So, you want to know what a saddle is in a lathe machine? Well, buckle up and let’s dive in!
In simple terms, the saddle is a crucial component of a lathe machine. It’s like the seat of the machine, allowing the cutting tool to move back and forth along the workpiece. Picture it as the “driver’s seat” of the lathe.
Think of the saddle as the superstar that controls the movement of the tool, ensuring precision and accuracy in the cutting process. It slides along the lathe’s bed, giving the operator full control over the tool’s position and direction.
Now that we’ve got the basic idea of what a saddle is, let’s explore its functionalities and how it contributes to the smooth operation of a lathe machine.

The Saddle in a Lathe Machine: An Essential Component
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the saddle in a lathe machine! In this article, we will explore the importance and functions of the saddle, an integral part of a lathe machine. Whether you are a seasoned machinist or a beginner, understanding the role of the saddle is crucial for operating a lathe machine effectively. So, let’s dive in and explore everything you need to know about the saddle in a lathe machine.
What is the Saddle in a Lathe Machine?
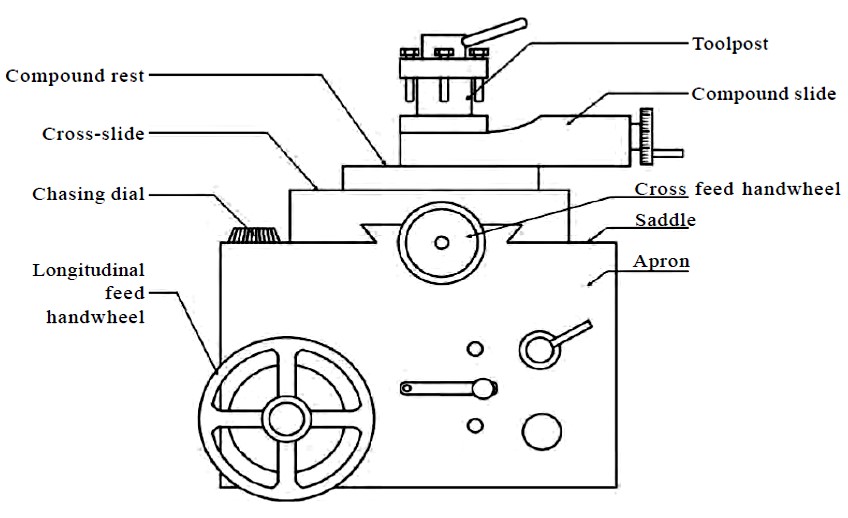
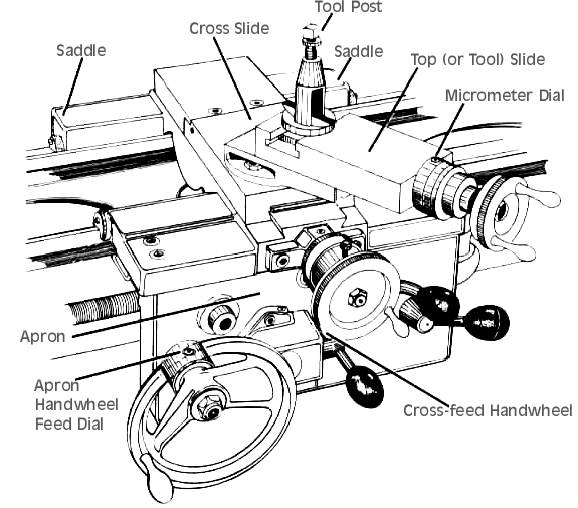
The saddle is one of the main components in a lathe machine. It is a sliding carriage that holds the cutting tool and is responsible for providing controlled movement along the bed of the lathe. The saddle moves along the lathe’s x-axis, also known as the longitudinal axis, allowing the cutting tool to create precision cuts and various operations on the workpiece.
The saddle typically consists of a dovetailed bed, which ensures precise alignment and smooth movement. It is equipped with a cross-slide, which holds and moves the cutting tool horizontally, and a compound rest for angled cuts. The saddle is mounted on the cross-slide and can be locked in position for stability during machining operations.
The saddle’s positioning and movement are controlled by the lathe’s feed mechanism, such as handwheels, leadscrews, or electronic controls, depending on the type of lathe. Its design allows for precise tool positioning, making it an essential component for turning, facing, threading, and other machining processes.
Functions of the Saddle
The saddle plays a vital role in the overall functioning of a lathe machine. Here are some of its key functions:
- Tool Movement: The saddle enables controlled movement of the cutting tool along the bed of the lathe, allowing for accurate machining operations.
- Precision Positioning: The dovetailed design of the saddle ensures precise alignment, enabling the accurate positioning of the cutting tool for precise cuts and desired outcomes.
- Cross-Feed: The saddle is equipped with a cross-slide, which moves the cutting tool horizontally. This cross-feed mechanism enhances versatility and enables operations such as grooving, facing, and taper turning.
- Compound Rest: The saddle also features a compound rest, which allows for angled cuts and intricate machining tasks, such as threading.
- Locking Mechanism: The saddle can be locked in position to ensure stability during machining processes, preventing any unwanted movement that may affect the accuracy of the cuts.
The saddle’s functions are critical in achieving precise and high-quality results when working with a lathe machine. Understanding how to effectively utilize these functions can greatly enhance the efficiency and output of machining operations.
Key Components of the Saddle
To have a complete understanding of the saddle in a lathe machine, it is essential to familiarize yourself with its key components. Let’s delve into the main components found in the saddle:
Dovetailed Bed
The dovetailed bed is the foundation of the saddle and provides a rigid and stable base for the entire assembly. It consists of a V-shaped groove machined into the bed of the lathe, along which the saddle slides. The dovetailed design allows for precise alignment and smooth movement without any unwanted play or backlash.
The dovetailed bed is typically made from hardened steel or cast iron, ensuring durability and longevity. It is meticulously machined to tight tolerances to ensure accuracy and smooth sliding motion of the saddle.
Cross-Slide
The cross-slide is an essential component mounted on top of the saddle. It holds the cutting tool in a tool holder and enables horizontal movement to perform tasks such as facing, grooving, and thread cutting. The cross-slide is equipped with axes for both longitudinal and transverse feeds, allowing precise control over the tool’s positioning.
The transverse movement of the cross-slide is controlled by the cross-feed screw, while the longitudinal movement is controlled by the carriage handwheel, which moves the saddle along the bed of the lathe machine. Both movements work in tandem to achieve accurate and precise machining operations.
Compound Rest
The compound rest is another crucial component attached to the saddle. It allows for the cutting tool to be set at various angles, facilitating tasks such as taper turning and thread cutting. The compound rest is adjustable, enabling machinists to achieve precise angles for specific machining requirements.
The compound rest is used in conjunction with the cross-slide to perform complex operations. By controlling the movement of both the cross-slide and the compound rest, machinists can create intricate cuts and angles, expanding the range of possibilities that can be achieved on the lathe machine.
The Importance of Proper Saddle Maintenance
Now that we have explored the functions and key components of the saddle in a lathe machine, it is vital to highlight the importance of proper saddle maintenance. Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and optimal functionality of the saddle, ultimately leading to better machining results. Here are some essential tips for saddle maintenance:
1. Lubrication:
Regularly lubricate the dovetailed bed, cross-slide, and compound rest to minimize friction and ensure smooth movement. Use the recommended lubricants specified by the lathe machine manufacturer and follow the recommended maintenance schedule.
2. Cleaning:
Regularly clean the saddle components to remove any dirt, dust, or chips that may accumulate during machining. This helps prevent any abrasive particles from causing premature wear or damage to the components.
3. Inspection:
Periodically inspect the dovetailed bed, cross-slide, and compound rest for any signs of wear or damage. Look for any loose or worn-out parts and address them promptly to prevent further issues and maintain the accuracy of the lathe machine.
4. Adjustment:
Ensure that the saddle components are properly adjusted for optimal performance. Check for any excessive play or backlash and make necessary adjustments to maintain the rigidity and precision of the saddle.
5. Professional Service:
If you encounter any significant issues or concerns with the saddle, it is recommended to seek professional assistance. Trained technicians can diagnose and address any underlying problems to ensure the saddle functions optimally.
By following these maintenance tips and adopting good machining practices, you can prolong the life of the saddle and maintain the accuracy and performance of your lathe machine.
Saddle Innovations and Future Trends
As technology continues to advance, there are ongoing developments in lathe machine design, including saddle innovations. Manufacturers are constantly striving to enhance the efficiency, precision, and user-friendliness of lathe machines. Here are some notable innovations and future trends in saddle design:
1. Digital Controls:
Many modern lathe machines are equipped with electronic controls that allow for precise control over the saddle’s movement. Digital readouts and programmable systems enable machinists to set specific parameters, reducing the margin of error and increasing overall efficiency.
2. Enhanced Materials and Coatings:
Manufacturers are exploring new materials and coatings for the saddle to improve durability, reduce friction, and enhance performance. Advanced alloys and surface treatments can increase wear resistance, extend the lifespan of the saddle, and minimize maintenance requirements.
3. Integrated Safety Features:
Saddle design is also evolving to incorporate built-in safety features. This includes features such as interlocks, emergency stops, and automated safety systems that prioritize the well-being of the operator and protect against potential accidents or mishaps.
These innovations and future trends aim to streamline machining processes, improve accuracy, and enhance user experience. Keeping abreast of these advancements can help machinists stay on the cutting edge and maximize the potential of their lathe machines.
Expanding Your Lathe Machine Knowledge
The saddle is a critical component of a lathe machine, enabling precise and controlled movement of the cutting tool. By understanding the functions and key components of the saddle, as well as proper maintenance practices, you can optimize your lathe machine’s performance and achieve exceptional machining results.
If you’re looking to further expand your knowledge of lathe machines, consider exploring topics such as spindle operations, tool selection, workholding methods, or advanced machining techniques. Continual learning and experimentation will empower you to unlock the full potential of your lathe machine and embark on exciting machining projects with confidence.
Remember, the saddle may be just one part of the lathe machine, but its significance cannot be overstated. With the right skills and expertise in utilizing the saddle, you have the ability to transform raw materials into precision-crafted workpieces that showcase your craftsmanship and machining prowess.
Key Takeaways:
- The saddle in a lathe machine is an important component that holds the cutting tool and moves along the bed.
- It allows the tool to move horizontally and perform various machining operations.
- The saddle is mounted on the carriage and can be manually operated or move automatically through power feed.
- It plays a crucial role in determining the accuracy and precision of the machining process.
- The saddle should be properly lubricated to ensure smooth movement and prevent wear and tear.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the world of lathe machines, the saddle plays a crucial role in the machining process. It is important to understand the function and significance of the saddle for a better understanding of lathe machines. Here are some frequently asked questions about the saddle in a lathe machine.
How does the saddle contribute to the functioning of a lathe machine?
The saddle in a lathe machine is a critical component that provides support and movement to the cutting tool. Located on the bed of the lathe, the saddle moves along the guides and carries the cross-slide, compound rest, and toolpost. It helps in supporting and positioning the workpiece accurately for machining operations. The saddle is responsible for longitudinal movement of the tool during turning operations.
By allowing smooth movement of the tool along the bed, the saddle ensures precise and accurate machining. Its design includes various adjustments to control the speed and feed of the cutting tool, providing flexibility and versatility in machining different workpieces. Overall, the saddle plays a vital role in the smooth operation and functioning of a lathe machine.
What materials are commonly used to make the saddle in a lathe machine?
The saddle of a lathe machine is typically made from high-quality cast iron or steel materials. Cast iron is a popular choice due to its excellent vibration damping properties, stability, and durability. It helps minimize vibration during machining operations, ensuring better precision and accuracy in the final product.
In some cases, steel is used to manufacture the saddle, particularly in heavy-duty or industrial lathe machines. Steel offers higher tensile strength and hardness, making it suitable for handling heavier workpieces and more demanding machining tasks. Both cast iron and steel provide the necessary strength and rigidity required for the saddle to withstand the forces and stresses encountered during machining operations.
Can the saddle be adjusted to accommodate different workpiece sizes?
Yes, the saddle in a lathe machine can be adjusted to accommodate workpieces of different sizes. The lathe operator can move the saddle along the bed to position the cutting tool at the desired location for machining. This allows for flexibility in working with various workpiece lengths and diameters.
Additionally, the saddle may have features such as T-slots, which allow for the attachment of fixtures, clamps, or other devices to secure the workpiece during machining. These adjustable features and the ability to move the saddle make lathe machines versatile and capable of handling a wide range of workpiece dimensions and shapes.
What maintenance is required for the saddle in a lathe machine?
To ensure the smooth functioning and longevity of the saddle in a lathe machine, regular maintenance is essential. This includes keeping the saddle clean and free from chips, debris, or coolant that can accumulate during machining operations. Regular lubrication of the saddle’s sliding surfaces is also necessary to minimize friction and wear.
Periodic checks should be conducted to inspect the saddle for any signs of damage or excessive wear. Any issues should be addressed promptly to avoid further complications and ensure optimal performance. Overall, proper maintenance and care of the saddle will result in better accuracy, longevity, and reliability of the lathe machine.
Are there any safety considerations when working with the saddle of a lathe machine?
Working with the saddle of a lathe machine requires adherence to safety precautions to prevent accidents or injuries. Operators should ensure that the lathe machine is turned off and unplugged when making any adjustments to the saddle or performing maintenance tasks.
It is crucial to use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and work boots, to protect oneself from potential hazards. Proper training and knowledge of the lathe machine’s operation, including the saddle, are necessary to operate the machine safely and efficiently. Following safety guidelines and using caution while working with the saddle will help maintain a safe working environment.
Summary
The saddle in a lathe machine is a special part that moves along the bed. It carries the tool and controls the cutting process. The saddle plays a crucial role in shaping metals and creating various objects. It is important to understand how the saddle works to operate a lathe machine effectively.
In conclusion, the saddle is like the captain of a lathe machine that guides the tool and shapes the metal. Without the saddle, the lathe machine wouldn’t be able to do its job. So, next time you come across a lathe machine, remember the important role of the saddle!