If you’ve ever wondered about capstan lathes and their intricate parts, you’re in the right place! So, which of the following is not a part of a capstan lathe? Let’s dive in and find out the answer together.
Now, capstan lathes are fascinating machines used for precision machining, usually in manufacturing settings. They have various components that work together to create efficient and precise machining processes. But, there is one part that doesn’t belong to a capstan lathe.
So, are you ready to explore the world of capstan lathes and discover which part doesn’t quite fit in? Let’s get started!

Which of the Following is Not a Part of Capstan Lathe?
A capstan lathe is a type of machine tool used for precision turning operations. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. The capstan lathe consists of various parts that work together to achieve accurate and efficient machining. However, not all components are directly involved in the functioning of the capstan lathe. In this article, we will explore the different elements of a capstan lathe and identify the one that is not an essential part of this machine.
The Components of a Capstan Lathe: A Closer Look
Before identifying the component that is not a part of a capstan lathe, let’s familiarize ourselves with the various elements that make up this machine:
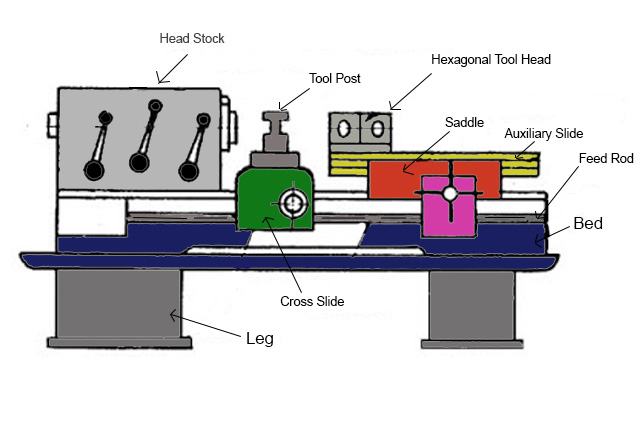
1. The Bed:
The bed is the foundation of the lathe and provides a rigid structure for mounting other components. It is typically made of high-quality cast iron and is designed to absorb vibrations during the machining process. The accuracy and stability of the bed determine the overall precision of the capstan lathe.
The bed also includes the guide rails or ways, which allow the movement of the carriage and tailstock along the length of the lathe. These ways are often equipped with hardened and ground surfaces to minimize wear and ensure smooth sliding motion.
The bed is an integral part of a capstan lathe, providing the necessary support and alignment for all other components.
2. The Headstock:
The headstock is the housing for the main spindle, which holds the workpiece during turning operations. It is positioned at the left end of the bed and houses various mechanisms such as gear trains, clutches, and pulleys.
The main spindle is driven by the motor through a series of gears, allowing the rotation of the workpiece at different speeds. The headstock is responsible for transmitting power from the motor to the spindle, ensuring precise and controlled rotation.
Within the headstock, you will also find the chuck, which is used to secure the workpiece firmly in place. The chuck can be operated manually or hydraulically, depending on the specific design of the capstan lathe.
3. The Carriage:
The carriage is the component that holds and moves the cutting tool across the workpiece. It consists of several parts, including the saddle, cross-slide, and tool post.
The saddle is mounted on the bed and provides support and rigidity to the carriage. It can move longitudinally along the ways, allowing the tool to traverse the workpiece.
The cross-slide is mounted on the saddle and provides a transverse movement to the tool. It enables the cutting tool to perform facing, turning, and other machining operations.
The tool post is attached to the cross-slide and holds the cutting tool securely in place. It allows for quick tool changes and adjustments, ensuring efficient machining.
4. The Tailstock:
The tailstock is located at the right end of the bed and provides additional support to the workpiece during machining. It consists of a movable barrel, which can be extended or retracted to accommodate different workpiece lengths.
The tailstock also includes a center, which aligns with the headstock center to ensure concentricity during turning operations. It is commonly used for drilling, reaming, and other operations that require precise axial alignment.
The tailstock can be locked in position to prevent movement while machining, providing stability and accuracy to the capstan lathe.
5. The Apron:
The apron is located on the front of the bed and contains various mechanisms for controlling the movement of the carriage. It houses components such as feed gears, leadscrew, and feed rod.
The feed gears enable the carriage to move longitudinally or transversely at different feed rates. The leadscrew, driven by the feed rod, converts rotary motion into linear motion, controlling the precise movement of the carriage.
The apron also includes controls and levers for engaging and disengaging feed, selecting the direction of movement, and setting the desired feed rate.
6. The Coolant System:
The coolant system plays a crucial role in capstan lathe operations. It helps dissipate heat generated during machining, lubricates the cutting tool and workpiece, and removes chips and debris from the machining area.
It typically consists of a coolant pump, reservoir, pipes, and nozzles. The coolant is circulated throughout the lathe, providing a continuous flow of lubrication and cooling during cutting operations.
The coolant system ensures the longevity of the cutting tool and improves the surface finish of the machined components.
7. The Control Panel:
The control panel is the interface between the operator and the capstan lathe. It houses various controls, switches, and indicators for adjusting and monitoring the machining process.
The control panel allows the operator to set the desired spindle speed, feed rate, and other parameters. It also provides feedback on the current operating conditions, such as spindle speed, tool position, and coolant flow.
Modern capstan lathes may feature digital displays and programmable controls for enhanced precision and automation.
Key Takeaways: Which of the Following Is Not a Part of Capstan Lathe?
- A capstan lathe is a type of lathe machine used for small precision jobs.
- The following are parts of a capstan lathe:
- Spindle
- Turret
- Chuck
- Collet
- Tailstock
- The tailstock is not a part of a capstan lathe.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to capstan lathes, there are different components that contribute to its functionality. However, there are certain parts that may not be included. Let’s explore some common questions related to the parts of a capstan lathe.
1. What is a capstan lathe and what are its main components?
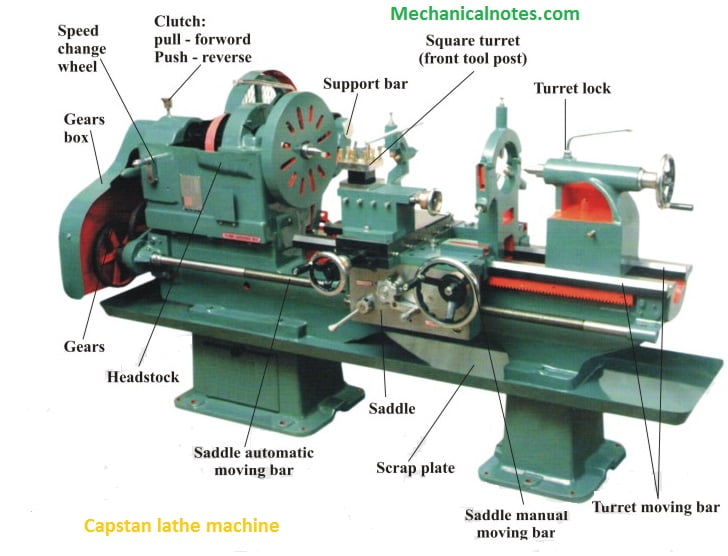
A capstan lathe is a type of lathe machine that is used for high-speed production work. It is specifically designed for machining long, slender workpieces. The main components of a capstan lathe include the headstock, the tailstock, the turret with tool holders, the cross-slide, and the saddle.
The headstock holds the main spindle, the tailstock is used for supporting the other end of the workpiece, the turret holds the various cutting tools, the cross-slide moves the cutting tools along the workpiece, and the saddle moves the turret and cross-slide horizontally.
2. What are some common parts that are usually found in a capstan lathe?
In addition to the main components, a capstan lathe may have other parts such as a chuck for holding the workpiece, a carriage to move the turret and cross-slide longitudinally, a coolant system for removing heat generated during machining, and an electric motor to drive the lathe’s spindle.
Furthermore, capstan lathes may include other accessories like a gearbox for changing spindle speed, a leadscrew for thread cutting, and a quick-change tool post for easily replacing cutting tools.
3. Is a tailstock part of a capstan lathe?
No, a tailstock is not typically part of a capstan lathe. Unlike a conventional lathe, a capstan lathe is designed for high-speed production work and focuses on machining long, slender workpieces. As a result, the tailstock, which is used for supporting the other end of the workpiece, is not commonly found in capstan lathes.
Instead, capstan lathes often rely on a combination of the headstock and a turret that holds multiple cutting tools to efficiently machine workpieces without the need for a tailstock.
4. What is the purpose of the turret in a capstan lathe?
The turret in a capstan lathe serves as a tool holder and allows for the use of multiple cutting tools in a single setup. This eliminates the need for manual tool changes and reduces the time required for tooling changes during the machining process.
The turret is typically equipped with a number of tool holders, each containing a cutting tool. The turret can be rotated to bring the desired tool into position, allowing for efficient and rapid machining operations.
5. Can a capstan lathe have different types of tool holders in its turret?
Yes, a capstan lathe can have different types of tool holders in its turret to accommodate various cutting tools. Common types of tool holders include single-point tool holders, multi-point tool holders, boring bar tool holders, and drilling tool holders.
These different types of tool holders allow for a wide range of machining operations to be performed on the capstan lathe, making it a versatile machine for high-speed production work.
Differences Between Capstan Lathe and Turret Lathe.
Summary
So, to recap, a capstan lathe is a type of lathe machine used for small-scale production. It has a turret with multiple tools that can be easily changed. The key parts of a capstan lathe include the main spindle, the turret, the turret slide, and the collet. The main spindle rotates the workpiece, while the turret holds the various cutting tools. The turret slide moves the turret horizontally, allowing the tools to be positioned for cutting. Finally, the collet holds the workpiece securely in place. Overall, a capstan lathe is designed for efficient and precise machining of small parts.
In conclusion, a capstan lathe is not a part of any machine; it is a specific type of lathe machine with its own unique features and functions. Understanding the different parts of a capstan lathe can help us appreciate its role in manufacturing and how it simplifies small-scale production. So, the next time you see a capstan lathe in action, you’ll have a better grasp of what makes it distinct from other types of lathes.