What is lathe back gear? Well, let’s dive into the fascinating world of lathes and gears! Imagine a machine that can shape, cut, and mold materials with precision. That’s where a lathe comes into play.
But wait, what exactly is a lathe back gear, and why is it important? Imagine if you were driving a car, and suddenly you needed to slow down or tackle a steep incline. That’s when you shift into a lower gear to provide more power. Similarly, a lathe back gear helps control the speed and power of a lathe machine.
So, are you ready to explore the ins and outs of lathe back gears? Let’s embark on this gear-filled journey together and discover the wonders of mechanical innovation!
Understanding Lathe Back Gear: A Comprehensive Guide
Lathe machines are essential tools in the manufacturing industry, used for shaping and machining various parts. Among the components that contribute to the functionality of a lathe machine, the back gear holds significant importance. In this guide, we will explore the concept of lathe back gear, its purpose, operation, and the benefits it offers to machine operators. Whether you are a professional machinist or a curious enthusiast, this article will provide you with in-depth knowledge about the fascinating world of lathe back gears.
1. What is a Lathe Back Gear?
A lathe back gear is a feature found in certain types of lathe machines that helps control the spindle speed. It is a mechanism consisting of gears and levers that allows you to adjust the rotational speed of the lathe spindle to suit different machining operations. The back gear is typically located at the rear of the lathe headstock and connects the main spindle to the motor or the primary power supply of the machine.
The purpose of the back gear is to provide enhanced torque at lower speeds, enabling the lathe to handle heavy-duty cutting tasks with ease. By reducing the rotational speed of the spindle, the back gear allows the operator to work with larger workpieces or materials that require slower cutting speeds for optimal precision and surface finish. In essence, the lathe back gear serves as a power transmission system that enables the lathe machine to adapt to different work requirements.
A Brief History of Lathe Back Gears
The concept of back gears dates back to the early days of lathe machines when power was primarily harnessed from antique belt-driven systems. Back then, the belts connecting the main spindle and the motor were often prone to slippage, limiting the torque and speed range of the lathe. To overcome this challenge, inventors introduced the back gear mechanism, consisting of an additional set of gears that reduced the rotational speed of the spindle, while increasing torque.
Despite the introduction of more advanced direct-drive systems in modern lathe machines, the back gear mechanism continues to be an essential feature in many models. Its ability to provide increased torque at lower speeds makes it indispensable for heavy-duty cutting and machining operations. Today, back gears have evolved and are often equipped with convenient controls and improved gear ratios to offer even greater flexibility and precision in lathe operations.
Key Takeaway: A lathe back gear is a mechanism that enables the operator to control the rotational speed of the lathe spindle. It provides increased torque at lower speeds, allowing for heavy-duty cutting tasks and precision machining operations. With its long history and continued relevance, the back gear remains an integral part of modern lathe machines.
2. How Does a Lathe Back Gear Work?
To understand how a lathe back gear works, let’s take a closer look at its internal components and their interactions. The back gear mechanism consists of various gears, levers, and controls that work together to regulate the spindle speed.
At the heart of the back gear system is the primary gear, which is connected to the spindle and driven by the motor or the main power source. This gear meshes with an idler gear, which, in turn, meshes with the back gear itself. The back gear is connected to a secondary gear, which is then linked to the spindle. By engaging or disengaging different sets of gears, the operator can alter the gear ratio and, consequently, the spindle speed.
Most lathe machines equipped with back gears offer different speed settings, ranging from high-speed configurations for lighter cuts and finishing work to low-speed settings for heavy-duty machining. The precise method of engaging the back gear and adjusting the speed may vary depending on the specific lathe model. Some machines have dedicated levers or buttons, while others utilize separate controls on the control panel.
It is important to note that not all lathe machines are equipped with back gear systems. Some modern lathes use electronic speed control or variable frequency drives to achieve speed control, eliminating the need for mechanical back gears. However, for heavy-duty work and enhanced torque, dedicated lathe machines with back gears remain a popular choice in many industrial settings.
Key Takeaway: The lathe back gear system relies on a combination of gears, levers, and controls to regulate the spindle speed. By engaging and disengaging appropriate gear configurations, operators can adjust the rotational speed of the lathe spindle to suit different machining requirements. While electronic speed control is becoming more prevalent, back gear-equipped lathe machines are still preferred for heavy-duty cutting tasks.
3. Advantages of Using Lathe Back Gear
The inclusion of a lathe back gear system in a lathe machine offers several advantages that make it a valuable feature for machinists. Here are some of the benefits of using a lathe machine with a back gear:
1. Increased Torque: The primary advantage of the back gear system is the ability to provide increased torque at lower spindle speeds. This enables the lathe machine to handle heavy-duty cutting tasks that require more power and force. By engaging the back gear, machinists can confidently work with larger workpieces or materials that are more challenging to cut.
2. Versatility: A lathe machine equipped with back gears offers greater versatility in terms of speed control. The ability to switch between high and low-speed settings allows operators to adapt the machine to a wide range of materials and cutting operations. Whether it’s delicate finishing work or heavy roughing, the back gear enables precise speed adjustments for optimum results.
3. Enhanced Surface Finish: When working with materials that require low cutting speeds, such as certain alloys or delicate components, the lathe back gear proves invaluable. By reducing the spindle speed, the back gear allows for smoother cutting action, resulting in improved surface finish and reduced chattering or vibration.
4. Safety: The back gear system also contributes to enhanced safety during lathe operations. The lower speed settings provided by the back gear allow operators to have better control over the cutting process, reducing the risk of accidents or tool breakage. It also enables safer handling of challenging workpieces that may require slower cutting speeds for stability.
5. Cost-effectiveness: Lathe machines equipped with back gears offer a cost-effective solution for heavy-duty machining requirements. By providing increased torque at lower speeds, the back gear eliminates the need for more expensive and specialized machinery for specific tasks. This versatility translates into cost savings and improved efficiency in the workshop.
Key Takeaway: Utilizing the capabilities of a lathe machine with a back gear system offers several advantages to machinists. These include increased torque for heavy-duty cutting, greater versatility in speed control, enhanced surface finish, improved safety, and cost-effectiveness. The back gear remains a crucial feature for achieving precision and efficiency in lathe operations.
4. Tips for Working with Lathe Back Gear
To make the most of the lathe back gear system, there are a few tips and best practices to keep in mind:
1. Familiarize Yourself: Before using a lathe machine with a back gear system, thoroughly familiarize yourself with the specific controls and operation of the mechanism. Read the user manual, seek guidance from experienced operators, and conduct practice sessions to ensure confidence and competence in using the back gear.
2. Understand Speed Requirements: Different machining operations and workpiece materials have unique speed requirements. Take the time to understand the recommended speed range for specific tasks and materials. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions when engaging the back gear and adjusting the spindle speed.
3. Lubrication and Maintenance: Like any mechanical component, regular lubrication and maintenance are essential for the smooth and efficient operation of the lathe back gear system. Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication intervals and use high-quality lubricants to prevent excessive wear and ensure optimal performance.
4. Monitor Cutting Forces: When working with the back gear engaged, monitor the cutting forces applied to the tool and the workpiece. Higher torque and reduced spindle speeds can increase stresses on the system. Constantly assess the cutting forces to prevent tool breakage, vibrations, or any potential damage to the machine.
5. Exercise Caution: While the back gear provides increased torque, it is important to exercise caution when working with heavy workpieces or using high cut depths. Take into account the capabilities of the lathe machine and avoid pushing it beyond its limits. Prioritize safety and use proper support and clamping mechanisms when dealing with large or challenging workpieces.
Key Takeaway: Working effectively with a lathe back gear requires understanding the specific controls, maintenance requirements, and speed considerations associated with the system. Familiarize yourself with the machine, follow recommended maintenance protocols, and exercise caution during heavy-duty operations. By adopting these tips, you can optimize the performance and longevity of your lathe machine equipped with a back gear system.
Exploring the Different Types of Lathe Back Gears
1. Standard Back Gears
Standard back gears consist of a set of gears mounted on the shaft of the lathe spindle and provide a fixed gear ratio for speed reduction. These gears are often enclosed within a housing for protection and are engaged or disengaged using a lever or knob. Standard back gears offer a reliable and straightforward mechanism for controlling the spindle speed, making them a common choice for many lathe machines.
2. Quick Change Gearbox with Back Gears
In lathe machines featuring quick-change gearbox systems, the back gears are often integrated within the gearbox itself. This configuration allows for rapid changes of gear ratios and offers increased convenience and flexibility for operators. By combining the back gear functionality with a quick-change gearbox, these lathe machines enable seamless transitions between various speed settings, further enhancing efficiency and productivity.
3. Electronic Variable Speed Control with Back Gears
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of lathe machines equipped with electronic variable speed control in conjunction with back gears. These machines utilize electronic control systems to regulate the motor speed, allowing for precise and programmable adjustments. The addition of back gears to such machines provides the benefits of increased torque at lower speeds, making them ideal for heavy-duty work that demands both high precision and flexibility.
Key Takeaway: Different types of lathe back gears exist to cater to the specific needs of operators. Standard back gears offer a reliable and fixed gear ratio for speed reduction, while quick change gearbox systems with integrated back gears provide convenience and rapid changes. Lathe machines with electronic variable speed control combined with back gears offer precision and programmability for heavy-duty machining tasks. The choice of back gear type depends on the desired level of control, convenience, and flexibility required in a particular lathe machine.
The Future of Lathe Back Gear Technology
As technologies continue to evolve, it is inevitable that the future of lathe back gear systems will witness advancements and innovations. Here are three potential developments that hold promise for the future:
1. Enhanced Automation: Integration of back gears with advanced automation systems could allow for seamless adjustments of spindle speeds based on pre-programmed settings. This could greatly increase efficiency and reduce the need for manual intervention in the machining process.
2. Smart Control Systems: Implementing smart control systems that utilize real-time data and artificial intelligence algorithms could enable the lathe machine to automatically optimize the back gear settings based on material properties, tool wear, and machining requirements. This would lead to improved precision, productivity, and machining outcomes.
3. Gearless Lathe Machines: In the pursuit of simplicity and increased reliability, future lathe machines may eliminate physical back gear systems altogether. Instead, they might rely solely on electronic variable speed control systems or alternative mechanisms to achieve the required torque and speed adjustments.
Key Takeaway: The future of lathe back gear technology holds exciting possibilities. Enhanced automation, smart control systems, and gearless lathe machines are potential avenues for innovation and improvements to the efficiency, precision, and adaptability of lathe machining operations. As these advancements unfold, machinists can look forward to even more streamlined and sophisticated manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, understanding the concept and operation of lathe back gears is crucial for machinists and enthusiasts alike. This mechanism allows for controlled speed adjustments, increased torque, and enhanced precision during lathe operations. By engaging the back gear, operators can optimize their machining processes for different materials, workpiece sizes, and cutting requirements. The future of lathe back gear technology promises further advancements that will revolutionize the industry and pave the way for more efficient and sophisticated machining operations.
Key Takeaways: What is Lathe Back Gear?
- Lathe back gear is a mechanical device used in lathes to control the speed of the spindle.
- It helps in achieving slower rotational speeds for heavy-duty cutting tasks.
- Back gears are typically engaged when higher torque and lower speeds are required.
- Using back gears can improve the cutting quality and reduce vibrations in the lathe machine.
- Understanding the operation and adjustment of lathe back gears is essential for achieving desired machining results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our Frequently Asked Questions section where we’ll answer some common queries about lathe back gears. Read on to learn more!
1. How do lathe back gears work?
Lathe back gears are an integral part of a lathe machine’s gear system that helps regulate the spindle speed. They consist of a set of gears situated at the back of the lathe machine. When engaged, the back gears transfer power from the motor to the spindle, allowing for a slower rotation speed. This enables the operator to work with larger workpieces or materials that require more torque.
Back gears operate by connecting the back gear spindle to an intermediate gear, which, in turn, connects to the main spindle. By adjusting the back gear’s position, the operator can select different gear ratios, affecting the spindle speed and torque output. This versatility is beneficial for tasks that require precision or heavy-duty machining.
2. What are the advantages of using lathe back gears?
Utilizing lathe back gears offers several advantages in machining operations. First and foremost, these gears enable the lathe machine to handle larger workpieces or materials that require slower rotational speeds. The back gear mechanism increases the torque output, making it easier to work on hefty pieces or metal alloys with high cutting resistance.
Furthermore, lathe back gears allow for precise control over the spindle speed. By manipulating the gear configuration, operators can select the ideal speed for specific machining operations. This fine-tuning capability contributes to achieving accurate and high-quality results. Lastly, back gears enhance the lathe machine’s versatility, accommodating a broader range of materials and projects.
3. When should I engage the lathe back gears?
You should engage the lathe back gears when you need to work with larger workpieces or when machining materials that require slower rotational speeds with increased torque. When facing an intricate or heavy-duty task, such as turning a large metal cylinder or drilling through thick steel, engaging the back gears is essential to attain the desired cutting speed and power.
It’s important to note that the decision to engage the back gears depends on the specific requirements of your machining operation. Always refer to the lathe machine’s user manual and take into account the material, dimensions, and desired outcome of your project for guidance on when to engage the back gears.
4. Can I use the lathe back gears for all materials?
The lathe back gears are suitable for a wide range of materials, including metal alloys, plastics, and wood. However, it’s important to consider the specific requirements and characteristics of the material you’ll be working with before engaging the back gears.
For softer materials or tasks that don’t require substantial torque, you may not need to engage the back gears. It’s crucial to evaluate the material’s density, hardness, and cutting resistance to determine whether using the back gears is necessary. Always refer to the lathe machine’s guidelines and the material’s specifications for the best machining approach.
5. Are lathe back gears difficult to operate?
Operating lathe back gears may require some initial practice and familiarity, especially if you’re new to using a lathe machine. However, with proper training and understanding of your specific lathe’s gear system, it becomes easier to engage and adjust the back gears to suit your machining needs.
It’s recommended to consult the lathe machine’s user manual and seek guidance from experienced operators or instructors to gain confidence in operating the back gears effectively. With time, practice, and a proper grasp of the gear system, you’ll be able to maneuver the lathe back gears with ease.
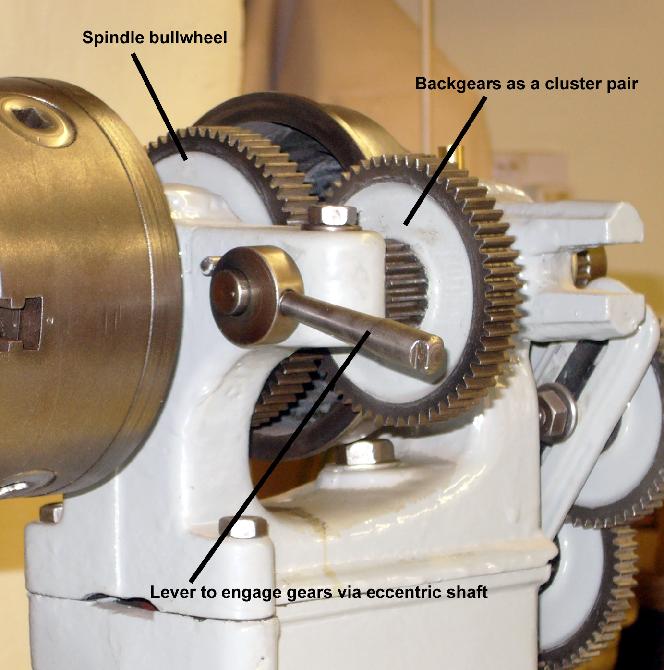
What are Back Gears and How to Use them
Summary
A lathe back gear is a part of a lathe machine that helps control its speed. Back gears slow down the rotational speed of the spindle, allowing for more precise cutting. These gears are important for cutting big and heavy materials.
By engaging the back gear, the lathe machine becomes more powerful and can handle tougher materials. The back gear mechanism consists of multiple gears, which work together to reduce the speed of the spindle. This is useful when working with large workpieces or when fine, accurate cuts are needed. Overall, the back gear is a crucial component that enhances the versatility and capabilities of the lathe machine.
