Welcome to the world of power tools! Have you ever wondered what size generator you need to run your power tools efficiently? Well, you’re in the right place! In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about finding the perfect generator for your tools.
Imagine this: you’re all set to tackle that weekend woodworking project or get started on those landscaping tasks, but you encounter a power outage. Don’t fret! With the right generator, you can keep your power tools running smoothly and avoid any delays.
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional tradesperson, understanding what size generator you need is essential for uninterrupted workflow. So let’s dive in and discover how to choose the right generator that will keep your power tools buzzing with energy!
What Size Generator Will Run Power Tools?
When it comes to using power tools, having a reliable source of electricity is crucial. But what if you’re in a location without access to a power outlet? This is where generators come in. Generators are portable devices that can provide power on the go. However, not all generators are suitable for running power tools. It’s important to choose the right size generator that can handle the power demands of your tools effectively. In this article, we will explore the factors to consider and provide a comprehensive guide on choosing the appropriate generator size for running power tools.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Generator Size
1. Power Requirements of Your Tools
The first step in determining the size of the generator you need is to understand the power requirements of your tools. Each power tool has a specific power rating, usually measured in watts or amps. You can find this information on the tool’s label or in the instruction manual. Make a list of all the tools you plan to run simultaneously and note down their power ratings. This will give you an idea of the total power requirement for your setup.
Keep in mind that different power tools have different starting and running power requirements. Some tools, like drills or sanders, may have a higher starting power requirement but a lower running power requirement. Others, such as circular saws or air compressors, may have a consistent power demand throughout operation. Take these variations into account when calculating the total power requirement for your tools.
Once you have the total power requirement in watts or amps, you can move on to selecting a generator that can meet or exceed this requirement.
2. Generator Power Output
Generators are available in different sizes and power output capacities. The power output capacity of a generator is typically measured in watts. When choosing a generator, it’s important to select one that can handle the total power requirement of your tools.
A general rule of thumb is to choose a generator with a power output capacity that is at least 20% higher than your total power requirement. This provides a buffer and ensures that the generator can handle the occasional power spikes that some tools may have during operation.
For example, if the total power requirement of your tools is 2000 watts, it would be wise to choose a generator with a power output capacity of at least 2400 watts. This will ensure that the generator can handle the power demands of your tools without being overloaded.
3. Efficiency and Fuel Consumption
Another important factor to consider when choosing a generator size is its efficiency and fuel consumption. Generators are not 100% efficient, meaning that some of the fuel they consume is wasted as heat. This inefficiency can vary depending on the type and model of the generator.
It’s important to choose a generator that is fuel-efficient and can provide power for an extended period without needing frequent refueling. This is especially crucial if you plan to use your power tools for long periods or in remote locations where fuel availability may be limited.
Consider generators with features like automatic idle control, which adjusts the engine speed to match the power demand, thereby conserving fuel. Additionally, look for generators with a reasonable fuel tank capacity that can provide sufficient runtime for your needs.
4. Portability and Noise Level
Portability and noise level are important considerations, especially if you plan to use the generator in different locations or in residential areas. Larger generators tend to be heavier and bulkier, making them less portable. If portability is important to you, opt for a smaller, more compact generator that is easy to transport.
Noise level is measured in decibels (dB). Generators can be noisy, and some neighborhoods or campsites may have noise restrictions. Look for generators that have noise reduction features like a muffler or soundproof casing. Additionally, check the noise level rating of the generator and opt for models that operate at lower decibel levels to minimize disturbance.
5. Budget Considerations
Lastly, consider your budget when choosing a generator size. Larger generators with higher power output capacities tend to be more expensive. It’s essential to find a balance between the power requirements of your tools and the price range that fits your budget.
Keep in mind that investing in a generator with a higher power output capacity than you currently require can provide flexibility for future needs. It can save you the hassle and expense of upgrading your generator down the line if you add more power tools to your collection.
Take into account the long-term benefits and potential savings when deciding on the generator size that best suits your needs.
Choosing the Right Generator Size
1. Determine Your Power Requirements
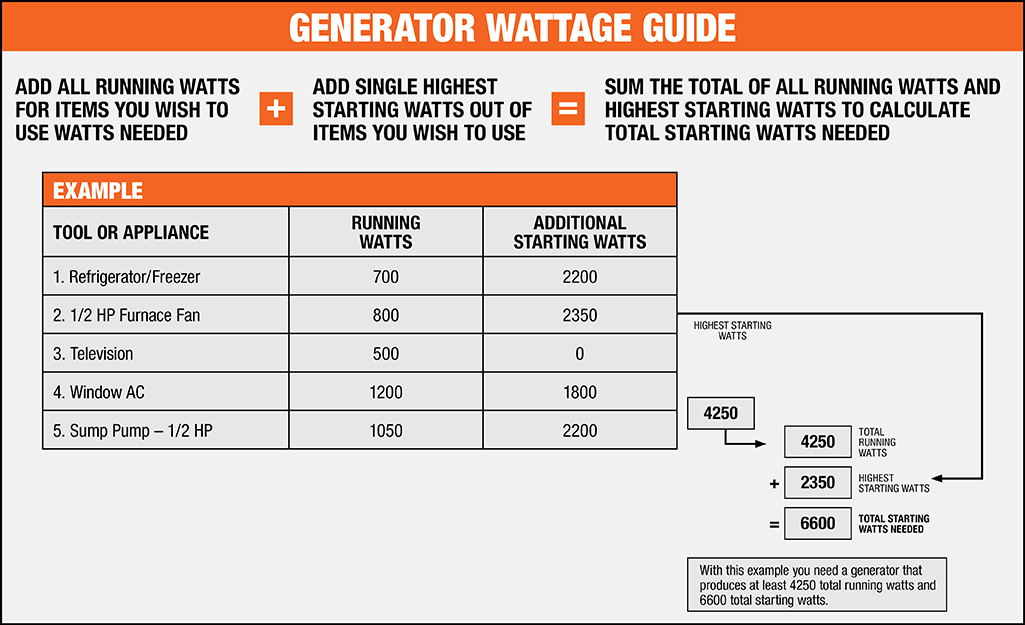
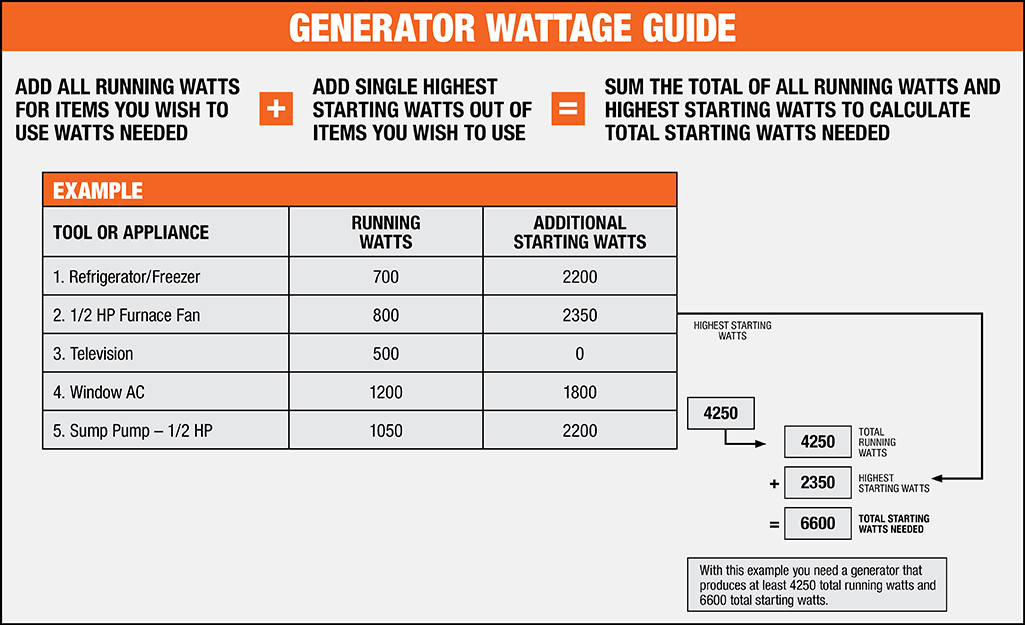
Start by making a list of all the power tools you plan to use simultaneously. Note down their power ratings, both for starting and running. Calculate the total power requirement in watts or amps.
For example, if you have a circular saw with a starting power requirement of 1500 watts and a running power requirement of 1200 watts, a drill with a starting power requirement of 800 watts and a running power requirement of 600 watts, and an air compressor with a consistent power requirement of 1800 watts, your total power requirement would be:
- Circular saw: Starting 1500 watts + Running 1200 watts = 2700 watts
- Drill: Starting 800 watts + Running 600 watts = 1400 watts
- Air compressor: 1800 watts
- Total power requirement: 2700 watts + 1400 watts + 1800 watts = 5900 watts
In this example, the total power requirement is 5900 watts, which will serve as the basis for choosing the right generator size.
2. Choose a Generator Size
Based on your total power requirement, choose a generator with a power output capacity that can handle the load. As mentioned earlier, it’s advisable to choose a generator with a power output capacity that is at least 20% higher than your total power requirement. This will ensure that the generator can handle the power demands of your tools without being overloaded.
In our example, a generator with a power output capacity of around 7000 watts or higher would be suitable to meet the power requirements of the circular saw, drill, and air compressor.
3. Consider Other Important Factors
While the power output capacity is crucial, don’t forget to consider other factors like efficiency, fuel consumption, portability, and noise level. These factors can significantly impact your overall experience and convenience when using the generator for powering your tools.
Look for generators with features that align with your specific needs, such as fuel efficiency, extended runtime, portability, and noise reduction. Assessing these factors will help you make a well-informed decision and choose the right generator size that ticks all the boxes.
Conclusion
Choosing the right size generator for running power tools is essential for seamless operation and optimal performance. By considering factors such as the power requirements of your tools, generator power output, efficiency and fuel consumption, portability, noise level, and budget considerations, you can make an informed decision. Remember to calculate the total power requirement of your tools and choose a generator with a power output capacity that can handle the load. By doing so, you can ensure a reliable and efficient power supply for all your power tool needs.
Key Takeaways: What Size Generator Will Run Power Tools?
- A generator with a wattage rating between 2,000 to 7,000 watts is generally sufficient for running power tools.
- Consider the power requirements of your specific tools and add up their wattage to determine the generator size needed.
- Some power tools, like circular saws and air compressors, may have higher startup wattage requirements, so choose a generator with enough surge power.
- Properly calculate the total wattage needed by considering the simultaneous usage of multiple power tools.
- Remember to account for any other electrical devices or appliances that may be running simultaneously with the power tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our Frequently Asked Questions section about what size generator will run power tools. Here, we provide answers to some of the common queries people have when it comes to choosing the right generator to power their tools.
1. Can any generator run power tools?
While not all generators are created equal, many generators are designed to run power tools. However, it’s important to consider the wattage requirements of your power tools and choose a generator with sufficient power output.
Generators are typically rated by their maximum power output, known as surge power, and their continuous power output. For power tools, it’s recommended to choose a generator that can handle the surge power of your tools, as well as provide enough continuous power to run them efficiently.
2. How do I determine the size of the generator I need for power tools?
The size of the generator you need for power tools depends on the total wattage requirements of your tools. To determine the size, start by listing all the power tools you plan to use simultaneously and their wattage ratings. Add up the wattage ratings to get the total wattage required.
Once you have the total wattage, choose a generator with a power output that exceeds this total. It’s recommended to have a buffer of around 20% to ensure smooth operation and account for any additional power needs that may arise.
3. Can a small generator run power tools?
A small generator can run power tools, but it’s important to check the power output and match it with the wattage requirements of your tools. Small generators typically have lower power outputs, limiting the number and type of power tools they can effectively run.
If you have a small generator, prioritize running power tools with lower wattage requirements and avoid running multiple high-power tools simultaneously, as this can overload the generator.
4. Can a generator damage power tools?
When used properly, generators should not damage power tools. However, it’s important to ensure that the generator provides stable power without voltage fluctuations. Unstable power can damage sensitive components in power tools, leading to decreased performance or even complete failure.
To protect your power tools, consider using a generator with built-in voltage regulation or investing in a voltage stabilizer. Additionally, follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for proper use and maintenance of both the generator and power tools.
5. Are there any safety precautions when using a generator for power tools?
Absolutely! When using a generator for power tools, it’s important to follow some safety precautions. First, always operate the generator outdoors or in a well-ventilated area to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
Additionally, make sure to use appropriate extension cords rated for the power output of the generator and the length needed. Regularly inspect the cords for any damage and replace them if necessary. Finally, never overload the generator by exceeding its power output capacity, as this can pose a safety risk and damage both the generator and your power tools.

Summary:
So, here’s the takeaway: When choosing a generator for your power tools, make sure to check the starting and running watts of the tools. Add up the running watts and choose a generator with a higher capacity to power them. Keep in mind that bigger tools may require a generator with more power. Don’t forget to consider the length of the extension cords and the fuel type needed for the generator. With these tips, you’ll be able to find the right-sized generator for your power tools and get the job done!