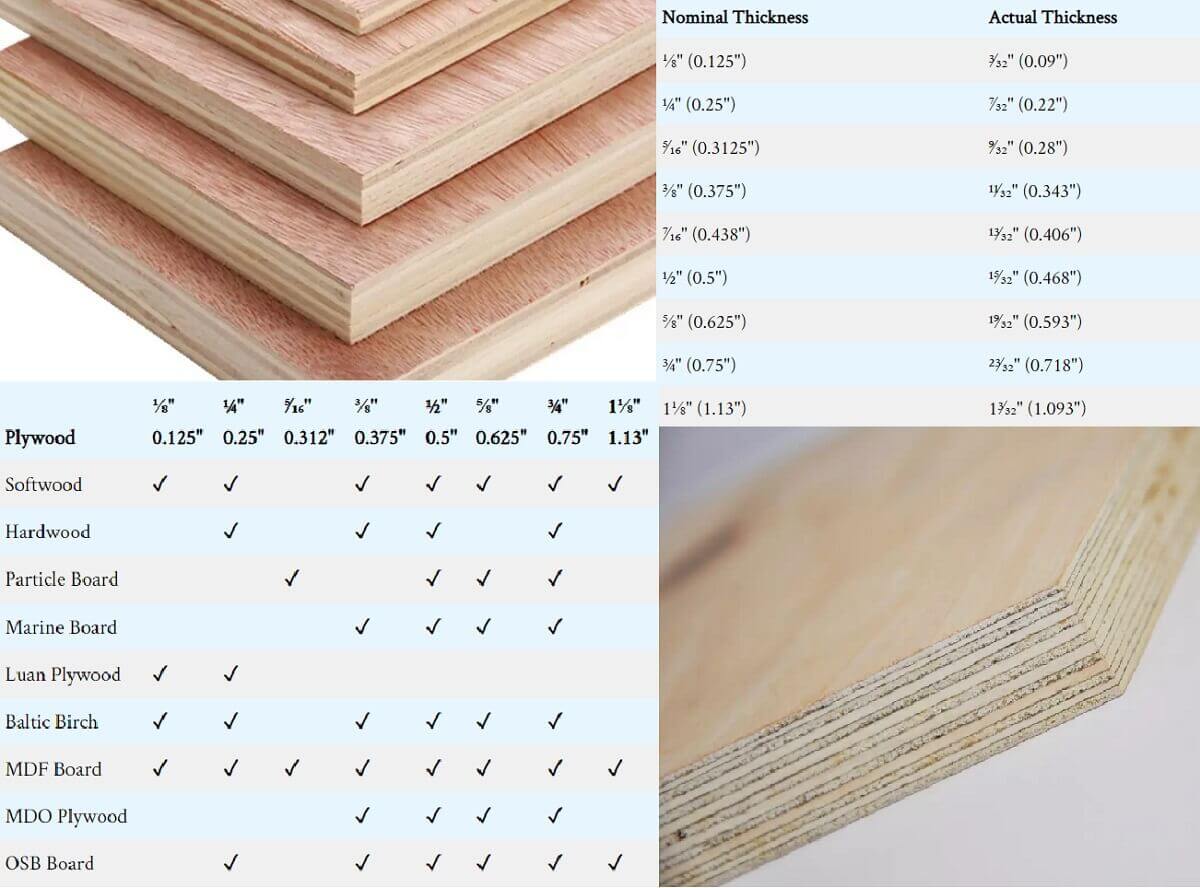
Standard Plywood Thicknesses: Finding the Right Fit
Plywood comes in various thicknesses, and selecting the appropriate thickness is crucial for the success and safety of your project. The standard thicknesses available in most markets range from 1/4 inch to 3/4 inch. However, specific industry or regional standards may differ.
The thickness of plywood determines its strength and rigidity. Thicker plywood is generally stronger and more suitable for heavy-duty applications, while thinner plywood is more flexible and lighter. It is important to consider the load and purpose of your project when selecting the right thickness.
Choosing the Right Plywood Thickness
Consider the following factors when selecting the plywood thickness:
1. Span: For large spans, thicker plywood is required to prevent sagging or bending.
2. Weight: Thinner plywood is ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as in furniture or aircraft construction.
3. Structural Requirements: Consult building codes and standards to determine the minimum thickness required for specific structural elements.
Understanding Plywood Glue Types: Ensuring Structural Integrity
The glue used to bond the layers of plywood together significantly impacts its strength and performance. Various glue types, such as urea formaldehyde, melamine, phenol formaldehyde, and polyvinyl acetate (PVA), are used in plywood production. Each glue type has different properties and suitability for specific applications.
To ensure structural integrity and resistance to moisture and temperature changes, it is crucial to select plywood with the appropriate glue type. Plywood with phenol formaldehyde or melamine glues, for example, offers excellent waterproofing properties, making it suitable for outdoor and humid environments.
Choosing the Right Glue Type
Consider the following factors when choosing the glue type for your plywood:
1. Environmental Exposure: Determine the level of moisture and temperature fluctuations the plywood will be subjected to.
2. Indoor or Outdoor Use: Outdoor applications require plywood with superior moisture resistance.
3. Adhesive Strength: Evaluate the need for high bond strength, especially for load-bearing structural elements.
Plywood Certifications: Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Certifications play a crucial role in verifying the quality and compliance of plywood with international standards. Look for certifications such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification, which ensures that the plywood comes from responsibly managed and sustainable sources.
Additionally, certifications like the Structural Plywood and OSB (oriented strand board) Certification Program offer confidence in the structural integrity and performance of plywood in construction applications.
Benefits of Certified Plywood
Using certified plywood offers several benefits:
1. Quality Assurance: Certifications provide assurance that the plywood meets industry standards for safety and performance.
2. Sustainability: Certified plywood supports responsible forest management and reduces the environmental impact of your project.
3. Compliance: Selecting certified plywood ensures compliance with building codes and regulations.
The Versatility of Plywood: Applications and Advantages
Plywood’s versatility has made it a popular choice among builders and designers for a wide range of applications. From construction and furniture-making to interior design and artistic creations, plywood offers numerous advantages.
One of the primary advantages of plywood is its strength and durability. It can withstand heavy loads, making it suitable for structural elements like beams, columns, and flooring. Additionally, plywood’s layered construction helps prevent warping and splitting, ensuring longevity in various environments.
Moreover, plywood’s smooth and consistent surface allows for easy finishing and painting. It can be easily cut, drilled, and shaped to meet specific project requirements. This adaptability makes it an excellent choice for both functional and aesthetic purposes.
Application Ideas for Plywood
Consider the following applications where plywood excels:
1. Construction: Plywood is commonly used in residential and commercial construction for wall sheathing, roofing, and formwork.
2. Furniture: It is a popular material for creating sturdy and stylish furniture pieces like cabinets, tables, and chairs.
3. Interior Design: Plywood can be used for wall paneling, flooring, and decorative elements, providing a modern and contemporary look.
4. Art and Crafts: Plywood serves as a versatile canvas for artists and crafters, allowing for unique and expressive creations.
Plywood in Home Improvement: A DIY Enthusiast’s Guide
Choosing the Right Plywood for Your Project
Whether you’re embarking on a small DIY project or a major home improvement task, selecting the right plywood is crucial for success. Consider the following tips to make an informed choice:
1. Determine the Purpose: Identify the specific use of plywood in your project, such as cabinetry, shelving, or flooring.
2. Assess Environmental Factors: Consider the levels of moisture, humidity, and temperature the plywood will be exposed to.
3. Research Grading Systems: Familiarize yourself with the grading system used in your region to understand the quality of plywood available.
4. Seek Expert Advice: Consult with professionals or visit reputable suppliers for guidance on the suitable plywood type and specifications.
Preparing Plywood for Painting or Finishing
To achieve a professional finish on your plywood project, proper preparation is essential. Follow these steps to ensure the best results:
1. Sanding: Start by sanding the plywood surface to create a smooth and even finish. Use fine-grit sandpaper in a circular motion to remove any imperfections.
2. Priming: Apply a coat of primer specifically designed for plywood. This will seal the surface and provide a better base for paint or finish.
3. Painting/Finishing: After the primer has dried, apply your chosen paint or finish using even strokes. Multiple coats may be necessary for full coverage.
4. Sealing: To protect your plywood from moisture and wear, consider applying a clear sealer or varnish as a final protective layer.
Tips for Proper Plywood Installation
Installing plywood correctly is crucial for ensuring its longevity and performance. Follow these tips for a successful installation:
1. Allow for Expansion: Leave a small gap, typically 1/8 inch, between plywood sheets to accommodate natural expansion and prevent buckling.
2. Use Proper Fasteners: Choose appropriate screws or nails based on the thickness and intended use of the plywood. Make sure they penetrate the underlying support adequately.
3. Optimize Support: Install plywood on a stable and level surface, ensuring proper support underneath. Use blocking or additional joists for added strength if needed.
4. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific installation guidelines, as they may vary based on the particular plywood product.
Conclusion
Understanding the standard for plywood is essential for making informed decisions when it comes to selecting the right material for your projects. From plywood grading to glue types and certifications, each aspect plays a role in determining the quality, durability, and suitability of plywood for various applications. By considering these factors and following proper installation and finishing techniques, you can ensure the success and longevity of your projects. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional, armed with this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the world of plywood and unlock its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- Plywood standards ensure consistency and quality in the manufacturing process.
- There are different standards for plywood depending on the country or region.
- The most widely used standard for plywood is the one set by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
- Standard plywood sizes are typically 4×8 feet, but other dimensions are also available.
- Knowing the standard for plywood can help ensure you select the right type for your project.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Are there specific standards for plywood?
Q: What are the standard specifications for plywood?
Plywood is subject to various standards to ensure its quality and appropriate usage. The most common standards for plywood include size, thickness, and grade. The standard sizes of plywood sheets are typically 4 feet by 8 feet or 3 feet by 6 feet, while thicknesses can range from 1/8 inch to 1 1/4 inches. Grades refer to the veneer quality and are usually classified as A, B, C, or D, with A being the highest quality.
The standard also covers the moisture content, adhesive bonding, formaldehyde emission levels, and other performance criteria. These standards are set by authoritative bodies, such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), to ensure plywood meets specific requirements for construction and industrial use.
Q: How do I choose the right plywood standard for my project?
Choosing the appropriate plywood standard depends on the specific needs of your project. Factors to consider include the type of application, environmental conditions, and desired aesthetic appeal. If you require high-quality finish surfaces, you might opt for plywood with a higher grade standard, such as A-grade, as it exhibits fewer defects and a smoother finish.
For construction purposes, like framing or sheathing, a lower grade plywood might be suitable, as long as it meets the strength and durability requirements. It’s essential to consult industry professionals and refer to building codes to select the right plywood standard for your project. Ultimately, understanding the standard specifications and consulting with experts can help you make an informed decision.
Q: Can plywood standards vary between countries?
Yes, plywood standards can vary between countries due to differences in climatic conditions, manufacturing practices, and quality requirements. While some countries may follow the standards set by international organizations like ISO, others might have their own specific standards.
For instance, in the United States, the ASTM International standards and the APA – The Engineered Wood Association guidelines are widely used. In Europe, the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) sets standards for plywood. It’s crucial to understand and adhere to the plywood standards applicable in your country or the country where the plywood will be used to ensure compliance with local regulations and best practices.
Q: Are there any safety standards for plywood?
Yes, safety standards are an essential aspect of plywood manufacturing. Safety standards focus on factors such as formaldehyde emissions, which can impact indoor air quality. Formaldehyde emissions are regulated by organizations like the California Air Resources Board (CARB) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States.
The safety standards for plywood also cover protection against fire, chemicals, and other hazardous substances. Compliance with these safety standards ensures that plywood products are safe for human health and the environment. It’s crucial to be aware of and select plywood that meets the necessary safety standards based on the intended use and local regulations.
Q: Are there specific standards for marine plywood?
Yes, marine plywood has its own specific standards due to its unique properties and applications. Marine plywood is designed to withstand moisture, humidity, and exposure to water without delaminating or losing strength. The British Standard BS 1088 is an internationally recognized standard for marine plywood.
This standard specifies the quality of veneers used, the bonding strength between layers, and the type of adhesive used, typically a phenolic resin. Marine plywood that conforms to the BS 1088 standard is considered suitable for marine and exterior construction projects where durability and water resistance are crucial.

From the Ground Up 10 – OSB VS Standard Veneer Plywood
Summary
Okay, so let’s wrap this up! Plywood is a type of wood that’s made up of thin layers glued together. It’s used for lots of things like furniture, flooring, and even construction. But is there a standard for plywood? Well, the answer is both yes and no. There are different types and grades of plywood that have different qualities and uses. So, it really depends on what you need it for. Some types of plywood are stronger than others, and some are more water-resistant. So, before you buy plywood, make sure you know what you’ll be using it for because there’s no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to plywood standards.
In conclusion, plywood is a versatile material with varying qualities and uses. It’s important to consider your specific needs and the different types and grades of plywood available to make sure you choose the right one. So, whether you’re building a bookshelf or renovating your home, remember to do your research before buying plywood.
