What does the tailstock do on a lathe? If you’ve ever wondered about it, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of lathes and explore the important role of the tailstock. So, buckle up and get ready to discover how this component plays a crucial part in shaping and crafting objects with precision and accuracy!
When it comes to lathes, the tailstock is a key player. Sitting at one end of the machine, it complements the headstock and helps stabilize the workpiece. Think of it as the yin to the headstock’s yang! But what exactly does the tailstock do? Well, for starters, it provides support to the opposite end of the workpiece, ensuring that it remains steady and secure as it spins.
Now, you might be wondering, why is stability so important? Well, the tailstock’s primary job is to hold the workpiece in place while the cutting tool does its magic. By keeping the workpiece steady, it prevents any unwanted vibrations or movement that could affect the accuracy of the cutting process. In simpler terms, the tailstock ensures that the workpiece doesn’t wobble or shift, allowing you to create smooth, precise cuts. Awesome, isn’t it? So, let’s dive deeper into the functionality of this crucial component.

What Does the Tailstock Do on a Lathe?
When it comes to operating a lathe machine, one of the key components to understand is the tailstock. The tailstock plays an important role in supporting and stabilizing the workpiece during turning operations. It provides additional rigidity to the workpiece, allowing for precise and accurate machining. In this article, we will delve into the functions and features of the tailstock, exploring its benefits and practical applications in the machining industry.
Understanding the Tailstock
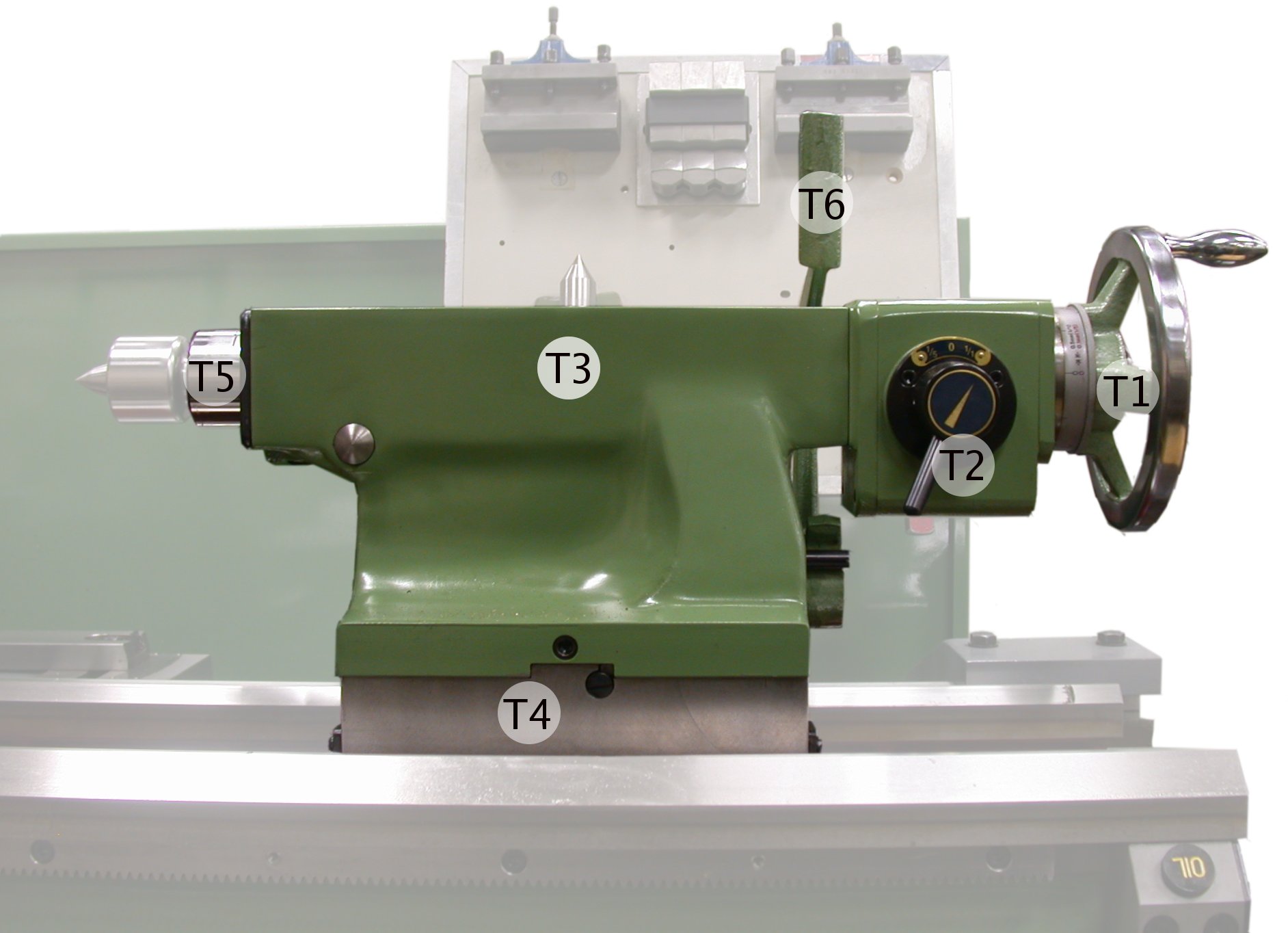
The tailstock is an essential part of a lathe machine, typically positioned at the opposite end of the headstock. Its primary purpose is to provide support to the workpiece while it rotates during machining. The tailstock consists of several components, including a spindle, quill, handwheel, and locking mechanism.
At the heart of the tailstock is the spindle, which is used to hold various tooling accessories or a live center. The spindle is adjustable along the axis of the lathe bed, allowing for precise positioning of the support mechanism. The quill, which is connected to the spindle, can be extended or retracted to accommodate different workpiece lengths. The handwheel is used to manually adjust the positioning of the quill, while the locking mechanism locks the quill in place once it is set at the desired position.
In addition to providing support, the tailstock also enables the use of various accessories, such as drill chucks, lathe centers, or boring bars. These accessories expand the capabilities of the lathe machine, allowing for a wider range of machining operations and increased versatility.
The Benefits of Using the Tailstock
The tailstock offers numerous benefits that enhance the efficiency and accuracy of lathe operations. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Improved Stability: By supporting the workpiece, the tailstock reduces vibrations and deflections during machining, resulting in improved surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
- Increased Machining Precision: The tailstock allows for the precise alignment and centering of the workpiece, ensuring symmetrical machining and reducing the risk of errors.
- Expanded Machining Capabilities: With the use of various accessories, the tailstock enables the machining of intricate shapes, such as drilling holes, reaming, tapping, or performing external and internal turning operations.
- Easy Workpiece Setup: The adjustable quill and locking mechanism make it quick and straightforward to set up the workpiece, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Tailstock vs. Headstock: Understanding the Differences
While the tailstock and headstock are both essential components of a lathe machine, they serve different purposes. The headstock is responsible for rotating the workpiece using a motor, while the tailstock supports the workpiece and provides stability.
The headstock contains the spindle and chuck, which hold and rotate the workpiece during machining. It also houses the motor that provides the necessary power for turning operations. In contrast, the tailstock does not have a motor and is primarily used for support. It can hold accessories such as drill chucks or lathe centers, which are used for various machining operations.
The tailstock and headstock work in tandem to ensure accurate and precise machining. While the headstock rotates the workpiece, the tailstock provides the necessary stability, preventing deflections and vibrations that can affect the machining quality.
Tips for Using the Tailstock Effectively
To maximize the benefits of the tailstock, here are some tips for using it effectively:
- Ensure proper alignment: Align the tailstock with the headstock to ensure that the workpiece is centered and properly supported.
- Use lubrication: Apply lubrication to the tailstock components to reduce friction and ensure smooth operation.
- Securely lock the tailstock: Always lock the tailstock in place once it is positioned to prevent movement during machining.
- Regular maintenance: Perform regular maintenance on the tailstock to keep it in optimal condition. Clean and lubricate the components as necessary and check for any signs of wear or damage.
Applications of the Tailstock
The tailstock is widely used in various industries that require precision machining, such as automotive, aerospace, and tool manufacturing. It is particularly valuable in the production of cylindrical components, where accurate centering and support are crucial.
Some common applications of the tailstock include:
- Drilling accurate holes in cylindrical workpieces
- Supporting long workpieces during turning operations
- Centering and aligning the workpiece for accurate machining
- Machining intricate shapes and contours using special accessories
Overall, the tailstock is an indispensable component of a lathe machine, enabling precise and accurate turning operations. By providing support and stability to the workpiece, it ensures that machining operations yield high-quality results. Understanding the functions and benefits of the tailstock is essential for anyone working with a lathe machine.
What Does the Tailstock Do on a Lathe?
- The tailstock on a lathe provides support for long workpieces.
- It helps hold the workpiece steady during machining operations.
- The tailstock can be locked in position to prevent movement.
- It is adjustable to accommodate different sizes of workpieces.
- The tailstock can also house a live center or drill chuck for additional functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to lathes, the tailstock is an important component that serves several functions. Below, we’ve answered some common questions about what the tailstock does on a lathe.
Q: How does the tailstock contribute to the functionality of a lathe?
A: The tailstock plays a vital role in providing support to the workpiece being machined on a lathe. It helps to stabilize the workpiece, preventing any unwanted movement or vibration during the turning process. This support is crucial, especially when dealing with long workpieces that may be prone to bending or flexing.
Additionally, the tailstock houses the tailstock quill, which can be extended or retracted to apply pressure against the workpiece. This pressure, known as tailstock pressure, can be adjusted to provide the necessary friction for secure machining and to prevent the workpiece from slipping while being turned.
Q: Can the tailstock be moved along the lathe bed?
A: Yes, in most lathes, the tailstock is designed to be adjustable along the lathe bed. This feature allows for versatility in accommodating workpieces of different lengths. By loosening the locking mechanism, the tailstock can be moved closer or further away from the headstock to match the length of the workpiece.
Once in the desired position, the locking mechanism is tightened to secure the tailstock in place. This adjustability ensures that the tailstock can be positioned near the end of the workpiece, providing optimal support and stability during the turning process. However, it’s important to note that not all lathes may have a tailstock that can be adjusted along the lathe bed, especially in smaller or more specialized models.
Q: What is the purpose of the center in the tailstock?
A: The center, also known as the live center or tail center, is a key component located in the tailstock of a lathe. It consists of a hardened point that protrudes from the tailstock quill, which aligns with the axis of rotation of the workpiece. The purpose of the center is to provide additional support to the workpiece, especially on the opposite end from the headstock.
By applying pressure against the workpiece through the center, it helps to reduce any deflection or movement during the turning process. The center creates a stable point of contact, ensuring that the workpiece rotates smoothly and accurately around its axis. Additionally, the center assists in maintaining the concentricity of the workpiece, which is crucial for achieving precise and symmetrical turning operations.
Q: Can the tailstock be removed from the lathe?
A: In most lathe models, the tailstock is designed to be removable. This feature provides flexibility in machining operations, particularly when working on large or irregularly shaped workpieces. By loosening the locking mechanism, the tailstock can be slid off the lathe bed, allowing for easier access to the workpiece or for the use of other specialized tooling or attachments.
However, it’s worth noting that the tailstock is an integral part of a lathe and should only be removed when necessary. When detached, proper care should be taken to ensure the tailstock is stored safely to avoid damage or misplacement. Additionally, guidelines provided by the lathe manufacturer should be followed when removing or reattaching the tailstock to maintain the overall stability and alignment of the lathe.
Q: Can the tailstock be used for drilling operations?
A: Yes, the tailstock on a lathe can be used for drilling operations. Many lathes are equipped with a Morse Taper hole in the tailstock quill, which allows for the insertion of a drill bit or other tooling. By aligning the tailstock center and the drill bit, the tailstock can be used to support and guide the drilling process, ensuring accuracy and preventing the workpiece from moving during drilling.
It’s important to note that the tailstock is primarily designed for providing support and stability to the workpiece during turning operations. While it can be used for drilling, it may have limitations compared to dedicated drilling machines. The depth of the hole that can be drilled with the tailstock may be limited by the length of the tailstock quill and the travel distance it allows.

Summary
The tailstock on a lathe is a handy tool that helps hold long workpieces securely. It supports the other end of the workpiece, allowing us to turn it without any wobbling. The tailstock has a quill that can move in and out, making it easy to adjust the distance between the cutting tool and the workpiece. This helps us create precise and accurate cuts. When using a lathe, the tailstock is an essential part that helps us make amazing creations.
In addition to providing stability, the tailstock can also be used for drilling holes. By attaching a drill bit to the quill, we can create precise holes in our workpieces. This adds versatility to the lathe and expands the range of projects we can work on. So, next time you see a lathe with a tailstock, remember that it’s not just for support, but also for drilling. It’s a multipurpose tool that makes woodworking even more fun and exciting.