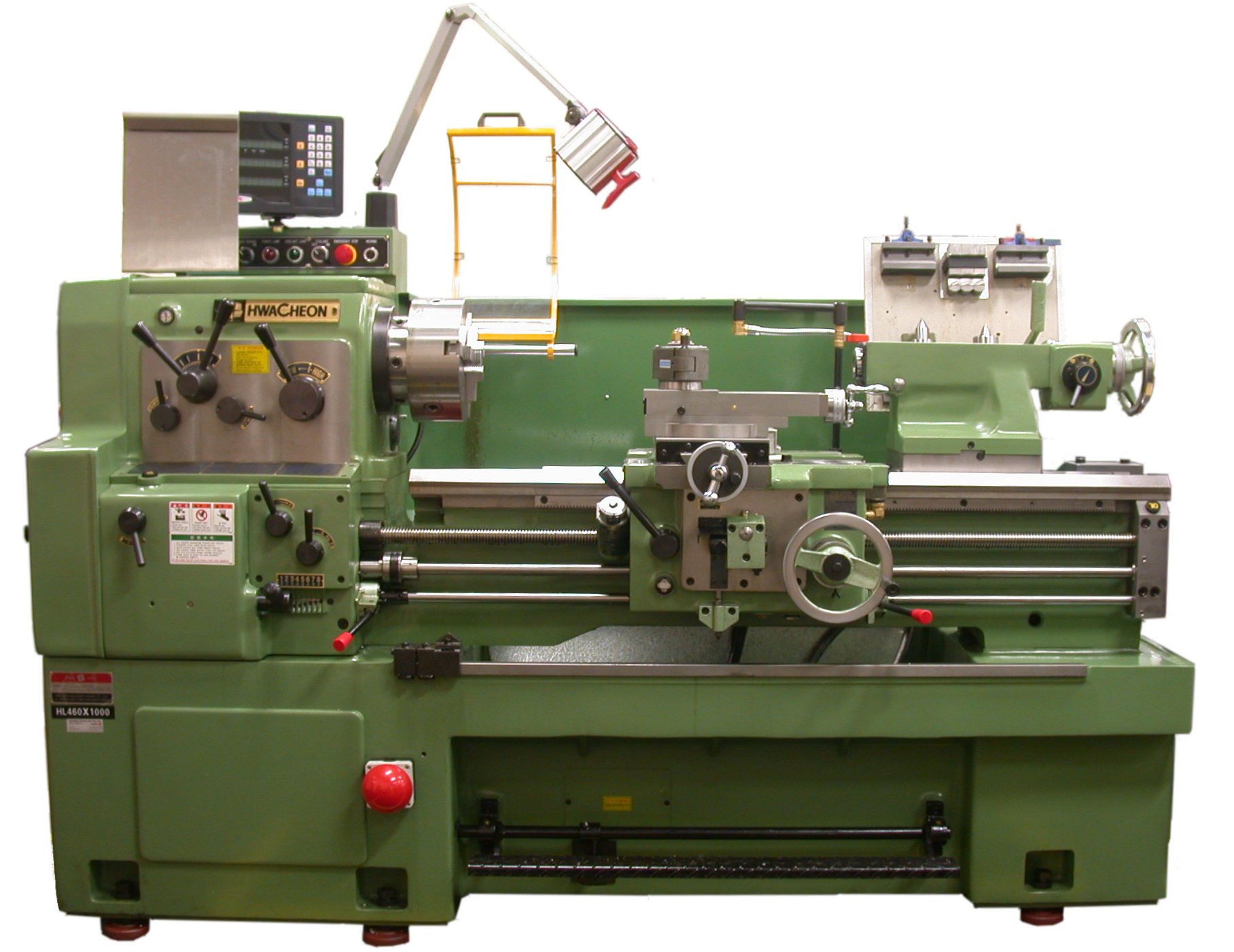
Did you ever wonder why they call it a lathe? Well, get ready to find out! In this article, we’ll dive into the fascinating history and origins of this amazing tool. So, sit back and prepare to be amazed by the story behind the name!
Imagine a time when craftsmen needed a way to shape and carve wood, metal, and other materials. Along came the lathe, a revolutionary invention that made this possible. But why do they call it a lathe? That’s the question that has puzzled many curious minds, and today, we’ll get to the bottom of it!
As we embark on this journey, we’ll explore the etymology of the word “lathe” and uncover its ancient roots. We’ll unravel the mystery and shed light on why this incredible machine is known by such a unique name. Get ready to discover the secrets behind the name “lathe” and delve into the captivating world of craftsmanship!

Why Do They Call It a Lathe?
Have you ever wondered why a particular tool or machine is called by a certain name? In the case of lathes, the name actually has a fascinating origin story. Lathes are versatile machines used in woodworking, metalworking, and other industries for shaping, cutting, or drilling materials. But where did the name “lathe” come from? In this article, we will delve into the history and etymology of the term “lathe” to uncover its origins and shed light on this intriguing question.
The Origins of the Word “Lathe”
When exploring the history of the word “lathe,” we discover that it has roots dating back to ancient times. The term can be traced back to Old English, where it was spelled “læðe” or “læde.” In Old English, “læðe” referred to a machine or tool used for turning or shaping objects. This Old English word, in turn, can be traced back to the Proto-Germanic word “lēþō,” which meant a lathe, turning lathe, or turning machine. It is interesting to note that lathes have been in use for centuries, with evidence of their existence dating back to the ancient Egyptians and Greeks.
The term “lathe” itself evolved over time. In Middle English, it was spelled as “lath” or “lathe,” and by the 16th century, the spelling “lathe” became more standardized. The word “lathe” has its origins in the verb “lade,” which means to turn, shape, or cut with a lathe. The verb “lade” is related to the Old Norse word “hlatha,” which means to load or to pack. This linguistic connection between “lade” and “hlatha” highlights the association between the action of loading or packing and the rotational movement of a lathe.
An Ancient Invention
The use of lathes can be traced back to ancient civilizations. The ancient Egyptians and Greeks used lathes for various purposes, including woodworking and pottery. These early lathes were often operated by hand or foot, using a sharpened tool to shape the material being rotated. The ancient Romans further developed the lathe by introducing the concept of a turning wheel with a tool attached to it. This allowed for more precise and efficient shaping and cutting.
Throughout history, lathes have continued to evolve and improve. In the industrial revolution, lathes became mechanized, with steam engines and later electric motors powering the rotation. Modern lathes now have advanced features, such as computer numerical control (CNC) systems that enable automated precision machining. From their humble origins in ancient times to the sophisticated machines of today, lathes have played a crucial role in shaping and manufacturing the world around us.
The Versatility of Lathes
One of the reasons why lathes have retained their name throughout history is their versatility. Lathes can be used for various purposes, including woodworking, metalworking, glassworking, and even pottery. The core principle of a lathe remains the same across different industries – the rotation of a workpiece, allowing for shaping, cutting, or drilling.
In woodworking, lathes are used to turn wooden objects such as furniture legs, bowls, and spindles. The rotational movement allows woodworkers to shape and refine the contours of the material, creating intricate designs and smooth finishes. In metalworking, lathes are used to produce precision parts for machinery, engines, and other equipment. The ability to turn metal with precision is crucial in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Furthermore, lathes have also found applications in artistic endeavors. Glassworking lathes are used by glassblowers to shape and mold molten glass, creating beautiful and intricate glassware. Even in pottery, lathes are used to shape clay and create symmetrical vessels. The versatility of lathes has made them an essential tool across multiple industries, and their name has remained unchanged, a testament to their enduring significance.
Advancements in Lathe Technology
As technology has advanced, so has the design and capabilities of lathes. From the manual lathes of the past to the modern CNC lathes, there have been significant developments that have revolutionized the industry.
CNC lathes, or computer numerical control lathes, have greatly increased precision and automation in lathe operations. These lathes can be programmed to produce complex designs and shapes with minimal human intervention. They have also contributed to greater efficiency and productivity in various industries.
Another notable advancement is the introduction of multi-axis lathes, which can rotate the workpiece in multiple directions simultaneously. This capability allows for the creation of intricate and complex shapes that were previously challenging or impossible to achieve.
The Legacy of the Lathe
The name “lathe” has stood the test of time, remaining unchanged for centuries. Its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where the concept of turning and shaping materials first emerged. Today, lathes continue to play a crucial role in shaping and manufacturing various objects, from furniture and machine parts to artistic glassware and pottery.
The versatility and adaptability of lathes have allowed them to evolve and remain relevant across different industries. As technology advances, lathes will continue to push the boundaries of precision and automation, contributing to the development of new innovations.
The Evolution of Lathe Technologies
The development of lathe technologies has been driven by the need for more efficient and precise manufacturing processes. Over the years, different types of lathes have emerged, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Let’s explore the evolution of lathe technologies and how they have shaped the manufacturing industry.
Woodworking Lathes
Woodworking lathes have a long history, dating back to ancient times. Early woodworking lathes were operated manually, with the craftsman using a foot pedal or a hand-operated crank to rotate the workpiece. These lathes were primarily used for turning wooden objects such as furniture legs, spindles, and bowls.
In the 19th century, the introduction of steam-powered lathes revolutionized the woodworking industry. These lathes were larger and more powerful, capable of turning larger workpieces with greater precision. Steam-powered lathes were commonly used in furniture and shipbuilding industries, where mass production was necessary.
With the advent of electric motors, woodworking lathes became even more efficient and accessible. Electric-powered lathes allowed for smoother and more controlled rotations, resulting in higher-quality finishes. Today, modern woodworking lathes often feature variable speed control and other advanced features, making them versatile tools for both professional woodworkers and hobbyists.
Metalworking Lathes
Metalworking lathes have played a crucial role in the manufacturing industry, allowing for the production of precision parts and components. The earliest metalworking lathes were similar in design to woodworking lathes, but with modifications to accommodate the harder materials used in metalworking.
In the 19th century, the introduction of the screw-cutting lathe revolutionized metalworking. This type of lathe featured a leadscrew and a mechanism that allowed for accurate and efficient threading. Screw-cutting lathes enabled manufacturers to produce standardized parts with threaded connections, leading to the development of complex machinery.
Today, metalworking lathes come in various types and sizes, ranging from small benchtop lathes used by hobbyists to large industrial lathes used in mass production. Modern metalworking lathes often utilize computer numerical control (CNC) systems, which allow for precise and automated machining processes. CNC metal lathes can produce complex parts with minimal human intervention, enhancing productivity and accuracy in manufacturing.
Glassworking Lathes
Glassworking lathes are specialized lathes used by glassblowers and glass artists to shape and manipulate molten glass. These lathes have a horizontal spindle that holds the glasswork and can rotate it at various speeds.
Glassworking lathes come in different sizes and configurations, depending on the specific needs of the glass artist. The rotation of the workpiece allows for even heating and shaping of the glass, enabling the creation of intricate designs and delicate forms. Glassworking lathes often feature a motorized cutting tool that can be used to carve or engrave the glass.
Glassblowing lathes have been instrumental in the development of artistic glassware and scientific glass instruments. These lathes allow for precise control and manipulation of the glass material, giving artists and scientists the ability to create unique and beautiful pieces.
The Benefits of Using Lathes
There are numerous benefits to using lathes in various industries and applications. Let’s explore some of the key advantages that lathes offer:
Precision and Accuracy
Lathes are known for their ability to produce highly precise and accurate results. The rotational movement of the workpiece allows for the shaping and cutting of materials with great precision. This level of accuracy is crucial in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, where precision components are required for optimal performance and safety.
Efficiency and Productivity
Lathes enable efficient and productive manufacturing processes. The rotational motion of the workpiece allows for continuous machining, resulting in faster production times. In addition, advanced features such as CNC control and automatic tool changers further enhance efficiency by reducing setup times and minimizing human intervention.
Versatility and Adaptability
Lathes are versatile machines that can be used for a wide range of applications. Whether it’s woodworking, metalworking, glassworking, or pottery, lathes offer the flexibility to shape and manipulate different materials. This versatility makes lathes valuable tools in various industries, allowing for diverse manufacturing processes.
Quality and Finishing
Using a lathe often results in high-quality finishes and smooth surfaces. The rotational movement allows for consistent and even cutting, reducing the likelihood of imperfections or rough edges. This is particularly important in applications where aesthetics and precision are paramount, such as furniture making, instrument manufacturing, and artistic creations.
Cost-Effectiveness
In the long run, lathes can be cost-effective solutions for manufacturing. By streamlining and automating production processes, lathes help reduce labor costs and minimize material waste. Additionally, the ability to produce precise and accurate components ensures a higher level of quality control, reducing the need for rework or repairs.
Lathe vs. Other Machining Tools
When it comes to machining processes, lathes are just one of the many tools available. Let’s compare lathes with some other commonly used machining tools to understand their differences and applications:
Lathes vs. Milling Machines
While lathes and milling machines may appear similar, they have distinct differences in their operations and applications. Lathes are primarily used to shape and cut materials by rotating them against a fixed cutting tool. On the other hand, milling machines use rotating cutting tools to remove material from a stationary workpiece.
Lathes excel at producing cylindrical or rotational parts, such as shafts, rods, and cylindrical components. They are ideal for tasks like turning, facing, and drilling. Milling machines, on the other hand, are better suited for producing flat or angular surfaces, slots, and grooves. They are commonly used for operations like milling, drilling, and tapping.
Both machines play crucial roles in manufacturing, with their application often depending on the desired outcome and the specific requirements of the project. In some cases, both machines may be used in conjunction with each other to achieve certain results.
Lathes vs. CNC Routers
CNC routers and lathes are both computer-controlled machines used in manufacturing. The primary difference lies in their modes of operation and their applications.
A CNC router operates by moving the cutting tool in multiple directions to carve or shape a material. It is commonly used for woodworking, plastic fabrication, and signage production. CNC routers are designed to cut and shape flat or slightly curved surfaces.
On the other hand, lathes rotate the material while a cutting tool shapes it. Lathes are primarily used for cylindrical or rotatory parts and are commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, and glassworking.
While both CNC routers and lathes are versatile machines, their capabilities and applications differ. The decision to use one over the other depends on the specific requirements of the project and the desired outcome.
Lathes vs. 3D Printers
Lathes and 3D printers are fundamentally different in terms of their processes and applications. Lathes rely on subtractive manufacturing, where material is removed to shape the final product. In contrast, 3D printers use additive manufacturing, where the product is built layer by layer using a filament or other material.
3D printers are commonly used for rapid prototyping, small-scale production, and complex geometries. They excel at creating intricate designs and prototypes quickly and cost-effectively. However, they may not be suitable for high-strength, high-precision, or large-scale manufacturing.
Lathes, on the other hand, are ideal for producing precise and accurate components in various materials, including metals, wood, and glass. They are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where tight tolerances and high-quality finishes are required.
While both 3D printers and lathes have their respective strengths, the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the project and the desired end result.
Tips for Using Lathes
Using a lathe can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience. Whether you are a professional machinist or a hobbyist woodworker, here are some tips to help you make the most of your lathe:
1. Safety First
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety goggles, gloves, and ear protection.
- Familiarize yourself with the safety features and emergency stop mechanisms of your lathe.
- Ensure that the workpiece is securely clamped or held in place to prevent accidents.
2. Choose the Right Cutting Tools
- Select cutting tools appropriate for the material you are working with.
- Ensure that the cutting tools are sharp and properly maintained for optimal results.
- Consider using carbide inserts or other high-performance cutting tools for improved efficiency and longevity.
3. Secure the Workpiece Properly
- Ensure that the workpiece is held securely in place to prevent movement or shifting during machining.
- Use appropriate clamps, chucks, or centers depending on the type of lathe and workpiece.
- Regularly check and tighten any holding devices to maintain stability during machining operations.
4. Start with Light Cuts
- When beginning a machining operation, start with light cuts to test the setup and make any necessary adjustments.
- Increase the depth of cuts gradually to avoid overloading the lathe or causing damage to the workpiece.
- Pay attention to the sound and feel of the machining process to ensure that everything is running smoothly.
5. Maintain Proper Lubrication
- Use appropriate lubricants or cutting fluids to reduce friction, dissipate heat, and prolong tool life.
- Regularly check and refill lubricant reservoirs to ensure proper lubrication during machining.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types of lubricants to use.
6. Clean and Maintain Your Lathe
- Regularly clean your lathe to remove dust, debris, and excess lubricants.
- Inspect and clean the cutting tools, tool holders, and other accessories to ensure optimal performance.
- Check and adjust the alignment of the lathe components periodically to maintain accuracy and precision.
7. Practice and Experiment
- Like any skill, becoming proficient with a lathe takes time and practice.
- Experiment with different cuts, speeds, and feeds to understand the capabilities and limitations of your lathe.
- Seek guidance from experienced machinists or woodworkers to learn new techniques and refine your skills.
By following these tips, you can enhance your lathe experience and achieve better results in your machining projects.
Conclusion
The term “lathe” has a rich history and intriguing origins that can be traced back to ancient civilizations. From woodworking and metalworking to glassworking and pottery, lathes have found their place in various industries and applications. The evolution of lathe technologies has paved the way for more efficient and precise manufacturing processes, contributing to advancements in different fields.
Whether you are a professional machinist or a hobbyist, lathes offer a versatile and powerful tool for shaping, cutting, and drilling materials. By understanding the differences between lathes and other machining tools, you can choose the right equipment for your specific needs. With proper safety precautions, appropriate cutting tools, and regular maintenance, you can maximize the performance of your lathe and achieve outstanding results.
Remember to always prioritize safety and continue learning and experimenting to expand your skills and knowledge in the fascinating world of lathes.
Key Takeaways: Why do they call it a lathe?
- A lathe is a machine used to shape and cut wood, metal, or other materials.
- The term “lathe” comes from the Old English word “laða,” which means a “lath” or a piece of wood used as a support.
- Early lathes were primarily used for turning wood, but over time, they evolved to also work with metals and other materials.
- The name “lathe” stuck to these machines even as their capabilities expanded.
- Today, lathes are versatile tools in machining that enable precise shaping, drilling, and cutting of various materials.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are you curious about why woodworking machines are called lathes? Get your answers here!
What is a lathe used for in woodworking?
A lathe is a woodworking machine used to shape wood by rotating it against a cutting tool. The wood is secured on a spindle that rotates at high speeds, allowing the operator to remove material and create intricate designs. Lathes are commonly used to turn wood into round objects like table legs, bowls, and even baseball bats. With the right tools, a lathe can also be used for cutting threads, making fluted columns, and creating decorative patterns on wooden surfaces.
The name “lathe” originated from the Old English word “læððe,” which means “a turning machine.” This term accurately describes the primary function of a lathe, as it revolves the woodwork piece on its axis as the cutting tool shapes it.
How does a lathe work?
A lathe works by rotating the wood on a spindle while a cutting tool called a chisel is pressed against it. The spindle, powered by an electric motor, spins at variable speeds, depending on the desired result and the type of wood being used. The operator guides the tool along the wood’s surface, removing material and shaping it to the desired form. The cutting tool can be adjusted to create different shapes, depths, and contours.
The rotating motion of a lathe allows for precision and accuracy in wood shaping, as it evenly distributes the cutting force and minimizes the risk of tear-out or splintering. This methodical process ensures smooth and consistent results, providing woodworkers with a versatile machine for their artistic creations.
Who invented the lathe?
The lathe is an ancient tool, with its origins traced back to ancient Egypt around 1300 BCE. However, the concept of a lathe, as we know it today, evolved over the centuries through various civilizations. Ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans all had versions of lathes used for wood and metalworking.
One notable figure in the history of lathe development is Leonardo da Vinci, who designed a lathe powered by a rope-and-pulley system in the late 15th century. His design improved the control and precision of the machine, setting the stage for further advancements in lathe technology.
Are there different types of lathes?
Yes, there are various types of lathes designed to cater to different woodworking needs. The most common types include benchtop lathes, which are compact and suitable for small projects; midi lathes, which offer a balance between size and power; and full-size floor lathes, which are robust machines used for larger and more professional applications.
Additionally, there are specialized lathes such as pen lathes, used specifically for turning pens, and bowl lathes, designed for crafting bowls. Each type of lathe has its own unique features and capabilities, allowing woodworkers to choose the one that best suits their needs and the scale of their projects.
Can a lathe be used for metalworking too?
Yes, lathes can be used for metalworking as well. Metal lathes are designed specifically for shaping and machining metal materials. They work on similar principles as wood lathes, employing rotating spindles and cutting tools to remove material and shape the metal piece. Metal lathes often have additional features, such as coolant systems, to handle the increased heat generated during metalworking operations.
Metal lathes are commonly used in industries like machining, engineering, and automotive manufacturing. They are essential tools for creating precision components, turning metal rods and shafts, and accomplishing various metalworking tasks with accuracy and efficiency.
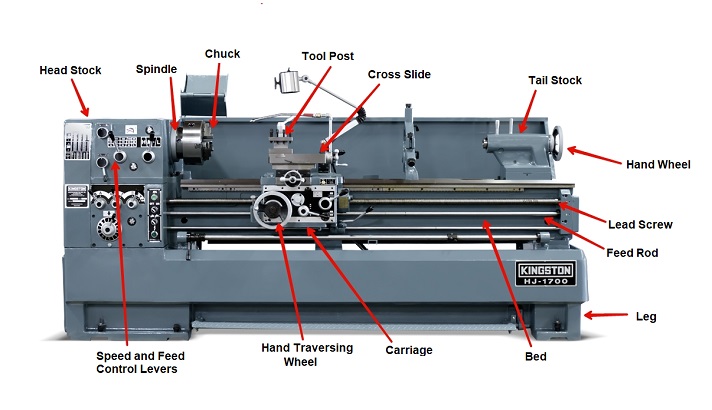
Summary
Ever wondered why it’s called a lathe? Well, it’s because of its ancient origins! The word “lathe” comes from the Old English word “lædan,” which means “to guide or lead.” This clever machine guides and shapes materials like wood or metal, making it really handy for crafting purposes.
The lathe’s basic function is to rotate an object and hold it firmly while you shape it using various cutting tools. From woodworking to metalworking, this versatile machine has been used for centuries to create intricate designs and smooth finishes. So next time you see a lathe, you’ll know why it’s called what it is!
