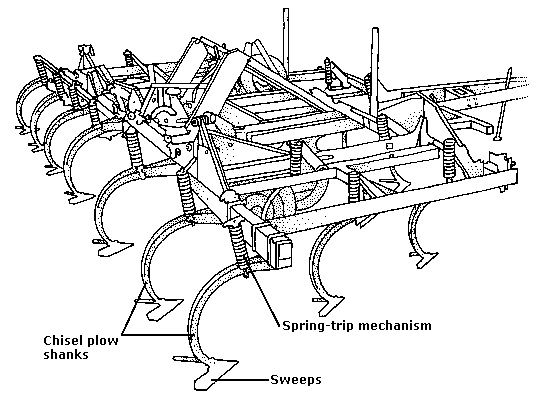
Looking to learn about the parts of a chisel plow? You’ve come to the right place!
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of agriculture and discover the essential components that make up this crucial farming implement.
From the shanks to the points, we’ll explore each part and uncover their unique roles in the chisel plow’s operation. So, buckle up and get ready to dig deep into the world of chisel plows!
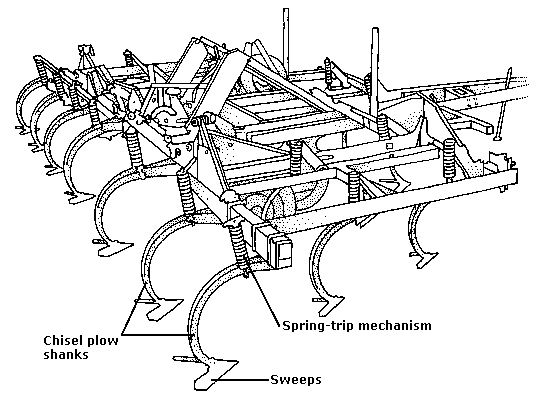
The Parts of a Chisel Plough: A Comprehensive Guide
Chisel ploughs are essential agricultural implements used for tillage and soil preparation. They are specifically designed to break up compacted soil, improve drainage, and prepare the land for planting. Understanding the different parts of a chisel plough is crucial for its proper operation and maintenance. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various components that make up a chisel plough and how they contribute to its functionality and efficiency.
1. Frame
The frame is the backbone of a chisel plough, providing the structure and strength to withstand the rigorous tasks it must perform. Typically made of durable steel, the frame is designed to support the weight of the plough and distribute the forces evenly. It acts as a base for attaching the other components and ensures the stability and proper alignment of the entire implement. The frame may vary in size and shape depending on the specific model and the intended use of the chisel plough.
The frame of a chisel plough is usually constructed with a combination of main beams and cross members, creating a sturdy and rigid structure. The main beams run lengthwise along the plough and are responsible for bearing most of the load. Cross members connect the main beams and provide additional reinforcement. The frame also includes mounting points for the shanks, coulters, and other components, allowing for easy adjustment and customization.
2. Shanks
Shanks are one of the most critical components of a chisel plough. They are responsible for penetrating the soil and breaking up the compacted layers. Typically made of hardened steel, shanks are designed to withstand the immense pressure and stress exerted during the tillage process. They are attached to the frame of the plough and extend downwards into the soil.
The number and arrangement of shanks can vary depending on the size and model of the chisel plough. They are often spaced evenly along the frame and can be adjusted to meet specific soil conditions and tillage requirements. Shanks may feature various designs, such as straight or curved, to optimize soil penetration and reduce the likelihood of clogging. Some chisel ploughs also offer replaceable shank tips that can be changed to match different soil types and conditions.
3. Ground Engaging Tools (GETs)
Ground engaging tools (GETs) are the components of a chisel plough that directly interact with the soil. They are attached to the shanks and are responsible for loosening and aerating the ground. GETs come in various forms, including sweeps, chisel points, and twisted shovels. The selection of the appropriate GET depends on the desired depth, soil type, and the level of tillage required.
Sweeps, also known as wings or blades, are flat or concave-shaped components that effectively cut through the soil, creating a furrow. They are excellent for breaking compacted layers and mixing organic matter into the soil. Chisel points, on the other hand, have a more pointed and narrow design, allowing for deeper penetration and minimal soil disturbance. Twisted shovels combine the advantages of sweeps and chisel points, with an angled or twisted shape that facilitates soil inversion and creates a well-tilled seedbed.
4. Coulters
Coulters are additional cutting tools that work in tandem with the shanks to enhance the performance of a chisel plough. They are mounted in front of the shanks and are responsible for cutting through crop residue, vegetation, and surface debris, creating a clear path for the shanks to penetrate the soil. Coulters can minimize clogging, improve the effectiveness of the shanks, and help maintain a consistent working depth.
There are various types of coulters available, including disc coulters and disc ripple coulters. Disc coulters consist of round rotating blades that slice through the surface residues, while disc ripple coulters feature wavy or serrated edges that provide additional cutting action. The choice of coulters depends on the specific field conditions, crop residues, and the level of trash clearance required.
5. Depth Control System
To ensure accurate and consistent tillage, chisel ploughs feature a depth control system. This system allows the operator to adjust the working depth of the shanks according to the soil conditions and desired tillage depth. It typically includes depth wheels or skids that provide stability and maintain the desired cutting depth throughout the field.
Depth wheels are wheels mounted behind the shanks, allowing for precise depth adjustment. The wheels can be raised or lowered using a height adjustment mechanism, ensuring consistent depth across the field. Skids, on the other hand, are metal plates or bars that slide along the ground and control the depth of the plough. They are particularly useful when working in rocky or uneven fields.
6. Hydraulic System
Many modern chisel ploughs come equipped with a hydraulic system that provides additional convenience and control for the operator. The hydraulic system allows for easy adjustment of various components, such as the shanks and coulters, without requiring manual labor. It simplifies the process of changing the working depth, swapping out implements, and performing on-the-go adjustments.
The hydraulic system is usually operated using hydraulic cylinders, which provide the force necessary to move the components. These cylinders can be controlled from within the tractor cabin, allowing the operator to make quick and precise adjustments while in the field. The hydraulic system greatly improves efficiency and reduces downtime, as manual adjustments can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and less accurate.
7. Wheels and Transport Mechanism
Chisel ploughs are typically equipped with wheels and transport mechanisms to facilitate movement on and off the field. The transport mechanism allows the plough to be lifted from the ground and transported safely between locations. This mechanism can vary depending on the specific chisel plough model but is typically hydraulically or mechanically operated.
Wheels are an essential part of the transport mechanism. They provide stability, support the weight of the plough during transport, and allow for easy maneuverability. Some chisel ploughs have removable or foldable wheels to reduce the overall width of the implement, making transportation through narrow roads or gateways more manageable.
In conclusion, a chisel plough consists of several integral components that work together to prepare the soil for planting. Understanding the different parts of a chisel plough, such as the frame, shanks, ground engaging tools, coulters, depth control system, hydraulic system, and wheels, is crucial for proper operation and maintenance. By familiarizing yourself with these components and their functions, you can optimize the performance and efficiency of your chisel plough, leading to better soil quality and higher crop yields.
Key Takeaways: What Are the Parts of Chisel Plough?
- A chisel plough consists of five main parts: frame, shanks, coulters, depth control, and wheels.
- The frame is the backbone of the chisel plough and holds all the other parts together.
- Shanks are long, pointed metal bars that penetrate the soil and break it up.
- Coulters are rotating discs or blades attached to the shanks that cut through residue and vegetation.
- Depth control mechanisms allow the operator to adjust the depth at which the chisel plough operates.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does a chisel plough work?
The chisel plough is a type of agricultural equipment used for tillage operations. It works by using chisel-like blades to cut through the soil and break it up. These blades are commonly referred to as chisel tines or shanks. When the chisel plough is pulled through the field, the blades penetrate the soil, breaking up any compacted layers or crop residues. This helps improve soil aeration, water infiltration, and root penetration.
The chisel plough has adjustable depth control, allowing farmers to set the desired working depth according to their specific requirements. The depth can typically range from 6 to 18 inches, depending on the type of soil and the crop being grown. The chisel plough is commonly used in conservation tillage practices and is effective in reducing soil erosion.
2. What are the main parts of a chisel plough?
A chisel plough consists of several essential parts, each serving a specific purpose. The main parts of a chisel plough include:
– Frame: This forms the main structure of the chisel plough and provides stability and support.
– Chisel Tines or Shanks: These are the blades that penetrate the soil. They are usually made of high-quality steel and are attached to the frame.
– Coulter Knife: The coulter knife is a disc-shaped blade positioned in front of the chisel tines. It helps cut through crop residue and vegetation, making it easier for the chisel tines to penetrate the soil.
– Depth Control System: The depth control system allows the farmer to adjust the working depth of the chisel plough.
– Hitch: The hitch is the point where the chisel plough connects to the tractor. It ensures the proper transfer of power from the tractor to the implement.
3. What are the advantages of using a chisel plough?
Using a chisel plough offers several benefits for farmers. Some of the main advantages include improved soil structure, reduced soil erosion, and enhanced water management. The chisel plough helps break up compacted soil, allowing air, water, and nutrients to reach the plant roots more easily. This results in improved root development and overall plant health.
Another advantage of using a chisel plough is its ability to reduce soil erosion. By breaking up compacted soil and crop residues, the chisel plough helps create a more favorable soil surface that withstands erosion caused by wind and water.
Additionally, the chisel plough can also help manage water more efficiently. By breaking up compacted layers and improving soil structure, it promotes better water infiltration and reduces surface runoff. This can be especially beneficial in areas with high rainfall or irrigation.
4. Can a chisel plough be used in all types of soil?
While a chisel plough can be used in various soil types, its effectiveness may vary depending on the specific conditions. Chisel ploughs are most commonly used in soils with medium to high moisture content and moderate levels of compaction. These conditions allow the chisel tines to penetrate the soil and break it up effectively.
In heavy clay soils or very dry and hard soils, a chisel plough may not be as effective. The compacted soil in these conditions may require more aggressive tillage methods to break it up.
Before using a chisel plough, it is essential to consider factors such as soil type, moisture content, and compaction levels. It is also recommended to consult with local agricultural experts to determine the suitability of a chisel plough for specific soil types and conditions.
5. Is there any maintenance required for a chisel plough?
Like any other agricultural equipment, a chisel plough requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Some of the maintenance tasks for a chisel plough include:
– Cleaning: After each use, remove any soil or debris that may have accumulated on the blades or frame. This prevents rust and helps maintain the quality of the equipment.
– Lubrication: Apply lubricant to moving parts such as hinges and pivots to reduce friction and prevent wear and tear.
– Blade Inspection: Regularly inspect the chisel tines and coulter knife for any damage or wear. Replace any worn or damaged blades to maintain optimal performance.
– Frame Inspection: Check the frame for any cracks or structural issues. Repair or replace any damaged parts promptly to ensure safe and efficient operation.
– Storage: When not in use, store the chisel plough in a clean and dry location to prevent rust and damage. Consider covering it to protect it from the elements.
By following these maintenance practices, farmers can ensure that their chisel plough remains in good working condition, providing reliable performance for years to come.
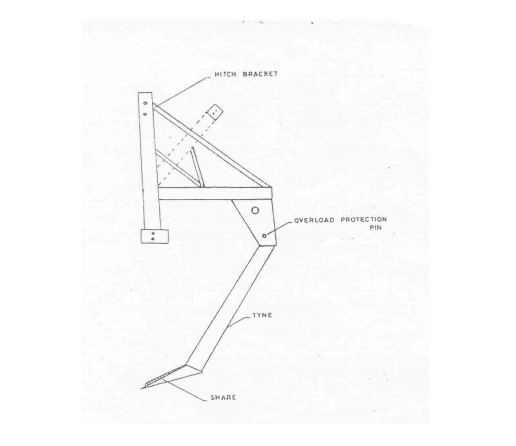
Summary
I hope you now know more about chisel ploughs! They are used for loosening soil, and have a few main parts. The frame holds everything together. The tines do the digging, and they can be adjustable. Finally, the shanks connect the tines to the frame. Happy farming!
In conclusion, chisel ploughs are important tools for preparing soil for planting crops. They have a sturdy frame, adjustable tines for digging, and shanks to connect everything. Now you’re ready to dig in and learn even more about farming equipment!