Have you ever wondered what those letters mean on plywood? Well, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ll unravel the mystery and explain what those perplexing letters actually stand for. So, let’s dive right in and discover the secrets of plywood letters!
Now, you might be thinking, “What’s the big deal with these letters? Can’t I just ignore them?” Well, not quite! Those letters on plywood actually hold important information about the quality and characteristics of the wood. Understanding what they mean can help you make informed decisions when choosing the right plywood for your projects.
So, whether you’re a woodworking enthusiast or simply curious about the world of plywood, we’ll demystify those letters and make the plywood aisle at the hardware store a lot less intimidating. Get ready to unlock the hidden language of plywood letters and expand your knowledge in a fun and engaging way!
What Do the Letters on Plywood Mean? A Comprehensive Guide
Plywood is a popular building material known for its versatility and strength. However, navigating the different types and grades of plywood can be confusing, especially when faced with a multitude of letters and numbers. In this guide, we will demystify the letters on plywood and help you understand their meaning and significance. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional contractor, this information will empower you to make informed decisions when choosing the right plywood for your project.
Understanding Plywood Grades: A, B, C, and D
Plywood is typically graded with a system of letters, with each letter denoting a specific grade. The most common grading system for plywood includes A, B, C, and D. Each letter represents a quality of appearance, surface imperfections, and the number of knots.
Grade A plywood is considered the highest quality and offers a smooth and flawless finish. It is free of any visible defects, such as knots or blemishes, making it suitable for projects that require an aesthetically pleasing surface.
Grade B plywood is slightly lower in quality compared to Grade A. It may have some minor knots and surface defects but still maintains a decent appearance. Grade B plywood is often used for applications where appearance is important but not critical.
Grade C plywood contains more visible knots and surface imperfections, making it suitable for projects where appearance is less of a concern. It is commonly used in construction and non-visible areas where strength is the primary consideration.
Grade D plywood is the lowest grade and features numerous knots, cracks, and rough patches. It is typically used for structural purposes or in applications where aesthetics are not a concern, such as temporary structures or sheathing.
It’s important to note that while the grading system provides a general indication of plywood quality, the specific standards and tolerances may vary depending on the manufacturer. Therefore, it’s always advisable to consult the grading guidelines provided by the manufacturer when selecting plywood.
Decoding the Exposure Durability Ratings: Exterior and Interior
In addition to the grading system, plywood may also be labeled with exposure durability ratings. These ratings indicate the suitability of the plywood for different levels of exposure to moisture and weather conditions. The two main categories of exposure durability ratings are exterior and interior.
Exterior-rated plywood, denoted by the letter “X,” is designed to withstand long-term exposure to the elements. It is treated with chemicals or preservatives that make it resistant to moisture, rot, and insects. Exterior plywood is commonly used for outdoor applications such as roofing, siding, and decking.
Interior-rated plywood, denoted by the letter “I,” is intended for use in dry or controlled environments. It is not designed to withstand prolonged exposure to moisture or exterior elements. Interior plywood is commonly used for furniture, cabinetry, and other indoor applications.
When selecting plywood for your project, consider the intended use and the level of exposure to determine whether exterior or interior-rated plywood is suitable.
Understanding the Core Types: CDX, AC, and BC
The letters on plywood also indicate the type of core material used in its construction. The core is the inner layer or layers of wood that provide stability and strength to the plywood.
CDX plywood is a common type that is often used in construction. The letter “C” refers to the quality of the face veneer, while “D” represents the quality of the back veneer. The “X” denotes an exterior rating, indicating that the plywood is suitable for use in outdoor applications.
AC plywood is known for its smooth and sanded face veneer, making it an excellent choice for projects that require a high-quality finish. The “A” represents the quality of the face veneer, while “C” represents the quality of the back veneer. AC plywood is typically used for furniture, cabinets, and other interior applications.
BC plywood is a versatile type that offers a combination of strength and affordability. The “B” represents the quality of the face veneer, while “C” represents the quality of the back veneer. BC plywood is commonly used in construction, such as subfloors, roof decking, and shelving.
Choosing the Right Thickness: What the Numbers Mean
In addition to the letters, plywood is also labeled with thickness measurements. These measurements are represented in numbers and indicate the thickness of the plywood panel in inches.
For example, 3/4″ plywood is thicker than 1/2″ plywood. The thickness of the plywood will depend on the specific requirements of your project, such as load-bearing capacity and structural stability.
It’s important to note that plywood thicknesses may not always be uniform across different manufacturers. Therefore, it’s essential to consult the specifications provided by the manufacturer and consider the specific requirements of your project when selecting the appropriate thickness.
Understanding Specialty Plywood: Marine and Structural
In addition to the standard types of plywood, there are specialty options available as well. Two common specialty plywood types are marine plywood and structural plywood.
Marine plywood is specifically designed for use in marine environments, such as boat construction and dock building. It features a waterproof adhesive and higher quality veneers, making it resistant to delamination and moisture damage. Marine plywood is typically denoted by the letters “BS1088,” indicating compliance with a British standard for marine plywood.
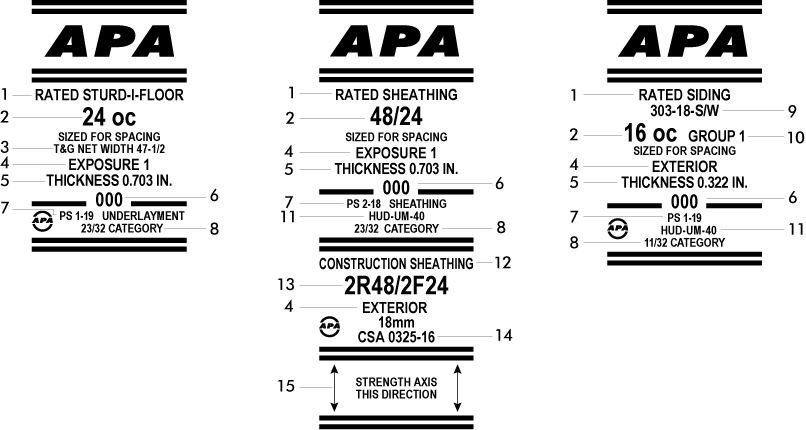
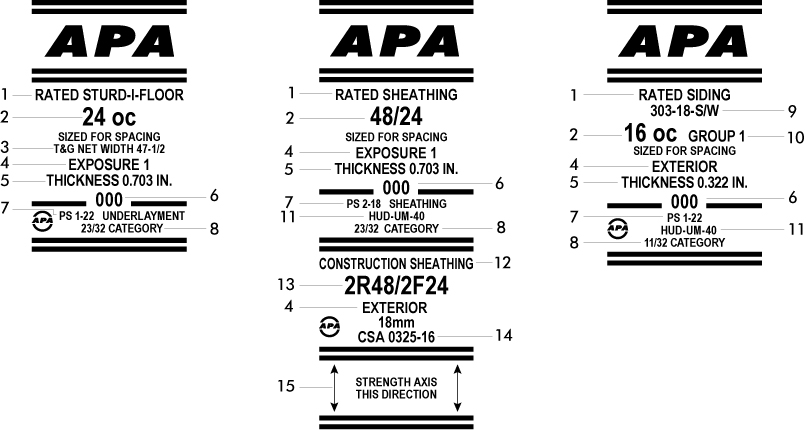
Structural plywood, as the name suggests, is engineered for structural applications where strength is crucial. It is typically used in construction for beams, headers, and other load-bearing elements. Structural plywood is often denoted by the American Plywood Association (APA) trademark, which ensures compliance with industry standards for strength and performance.
When considering specialty plywood, it’s important to understand the specific requirements of your project and select the appropriate type accordingly.
Additional Considerations for Choosing Plywood
Benefits of Using Higher-Grade Plywood
Using higher-grade plywood offers several benefits. It provides better aesthetics with a smoother and more uniform appearance, which is especially important for projects that require an attractive finish. Additionally, higher-grade plywood tends to have fewer defects and better overall strength, resulting in a more durable and long-lasting end product.
Comparing Plywood Grades: A vs. B, B vs. C
Understanding the differences between plywood grades can help you determine the most suitable option for your project. Comparing A-grade plywood with B-grade plywood allows you to make an informed decision based on your desired aesthetic and functional requirements. Similarly, comparing B-grade plywood with C-grade plywood can help you strike a balance between budget and quality.
Tips for Proper Plywood Storage and Handling
To ensure the longevity and quality of your plywood, proper storage and handling practices are essential. Store plywood in a dry and elevated area to avoid moisture absorption. Keep it away from direct sunlight and extreme temperature fluctuations. When handling plywood, use appropriate lifting equipment and avoid dropping or dragging the panels to prevent damage.
In conclusion, understanding the letters on plywood is crucial for selecting the right type for your project. The grading system helps determine the appearance and quality of the plywood, while exposure durability ratings indicate its suitability for different environmental conditions. Familiarizing yourself with the core types, thickness measurements, and specialty options will further aid you in making an informed decision. Remember to consider the specific requirements of your project, take advantage of higher-grade plywood for enhanced aesthetics and durability, and follow proper storage and handling practices to ensure the longevity of your plywood. With this knowledge, you can confidently embark on your woodworking or construction project, knowing you have chosen the right plywood for the job.
Key Takeaways: What Do the Letters on Plywood Mean?
- Plywood is a type of engineered wood made from layers of thin wood veneers.
- The letters on plywood indicate the quality and intended use of the plywood.
- Grade letters like AA, AB, BC, CD, etc. represent the veneer quality on each side of the plywood sheet.
- Exterior plywood is identified with the letter “X”, which means it can withstand exposure to moisture.
- Interior plywood is marked with an “I” and is suitable for use in dry, indoor applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on plywood! In this guide, we’ll address some common questions about the letters you may find on plywood sheets. Plywood is a versatile building material, and understanding these markings will help you choose the right type for your project.
Q: What do the letters on plywood mean?
A: The letters on plywood represent the grade and intended use of the wood. For example, “CDX” is a common type of plywood used in construction. The “C” stands for the face grade, which means that one side of the plywood has a smooth, knot-free finish suitable for paint or veneer. The “D” represents the back grade, which may have visible knots or other imperfections. Lastly, the “X” indicates that the plywood is exterior grade, meaning it can withstand exposure to weather conditions.
Other letters you may encounter include “AC,” which stands for “A” face grade and “C” back grade. This means that one side has a high-quality finish while the other side may have more visible imperfections. The letters “AB” represent a mix of high-quality and medium-quality surfaces. It’s important to note that the specific letter combinations can vary depending on the plywood manufacturer and location.
Q: Does the plywood grade affect its strength?
A: Yes, the grade of plywood can impact its strength and durability. Higher-grade plywood typically has fewer knots and imperfections, making it stronger and more suitable for structural applications. For example, plywood with an “A” face grade is usually smoother and has fewer defects, resulting in enhanced strength and stability. On the other hand, lower-grade plywood may have more visible knots and blemishes, which can affect its strength or aesthetic appeal.
It’s essential to consider the intended use of the plywood when choosing the appropriate grade. If you’re using it for a high-stress application, such as a subfloor or load-bearing wall, opt for a higher grade with better strength properties. For less demanding projects, such as shelving or non-structural applications, a lower grade may be sufficient. Always consult with the manufacturer or an expert to determine the best grade for your specific needs.
Q: Are there any quality differences between hardwood and softwood plywood?
A: Hardwood and softwood plywood differ in terms of the type of wood used. Hardwood plywood is made from trees classified as deciduous, such as oak or maple, while softwood plywood is derived from evergreen trees like pine or fir.
Generally, hardwood plywood is considered more durable and aesthetically pleasing due to the higher quality of the wood species. It is often used for furniture, cabinets, and other fine woodworking projects. Softwood plywood, on the other hand, is commonly used in construction, where strength and cost-effectiveness are prioritized over appearance.
Q: Can the type of glue used in plywood affect its performance?
A: Absolutely! The type of glue used in plywood can significantly impact its performance, especially when exposed to moisture or varying temperature conditions. Plywood is typically classified into various glue types, such as exterior, marine, and interior.
Exterior-grade plywood is manufactured with water-resistant adhesives, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Marine-grade plywood, which has the highest resistance to moisture, is commonly used in boat-building and other underwater environments. Interior-grade plywood, made with lower-grade glues, is suitable for protected indoor applications.
Q: Are there any regulations or standards governing plywood markings?
A: Yes, plywood markings are often regulated or governed by industry standards to ensure clarity and consistency. Plywood manufacturers typically follow grading rules established by associations such as the American Plywood Association (APA) or the International Panel Products Association (IPPA).
These associations have set standards for plywood grades, thicknesses, and structural properties. Additionally, industry-specific organizations or building codes may have their own specific requirements for plywood markings. It’s important to consult these standards and guidelines, as well as local building codes, to ensure you select the appropriate plywood for your project.

Plywood Grades Overview
Summary
Ever wondered what those letters on plywood mean? Well, they actually tell you about the quality and strength of the plywood.
The letters represent the different grades of plywood, from A to D. Grade A is the highest quality, while Grade D is the lowest. These grades determine the number of defects the plywood may have and how well it can hold up under different conditions. So the next time you see those letters, you’ll know exactly what they mean!