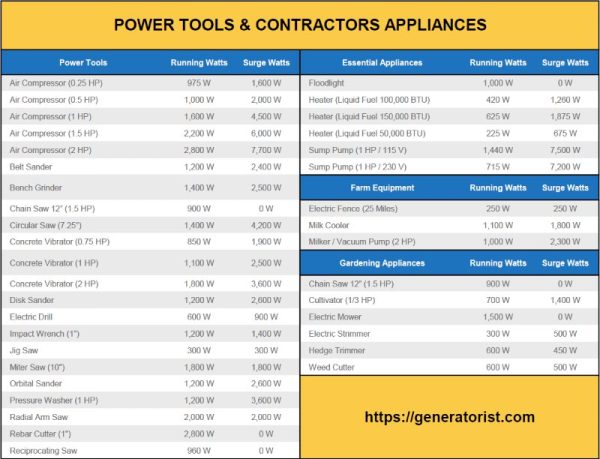
Did you ever wonder how many watts power tools use? Well, my young curious mind, you’ve come to the right place! Whether you’re tackling a home improvement project or just love learning about tools, understanding power tool wattage is key to using them safely and effectively. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of power tools and their wattage.
Power tools come in all shapes and sizes, from drills and saws to sanders and grinders. But have you ever stopped to think about how much power they consume? Watts, my friend, are the unit used to measure power consumption. And believe me, power tools can be real power-hungry creatures! Knowing how many watts your tools use is crucial because it helps you select the right extension cords, circuit breakers, and power sources to keep everything running smoothly.
So, are you ready to unleash your inner DIY expert and unravel the mysteries of power tool wattage? Great! In this article, we’ll explore the typical wattage ranges of popular power tools, discuss factors that influence power consumption, and offer tips on how to calculate power usage. Get your thinking cap on and let’s get started on this electrifying journey!
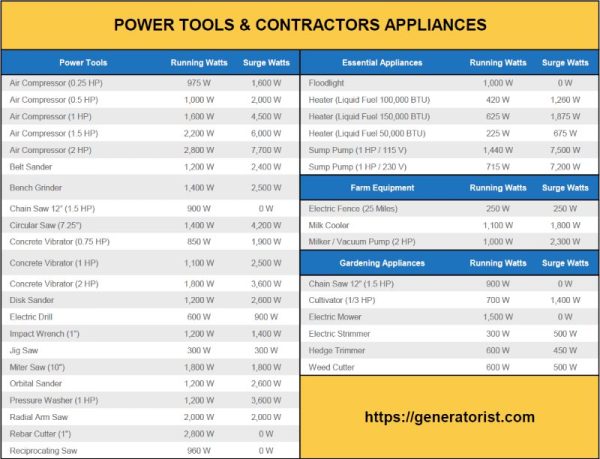
How Many Watts Do Power Tools Use?
In the world of DIY and construction, power tools are essential for getting the job done efficiently and effectively. But have you ever wondered how much power these tools consume? In this article, we will delve into the topic of power tool wattage and explore how many watts different types of power tools typically use. Whether you’re a professional tradesperson or a passionate DIY enthusiast, understanding power tool wattage can help you make informed decisions when it comes to purchasing, using, and managing your power tools.
The Basics of Power Tool Wattage
Before we dive into the specifics of how many watts different power tools use, let’s start with the basics. Wattage is a unit of measurement that quantifies the rate at which power is consumed or generated. In the context of power tools, wattage refers to how much electrical power a tool requires to operate. Understanding the wattage of your power tools is crucial because it determines the amount of electrical load they put on your circuits and influences factors such as the tool’s performance, efficiency, and overall power consumption.
1. Drills and Impact Drivers
Drills and impact drivers are versatile power tools commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, and construction projects. These tools rely on electric motors to provide rotational force to drill holes or drive screws into various materials. The wattage of drills and impact drivers typically ranges from 600 watts to 1200 watts. Higher-powered models are often capable of more demanding tasks and can handle drilling through tough materials, such as concrete or metal. However, it’s essential to note that the wattage of a drill or impact driver alone does not determine its overall performance. Factors like speed, torque, and quality of construction also contribute to their effectiveness.
When operating drills or impact drivers, it’s essential to consider the power supply and ensure it can deliver sufficient wattage to meet the tool’s demands. Additionally, using extension cords that are rated to handle the necessary wattage is crucial to prevent overheating or damage to the tool or the electrical system.
2. Circular Saws
Circular saws are indispensable tools for making straight or bevel cuts in various materials, including wood, plastic, and metal. These powerful tools employ a rotating blade to cut through the workpiece. The wattage of circular saws typically ranges from 1200 watts to 2400 watts, with higher-powered models delivering greater cutting capability and performance. Keep in mind that circular saws with higher wattage consume more electricity and may require a more robust power supply to operate optimally. It’s advisable to check the tool’s wattage requirements and ensure your electrical system can accommodate the power demands.
When using circular saws, safety should always be a top priority. Proper handling, appropriate protective gear, and secure workpiece clamping can help prevent accidents and ensure smooth, precise cuts.
3. Angle Grinders
Angle grinders are versatile tools commonly used in metalworking and construction projects. They are primarily used for cutting, grinding, and polishing various materials, such as metal, stone, and concrete. Angle grinders feature a rotating abrasive disc powered by an electric motor. The wattage of angle grinders typically ranges from 800 watts to 2500 watts. Higher-powered models are often preferred for heavy-duty grinding or cutting tasks that require more power.
When using angle grinders, it’s crucial to exercise caution due to their high-speed rotation and potential kickback. Adequate eye and ear protection, as well as the use of suitable discs and guards, are vital for safety.
4. Sanders
Sanders are power tools used for smoothing and finishing surfaces by abrasion. They vary in size and functionality, with common types including belt sanders, orbital sanders, and detail sanders. The wattage of sanders typically ranges from 200 watts to 1200 watts, depending on the type and capabilities of the tool. Higher wattage sanders are often preferred for heavier sanding tasks or working with more robust materials.
When using sanders, proper technique and patience are essential to achieve the desired results. It’s important to let the tool do the work rather than exerting excessive force, as this can lead to uneven sanding or damage to the workpiece.
5. Reciprocating Saws
Reciprocating saws, also known as sabre saws or recip saws, are versatile tools used for cutting through various materials, including wood, metal, and plastic. These tools utilize a push-and-pull motion to move the blade back and forth rapidly, enabling efficient cutting. The wattage of reciprocating saws typically ranges from 800 watts to 1500 watts. Higher wattage models are often preferred for heavy-duty cutting tasks, while lower wattage models are more suitable for lighter applications.
When using reciprocating saws, always choose the right blade for the material you’re cutting and apply steady, controlled pressure to ensure safe and accurate results.
6. Rotary Tools
Rotary tools, such as Dremel tools, are compact handheld devices with a motor that drives a rotating bit or attachment. These tools are commonly used for precision tasks like engraving, carving, cutting, grinding, and polishing in various materials. The wattage of rotary tools typically ranges from 100 watts to 400 watts, making them relatively low-powered compared to other power tools. However, their compact size and versatility make them ideal for intricate projects that require precision and control.
When using rotary tools, apply light pressure and let the tool do the work. It’s important to wear eye protection and use the appropriate bits or attachments for each specific task.
7. Nail Guns
Nail guns, also known as nailers, are pneumatic, electric, or fuel-powered tools that drive nails quickly and efficiently into various materials. They are commonly used in construction, woodworking, and furniture-making projects. The wattage of nail guns varies depending on the type and power source of the tool. Electric nail guns typically range from 100 watts to 1000 watts, while pneumatic nail guns rely on an air compressor for power. Fuel-powered nail guns utilize gas cartridges or fuel cells to generate the necessary power.
When using nail guns, always follow manufacturer instructions and take necessary safety precautions to prevent accidents or injuries. Proper handling, correct nailing techniques, and appropriate protective gear are essential.
Additional Considerations for Power Tool Usage
Now that we’ve explored the wattage ranges for various power tools, here are a few additional considerations to keep in mind when using power tools:
1. Efficiency and Power Consumption
While wattage is an important factor in determining a power tool’s performance, it’s not the sole indicator of efficiency. Higher wattage doesn’t always translate to better performance. Factors like motor efficiency, design quality, and the type of task being performed also play significant roles. Consider factors beyond wattage when evaluating a power tool’s overall performance and efficiency.
2. Safety Precautions
Safety should always be a top priority when using power tools. Follow manufacturer instructions, wear appropriate protective gear, and use tools as intended. Inspect tools for damage before use, keep cords and extension cords in good condition, and ensure a stable work surface. Taking these precautions can help prevent accidents and maintain a safe working environment.
3. Power Supply and Circuit Capacity
To ensure optimal performance and prevent electrical issues, it’s crucial to consider your power supply and the capacity of your electrical circuits. Higher wattage power tools may require circuits with increased amperage or dedicated circuits. Consult an electrician if you’re unsure about your electrical system’s capacity or need to make any modifications.
In conclusion, understanding the wattage of power tools is essential for making informed decisions when it comes to purchasing, using, and managing these tools. Different power tools have varying wattage ranges, with higher wattage models generally offering increased performance and capability. However, wattage alone does not determine a tool’s overall effectiveness, and factors like speed, torque, and quality of construction also contribute to their performance. By considering the wattage of power tools and following proper safety precautions, you can ensure efficient and safe use of these indispensable tools in your DIY or professional projects.
Key Takeaways: How Many Watts Do Power Tools Use?
- Power tools can use different wattages depending on their type and size.
- Smaller power tools like drills typically use around 600-800 watts.
- Larger power tools like circular saws may require 1200-1800 watts.
- Air compressors can use anywhere from 1000 to 3000 watts.
- It’s important to check the wattage of a power tool before using it to ensure it matches the capacity of your electrical system and outlets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on power tools and their watt usage. Below, we have answered some common questions related to how many watts power tools use. Read on to find out more!
What factors determine the wattage of a power tool?
The wattage of a power tool depends on various factors. The type of tool, its size, its purpose, and its motor’s power all play a role in determining the wattage. Larger tools, such as table saws or air compressors, tend to require more power and therefore have higher wattage. Additionally, tools that have multiple functions or that are equipped with additional features may also have higher wattage requirements. It’s important to consider all of these factors when determining the wattage of a power tool.
Why is knowing the wattage of a power tool important?
Knowing the wattage of a power tool is important because it helps you understand its power requirements and compatibility with your electrical system. It allows you to determine if the tool can be safely used with your current power source or if you need to make any electrical adjustments. Moreover, being aware of the wattage helps you avoid overloading your circuit and potential electrical hazards that can arise from using a tool that requires more power than your system can handle.
How can I find the wattage of a power tool?
Finding the wattage of a power tool is relatively straightforward. You can typically find this information in the tool’s specifications, which may be listed on the packaging or in the user manual. If you’re unable to find the wattage in those sources, you can try checking the manufacturer’s website, as they often provide detailed information about their products. Another option is to contact the manufacturer directly and inquire about the wattage of a specific tool model. This way, you can ensure that you have accurate and reliable information on the tool’s wattage.
Can different power tools have the same wattage?
Yes, it’s possible for different power tools to have the same wattage. Since the wattage of a power tool depends on various factors like motor power and size, it’s not uncommon for tools from different categories to have similar wattage requirements. For example, a circular saw and a power drill could have the same wattage if their motors have similar power ratings. Similarly, a small air compressor and a bench grinder could have the same wattage if they are designed with similar motor configurations. Therefore, when comparing power tools, it’s important to consider the wattage along with other factors to ensure that the tool meets your specific needs and requirements.
What can happen if I use a power tool with a wattage higher than my electrical system can handle?
If you use a power tool with a wattage higher than your electrical system can handle, it can lead to several issues. First, it can cause an overload on your circuit, causing a circuit breaker to trip or a fuse to blow. This can interrupt power supply to other devices on the same circuit. Additionally, using a power tool with excessive wattage can generate excessive heat in the wiring, potentially leading to a fire hazard. It’s essential to ensure that you use power tools with wattage requirements that are within the capacity of your electrical system to prevent these safety risks.

Volts, Amps, and Watts Explained
Summary
Power tools come in different sizes and types, which determine how many watts they use. Smaller tools, like drills and sanders, usually use around 500 to 1000 watts, while bigger tools, like table saws and miter saws, can use up to 2000 or more watts. It’s important to check the wattage requirement of each tool before using it.
It’s also crucial to use the right extension cords that can handle the wattage of the power tool. The length and thickness of the cord affect the amount of power it can handle. Be sure to match the cord’s gauge and length with the tool’s wattage to ensure safe and efficient operation. Understanding the wattage of power tools can help you choose the right tools for your projects and avoid electrical issues.