If you’ve ever wondered which way a lathe turns, you’re in the right place! Let’s dive into the fascinating world of lathes and find out their secret.
So, you might be asking, “Which way does a lathe turn?” Well, my friend, it all depends on the type of lathe you’re using.
But don’t worry, I’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll explore the different types of lathes and their rotation directions. Get ready to have your lathe-turning curiosity satisfied!
When operating a lathe, it’s important to know which way it turns. The direction depends on the specific lathe and its settings. To determine the rotation direction, locate the rotation arrow on the lathe and refer to the machine’s manual. Following the manufacturer’s instructions will ensure safe and accurate operation. Stay mindful of the safety precautions and always wear appropriate protective gear when using a lathe. Happy turning!
Which Way Does a Lathe Turn?: A Comprehensive Guide
The direction in which a lathe turns is a fundamental aspect of the machine’s operation. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced machinist, understanding the rotation of a lathe is essential for ensuring safety and achieving precise results. In this article, we will explore the topic of lathe rotation in detail, covering its importance, common practices, safety considerations, and troubleshooting tips. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mystery of which way a lathe turns!
Lathe Rotation: Clockwise or Counterclockwise?
Lathe rotation refers to the direction in which the spindle and workpiece rotate during turning operations. The standard convention for lathe rotation is counter-clockwise (or anti-clockwise) when viewed from the operator’s perspective. This means that the spindle and workpiece rotate in a direction opposite to the movement of the hands of a clock. The counter-clockwise rotation is commonly used in most lathes, as it allows for efficient chip removal and smooth cutting action. However, it is important to note that there are instances where lathes may have a reversible rotation feature, allowing users to switch between clockwise and counterclockwise rotation based on their specific needs.
Importance of Lathe Rotation Direction
Understanding and following the correct lathe rotation direction is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures consistent and predictable cutting forces, allowing for better control and accuracy. This is particularly important when turning cylindrical or tapered shapes, as the direction of rotation affects the cutting action and the final surface finish. Moreover, following the standard rotation direction ensures compatibility with tooling systems and workholding devices designed for counterclockwise rotation lathes. Deviating from the recommended rotation direction can lead to poor cutting performance, increased tool wear, and unwanted vibrations. Therefore, it is essential to always double-check the lathe’s rotation direction before starting any machining operation.
Safety Considerations
Operating a lathe involves inherent risks, and maintaining safety should be a top priority. When it comes to lathe rotation, there are specific safety considerations to keep in mind. Firstly, always ensure that the lathe is powered off and properly locked out before changing the rotation direction. This prevents accidental starts and potential injuries. Additionally, carefully inspect the workpiece, tooling, and cutting tools for any damage or wear before starting the lathe. A damaged workpiece or tool can lead to unpredictable behavior during rotation, posing a safety hazard. Lastly, be mindful of the direction of the cutting tools and the rotation of the lathe to avoid accidental contact, especially when hand-feeding the workpiece.
Troubleshooting Lathe Rotation
In some cases, you may encounter issues with the rotation of your lathe spindle. Here are a few troubleshooting tips to help you address common problems:
1. Check the power supply: Ensure that the lathe is receiving the correct voltage and that the power supply is stable. Inconsistent power can affect the rotation speed.
2. Check the motor and drive belts: Inspect the motor and drive belts for any signs of wear or damage. Loose or worn belts can cause slipping and affect the rotation.
3. Evaluate the control settings: Review the lathe control settings and make sure that the rotation direction is properly programmed. Sometimes, accidental changes can occur during operation.
4. Consult the lathe manual: If the issue persists, refer to the lathe’s manual or contact the manufacturer for further guidance. They will have specific troubleshooting steps for your particular lathe model.
Remember, if you’re unsure about any aspect of your lathe’s rotation or encounter persistent issues, seek professional assistance to ensure safe and optimal operation.
Benefits of Understanding Lathe Rotation
Understanding the correct rotation of a lathe provides several benefits for both beginners and experienced machinists. Here are some key advantages:
1. Improved safety: Following the recommended rotation direction reduces the risk of accidents and ensures safer operations.
2. Enhanced cutting performance: Correct rotation allows for optimal chip removal, reduced tool wear, and improved surface finish.
3. Compatibility with industry standards: By adhering to the standard rotation direction, you can easily find and use compatible tooling systems and workholding devices.
4. Efficient troubleshooting: If you encounter issues during lathe operation, knowing the correct rotation direction helps in diagnosing and resolving problems effectively.
5. Accuracy and precision: Proper rotation direction ensures consistent cutting forces, allowing for accurate dimensions and smooth surfaces.
6. Expanded tooling options: By using the standard rotation direction, you can access a wide range of tooling options designed specifically for counterclockwise rotation lathes.
Understanding the intricacies of lathe rotation not only makes you a more informed machinist but also contributes to safer and more efficient machining processes.
—
More H2 headings with details information after the main topic:
The Role of Spindle Speed in Lathe Rotation
Spindle speed is a crucial parameter that influences the rotation of a lathe. In this section, we will delve into the significance of spindle speed, how it affects the rotation direction, and the factors to consider when setting the appropriate speed for various turning operations.
The Impact of Cutting Tools on Lathe Rotation
The choice and proper usage of cutting tools play a significant role in lathe rotation. In this section, we will explore how different types of cutting tools affect the rotation process and the key considerations for selecting the right tool for specific machining tasks.
Advancements in Lathe Rotation Technology
As technology continues to advance, so does the field of lathe rotation. In this section, we will examine the latest developments in lathe rotation technology, including CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes, dual-direction rotation capabilities, and automated tool changers, among other innovations.
—
The Impact of Speed on Lathe Rotation
Speed is a critical factor in lathe rotation as it directly affects the cutting action and surface finish of the workpiece. The rotation speed is typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM) and is determined by the combination of the lathe’s spindle speed and the diameter of the workpiece. In general, higher rotation speeds are used for smaller diameter workpieces, while larger diameter workpieces require slower rotation speeds. However, it is essential to consider other factors, such as the material being machined and the type of cutting operation being performed, to determine the optimal rotation speed.
The Relationship Between Cutting Speed and Rotation Speed
Cutting speed refers to the speed at which the cutting tool engages with the workpiece during the turning process. It is directly related to the rotation speed of the lathe. The cutting speed is usually measured in surface feet per minute (SFM) or meters per minute (m/min) and is determined based on the desired material removal rate and the properties of the workpiece material. To calculate the cutting speed, the formula is as follows:
Cutting Speed (SFM) = (π x Diameter of the Workpiece x Rotation Speed) / 12
It’s important to note that different materials have specific cutting speed recommendations, which are typically provided by cutting tool manufacturers or can be found in machinist handbooks. Adhering to the recommended cutting speeds ensures optimal tool life, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy.
Benefits of Proper Rotation Speed
Using the appropriate rotation speed offers several advantages, including:
1. Longer tool life: Optimal rotation speeds reduce the wear and tear on cutting tools, resulting in extended tool life.
2. Improved surface finish: Proper rotation speed helps achieve a smoother surface finish on the workpiece, reducing the need for additional polishing or post-processing.
3. Enhanced dimensional accuracy: By maintaining the correct rotation speed, you can achieve more precise dimensions on the workpiece without any oversizing or undersizing issues.
4. Efficient chip evacuation: The right rotation speed facilitates efficient chip evacuation, preventing chip buildup and improving overall cutting performance.
5. Increased productivity: When the rotation speed is optimized, machining operations can be completed more quickly, resulting in higher productivity levels.
Tips for Optimizing Rotation Speed
Here are some tips for optimizing the rotation speed in lathe operations:
1. Understand the workpiece material: Different materials have different cutting speed requirements. Take into consideration the material’s hardness, heat resistance, and machinability to determine the appropriate rotation speed.
2. Consult cutting tool recommendations: Refer to the cutting tool manufacturer’s guidelines for recommended cutting speeds for specific materials. They provide valuable information on the ideal rotation speeds to achieve optimum performance and tool life.
3. Gradually increase the rotation speed: When starting a machining operation, begin with a lower rotation speed and gradually increase it while monitoring the cutting performance and surface finish. This allows for adjustments and ensures optimal results.
4. Balance the need for speed and accuracy: While higher rotation speeds can increase productivity, it’s crucial to strike a balance with dimensional accuracy and surface finish requirements. Avoid excessively high speeds that may compromise the quality of the workpiece.
5. Regularly inspect and maintain tools: Regularly inspect the cutting tools for signs of wear or damage. Dull or damaged tools can lead to poor cutting performance, requiring adjustments in rotation speed or tool replacement.
By understanding the relationship between rotation speed and cutting performance, and by implementing these optimization tips, you can ensure efficient and high-quality lathe operations.
Understanding Directional Threads on Lathe Rotation
One important aspect of lathe rotation is the use of directional threads, which determine the direction in which the spindle rotates when threaded attachments are installed. Directional threads ensure that the attachments are securely fastened and do not inadvertently unthread during operation. In this section, we will explore the different types of directional threads used in lathe rotation and their significance.
Left-Hand Threads
Left-hand threads are threads that read counter-clockwise, opposite to the standard right-hand threads. In lathe rotation, left-hand threads are often used for attaching accessories or chucks to the spindle. The clockwise rotation of the lathe tightens the left-hand thread, creating a self-locking mechanism that prevents the attachment from loosening during operation. Left-hand threads are commonly found on lathes with reversible rotation capabilities, allowing users to switch between clockwise and counterclockwise rotation based on their specific needs.
Right-Hand Threads
Right-hand threads are the conventional threads that read clockwise. They are typically used for attaching workpieces or tooling to the lathe spindle. The counter-clockwise rotation of the lathe tightens the right-hand thread, ensuring a secure and stable connection. Right-hand threads are the standard type of thread used in most lathes and are compatible with a wide range of tooling and workholding devices.
Benefits of Directional Threads
Directional threads offer several benefits, including:
1. Enhanced safety: Directional threads provide a secure attachment mechanism, reducing the risk of tools or workpieces becoming loose during rotation.
2. Versatility: Reversible rotation lathes with directional threads offer increased versatility, allowing users to adapt to different machining requirements without the need for additional modifications.
3. Compatibility with standard tooling: The use of right-hand threads as the standard rotation direction ensures compatibility with a wide range of tooling options available in the market.
4. Optimal torque transmission: Directional threads ensure an efficient transfer of torque from the lathe spindle to the attached accessories or workpieces, resulting in stable and consistent rotation.
Understanding the importance and usage of directional threads helps machinists select the appropriate attachments and ensures a secure and reliable connection between the lathe spindle and tooling/workpieces.
—
More H2 headings with details information after the main topic:
Common Mistakes in Lathe Rotation and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced machinists can make mistakes when it comes to lathe rotation. In this section, we will discuss some common mistakes and provide tips on how to avoid them, ensuring smooth and efficient lathe operations.
Lathe Rotation Techniques for Different Machining Operations
Different machining operations require specific lathe rotation techniques. In this section, we will explore the recommended rotation methods for various turning, facing, threading, and boring operations, offering insights into achieving optimal results.
Tips for Maintaining the Optimal Rotation of a Lathe
To ensure that your lathe operates smoothly and efficiently for years to come, proper maintenance is essential. In this section, we will share valuable tips for maintaining the optimal rotation of your lathe, including spindle alignment, lubrication, and regular inspections.
—
In conclusion, understanding the rotation direction of a lathe is crucial for safe and effective machining operations. The standard convention for lathe rotation is counterclockwise when viewed from the operator’s perspective. Adhering to the correct rotation direction ensures compatibility with tooling systems, improves cutting performance, and enhances safety. Additionally, optimizing rotation speed based on the workpiece material and specific machining requirements is essential for achieving accurate dimensions and a high-quality surface finish. Directional threads on the lathe spindle play a significant role in securely attaching accessories or workpieces.
By following best practices, troubleshooting common rotation issues, and staying informed about advancements in lathe rotation technology, machinists can operate their lathes with confidence and achieve excellent results. Remember to always prioritize safety, consult user manuals, and seek professional assistance when needed. With the knowledge gained from this comprehensive guide, you will be well-equipped to navigate the world of lathe rotation and unlock its full potential.
Key Takeaways: Which Way Does a Lathe Turn?
- A lathe typically turns in a clockwise direction.
- Turning a lathe counterclockwise can be dangerous and should be avoided.
- Always refer to the lathe’s user manual for specific turning directions.
- Ensure proper safety measures, such as wearing protective gear, when operating a lathe.
- Before starting a lathe, double-check the direction by using the handwheel or turning it on briefly at a low speed.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the world of lathes, there’s a lot to learn. From understanding different lathe types to mastering techniques, it’s important to start with the basics. One fundamental question that often arises is about the direction in which a lathe turns. Let’s explore this question further with the following FAQs:
1. How does the turning motion of a lathe work?
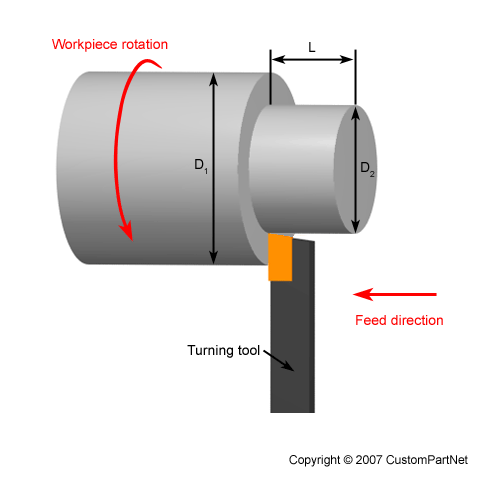
A lathe uses a spinning motion to shape and cut various materials. The turning motion is achieved through the rotation of the workpiece, which is secured in place and rotated along its central axis. The tool, such as a cutting tool or a chisel, remains stationary while the workpiece rotates against it. This process allows the lathe operator to shape, carve, or cut the material according to their desired outcome.
In summary, the turning motion of a lathe involves the workpiece rotating while the cutting tool remains in a fixed position, resulting in the desired shaping, carving, or cutting of the material.
2. Which way does the workpiece rotate on a lathe?
In most lathes, the workpiece rotates clockwise when viewed from the headstock end. This means that if you were standing at the headstock looking towards the tailstock, the workpiece would rotate in a clockwise direction. However, it’s important to note that there are certain exceptions in specialized lathes designed for specific purposes or industries, where the rotation may be reversed.
For the majority of lathes, understanding the clockwise rotation of the workpiece is crucial when it comes to setting up, aligning, and performing operations on the lathe.
3. Does the direction of the lathe’s rotation affect the outcome of the work?
The direction of the lathe’s rotation can indeed affect the outcome of the work. For example, when using a cutting tool, the direction of rotation can determine whether the material is being cut efficiently or causing unnecessary strain on the tool and the lathe components. In addition, the direction of rotation may be important for achieving specific effects or patterns when working with wood or other materials.
It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the recommended rotation direction for different lathe operations and materials, as following the proper rotation can lead to better results, increased safety, and longevity of the lathe and its components.
4. How do I determine the rotation direction of a lathe?
To determine the rotation direction of a lathe, it’s important to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or user manual. The rotation direction may be specified by the manufacturer or vary depending on the lathe model and design. Generally, the direction of rotation is established by the motor’s configuration and the positioning of the gears and belts within the lathe.
If you’re unsure about the rotation direction of your lathe, it’s best to seek guidance from an experienced lathe operator or refer to reputable instructional resources for your specific lathe model.
5. Can you reverse the rotation direction of a lathe?
Generally, it is possible to reverse the rotation direction of a lathe, especially on models that feature a variable-speed control or have adjustable belt configurations. However, it’s important to note that not all lathes have the ability to change the rotation direction. Reversing the rotation direction should be done with caution and following the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid damaging the lathe or compromising safety.
If you need to reverse the rotation direction, refer to the lathe’s user manual or consult an expert who is familiar with your specific lathe model. They can guide you on the proper steps and precautions to take in order to safely change the rotation direction of your lathe.

Summary
So, which way does a lathe turn? Well, it depends on whether it’s a metal or a wood lathe.
In a metal lathe, the workpiece turns while the cutting tool stays still. This helps create smooth and precise cuts. On the other hand, in a wood lathe, the cutting tool is stationary, and the wood spins to shape it into various forms. So, it’s essential to know what type of lathe you are using to figure out which way it turns.
