What’s up, curious minds! Ever wondered about the inner workings of a lathe machine? Specifically, what is the function of the headstock? Well, you’re in luck because today we’re diving into this fascinating topic. So, buckle up and get ready to explore the world of lathes and their amazing headstocks!
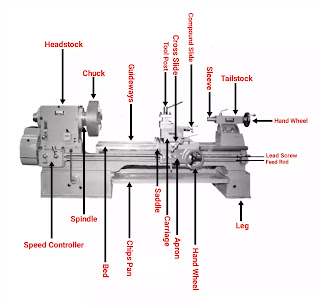
When it comes to lathe machines, the headstock is like the brain that powers the entire operation. It’s the part of the machine that holds the main spindle and houses the motor that drives it. In simpler terms, the headstock is where all the action begins!
So, what exactly does the headstock do? Well, one of its primary functions is to provide rotational motion to the workpiece. This allows the lathe to shape and form materials like metal or wood into the desired shape. Additionally, the headstock often includes various speed settings, allowing you to adjust the rotation speed to match the specific requirements of your project.
Now that we’ve scratched the surface of the headstock’s function, get ready to dive deeper into the world of lathe machines and uncover more incredible details. Keep reading to expand your knowledge and discover the endless possibilities this powerful machine has to offer!
The Function of Headstock in Lathe Machine: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the function of the headstock in a lathe machine. The headstock is a crucial component that plays a vital role in the operation and performance of a lathe machine. In this article, we will delve into the various functions and features of the headstock, and explore its significance in the machining process. Whether you are a seasoned machinist or a novice in the world of lathes, this guide will equip you with valuable knowledge about the headstock and its role in achieving precision and accuracy in turning operations.
Understanding the Headstock: The Powerhouse of a Lathe Machine
If you’ve ever wondered what makes a lathe machine tick, the answer lies in its headstock. The headstock is located on the left side of the lathe bed and serves as the control center for the entire machine. It houses the main spindle, which is responsible for holding the workpiece and rotating it at varying speeds. Additionally, the headstock contains other critical components, such as gears, belts, and pulleys, that facilitate the transmission of power and control the rotational movement of the spindle. Let’s explore the key functions of the headstock in more detail.
The Main Spindle: Holding and Rotating the Workpiece
The primary function of the headstock is to hold and rotate the workpiece securely. The main spindle, which is mounted within the headstock, serves as the axis of rotation for the workpiece. It is a hollow cylindrical shaft that extends through the headstock and protrudes from its front end. The workpiece is clamped onto the spindle using various holding devices, such as chucks, collets, or faceplates, depending on the nature of the workpiece and the machining operation. As the spindle rotates, it imparts the desired rotational motion to the workpiece, allowing for precise shaping, cutting, and finishing of the material.
In addition to providing rotational movement, the headstock may also offer other mechanisms to ensure maximum stability and precision during machining. For example, some lathes incorporate a spindle brake, which allows the machinist to quickly stop the rotation of the spindle when necessary. This feature is particularly useful for making rapid adjustments or performing delicate operations that require careful control of the workpiece.
Power Transmission: Gears, Belts, and Pulleys
Another critical function of the headstock is to transmit power from the lathe’s motor to the spindle. This power transmission is achieved through a system of gears, belts, and pulleys that are housed within the headstock. The motor provides the initial source of power, which is then transferred to the spindle at varying speeds, depending on the machining requirements. The arrangement of gears and pulleys allows for different speed settings, enabling the machinist to select the optimal rotational speed for the workpiece.
The gears within the headstock serve as the primary means of adjusting the rotational speed. By engaging different gears or changing their positioning, the machinist can achieve a wide range of rotational speeds, from high-speed cutting to slow-speed finishing. This versatility is crucial in achieving the desired surface finish and dimension accuracy of the machined workpiece. Proper gear selection and alignment are essential for smooth power transmission and minimizing unwanted vibrations that can compromise the machining process.
Auxiliary Functions: Thread Cutting and More
While the main spindle and power transmission are the primary functions of the headstock, it may also offer additional features to enhance the capabilities of the lathe machine. One such feature is thread cutting, a process commonly used for producing external or internal screw threads on a workpiece. Some lathes are equipped with a thread cutting attachment that is mounted on the headstock. This attachment enables precise and accurate thread cutting operations, allowing for the creation of various thread profiles and pitch sizes.
Furthermore, the headstock may incorporate other auxiliary functions, such as the provision of coolant or lubrication systems. These systems help to improve the machining process by reducing heat buildup, extending tool life, and enhancing surface finish. In some cases, the headstock may also accommodate additional accessories, such as live centers or steady rests, that provide additional support and stability for long or slender workpieces.
The Significance of a Well-Functioning Headstock
A well-functioning headstock is of paramount importance for achieving precision and accuracy in lathe operations. The proper alignment, smooth power transmission, and precise control of rotational speed are all essential factors that contribute to the overall performance of a lathe machine. A faulty or poorly maintained headstock can result in compromised machining quality, increased tool wear, and reduced productivity. Therefore, regular inspection, maintenance, and proper lubrication of the headstock are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of the lathe machine.
Choosing the Right Headstock for Your Lathe Machine: Factors to Consider
When it comes to selecting a lathe machine or considering an upgrade, the headstock plays a significant role. Various factors need to be taken into account to ensure the headstock meets your specific machining requirements and aligns with your business goals. Here are a few key factors to consider:
- Spindle capacity: Determine the maximum diameter and length of the workpiece that the headstock can accommodate.
- Speed range: Assess the available speed settings and determine if they align with your machining needs.
- Power transmission: Evaluate the efficiency and design of the power transmission system to ensure smooth and reliable operation.
- Thread cutting capabilities: If thread cutting is an essential aspect of your operations, ensure the headstock has the necessary features or attachments to facilitate this process.
- Auxiliary functions: Consider any additional functions or accessories that may enhance your machining capabilities or provide specific solutions for your applications.
Conclusion
The headstock is undeniably the powerhouse of a lathe machine, responsible for holding and rotating the workpiece, facilitating power transmission, and providing auxiliary functions. Understanding the functions and features of the headstock is crucial for achieving precision, accuracy, and desired results in lathe operations. By selecting the right headstock and maintaining it properly, machinists can harness the full potential of their lathe machine and explore a world of possibilities in the world of turning.
Key Takeaways: What is the Function of Headstock in Lathe Machine?
- The headstock is a key component in a lathe machine.
- It holds and rotates the workpiece, allowing for precision turning.
- The headstock contains the main spindle, which is connected to a chuck or faceplate.
- It provides the necessary power to rotate the workpiece at different speeds.
- The headstock also houses gears and belts, allowing for spindle speed adjustments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about the function of the headstock in a lathe machine:
1. How does the headstock contribute to the operation of a lathe machine?
The headstock is a crucial component of a lathe machine as it houses the main spindle. The main spindle is responsible for rotating the workpiece, allowing it to be machined. It provides the necessary torque and speed to facilitate various operations such as turning, facing, drilling, and threading. The headstock also contains the gears and pulleys required to regulate the spindle speed, allowing for versatility in machining different materials.
Furthermore, the headstock often incorporates a variety of mechanisms such as a chuck, collet, or faceplate to secure the workpiece firmly in place. Without the headstock, a lathe machine would not be able to perform its primary function of rotating and shaping workpieces effectively.
2. How does the headstock help in achieving accuracy in lathe machining?
The headstock plays a crucial role in ensuring accuracy in lathe machining. It provides a stable platform for the workpiece, minimizing any vibrations or deviations during the machining process. The rigid construction of the headstock helps in maintaining the alignment and concentricity of the workpiece, resulting in precise and consistent machining operations.
Additionally, the headstock is equipped with features such as a spindle lock, which allows for easy setup and alignment of the workpiece. Moreover, advanced lathe machines often have a precision alignment system within the headstock, ensuring the spindle remains parallel to the lathe bed, further enhancing the accuracy of the machining process.
3. Can the headstock accommodate different sizes of workpieces?
Yes, the headstock of a lathe machine typically includes various interchangeable components and accessories that allow it to accommodate different sizes of workpieces. The most common component is the chuck, which can securely hold and rotate the workpiece. Chucks come in different sizes and designs, allowing for compatibility with a wide range of workpiece diameters.
In addition to chucks, the headstock can also be equipped with different types of collets or faceplates, depending on the specific machining requirements. Collets are used for holding small diameter workpieces, while faceplates provide a flat surface for clamping irregularly shaped or large workpieces. These interchangeable components provide versatility and enable the headstock to handle workpieces of varying sizes and shapes.
4. Is the headstock motor-powered?
Yes, the headstock in a lathe machine is typically motor-powered. It contains an electric motor that provides the necessary power to rotate the main spindle. The motor is connected to the spindle via a system of gears and pulleys, allowing for variable speed control. This motor-driven rotation of the spindle enables the lathe machine to perform various machining operations.
The motor power may vary depending on the size and capacity of the lathe machine. It is crucial to select a lathe machine with an appropriately sized motor based on the intended workload and the materials to be machined. A well-powered motor ensures consistent and efficient machining processes.
5. Can the headstock be adjusted to different angles?
No, the headstock of a lathe machine is primarily designed to maintain a fixed horizontal position. It ensures stability and alignment throughout the machining process. However, certain lathe machines have additional features such as a swivel headstock or a compound rest that allows for limited adjustment in angles.
These adjustable features are particularly useful for machining tapered workpieces or creating angled cuts. Despite these adjustments, the headstock’s primary function remains maintaining the workpiece’s alignment and concentricity to achieve accurate and precise results. For more complex angular machining requirements, specialized machines like turret lathes or mill-turn machines may be employed.
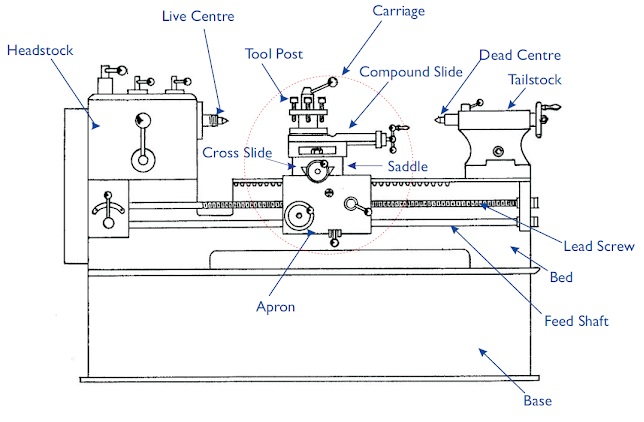
Summary
The headstock is an important part of a lathe machine, functioning as the main power source. It houses the spindle and motor, which rotate the workpiece for cutting or shaping. Without the headstock, the lathe machine wouldn’t be able to perform its tasks effectively.
The headstock also plays a crucial role in controlling the speed at which the workpiece rotates. By adjusting the belts and gears, the operator can choose the desired speed for different types of materials and cutting operations. This feature allows for versatility and precision in lathe machine operations. In conclusion, the headstock is a vital component in a lathe machine, providing power, rotation control, and enabling various cutting or shaping tasks.