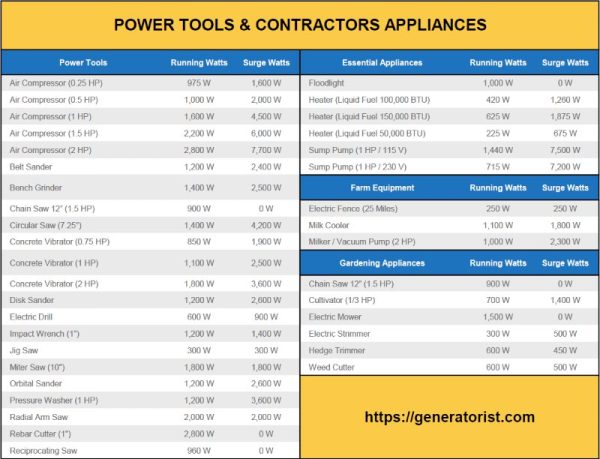
Hey there, curious minds! Have you ever wondered how many watts you need to power your favorite tools? Well, wonder no more! In this article, we’ll dive into the world of power tools and explore just how many watts it takes to make them go-go! So, grab your hard hat and join me on this electrifying adventure!
Picture this: you’re in your workshop, ready to take on a new project. You’ve got your trusty drill and jigsaw by your side, but before you can bring them to life, you need to know how many watts they require. That’s where we come in! We’ll uncover the power requirements of some common power tools, so you’ll never be left in the dark again.
Whether you’re a budding carpenter or a seasoned DIY enthusiast, understanding wattage is crucial. It’s like the horsepower of power tools. So, if you’re ready to unlock the secret to powering up your tools, let’s get this wattage party started! Get ready to turn it up to the max and unleash the true potential of your power tools!
Running power tools requires the right amount of wattage. To determine how many watts you need, follow these steps:
- Identify the power consumption (in watts) of each tool you’ll be using.
- Add up the wattages of all the tools.
- Consider any surge or startup wattage requirements.
- Factor in the efficiency rating of your power source.
- Choose a generator or power supply with a wattage capacity that exceeds your total requirements.
With these steps, you can ensure you have the right amount of power for your power tools.
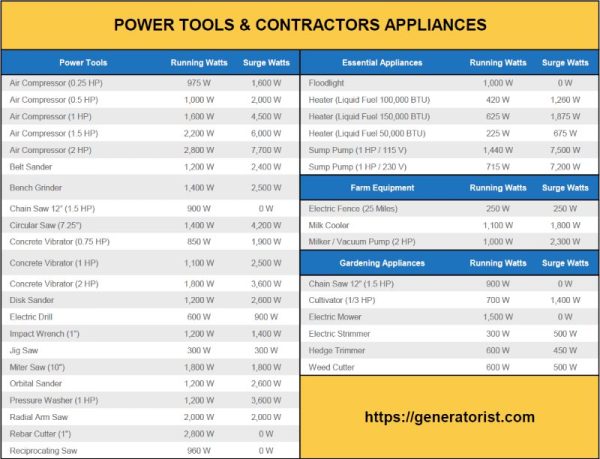
How Many Watts Do You Need to Run Power Tools?
Running power tools requires the right amount of wattage to ensure optimal performance. However, determining the exact number of watts needed can be a bit confusing. Factors such as the type of power tool, its power consumption, and the intended use all come into play. In this article, we will explore the world of power tools and break down how many watts you need to effectively operate them.
1. Understanding Power Tool Wattage
Power tools come in various sizes and types, each with its own power requirements. To understand the wattage needed to run power tools, it’s important to first grasp the concept of power consumption. Power consumption refers to the amount of electrical energy a device uses while in operation. This is typically measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
When considering how many watts you need to run power tools, it’s essential to look at both continuous and peak power requirements. Continuous power refers to the amount of power a tool uses during normal operation, while peak power refers to the maximum power it may consume for brief intervals. Determining the correct wattage for a power tool involves assessing its continuous power usage to ensure your power supply can handle it.
2. Calculating Wattage for Different Power Tools
The wattage required for power tools varies depending on the type of tool and the specific task at hand. Here are some common power tools and their typical wattage ranges:
– Circular saw: A circular saw typically requires around 1200 to 1800 watts of power. However, larger, more heavy-duty models may require up to 2300 watts.
– Drill: Electric drills usually range from 500 to 1000 watts, while cordless drills operate on lower wattages due to their battery-powered nature.
– Angle grinder: Angle grinders can require anywhere from 500 to 2500 watts, depending on their size and motor power. Higher-powered angle grinders are often used for more demanding tasks.
– Jigsaw: Jigsaws typically consume between 400 and 800 watts. Smaller, less powerful jigsaws may operate on the lower end of the wattage range.
– Power sander: The wattage for power sanders ranges from 200 to 1000 watts. Larger belt sanders generally require more wattage compared to smaller palm sanders.
Keep in mind that these wattage ranges are general guidelines and may vary depending on the specific brand and model of the power tool. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for accurate wattage requirements.
3. Tips for Determining Wattage and Power Supply
To determine the wattage you need to run power tools, follow these tips:
1. Check the power tool’s manual: The manufacturer’s manual usually provides detailed information about the wattage requirements for the tool.
2. Consider the task at hand: Different tasks may require more or less power. For heavy-duty or continuous use, opt for power tools with higher wattage capabilities.
3. Invest in a suitable power supply: Ensure your power supply, such as a generator or electrical outlet, can handle the wattage required by your power tools. Avoid overloading circuits by utilizing outlets on separate circuits or using a portable generator with adequate wattage.
4. Beware of power surges: Some power tools, especially those with motors, may experience power surges during startup. Make sure your power supply has the necessary surge protection to prevent damage to the tool or electrical system.
By understanding power tool wattage, calculating the wattage needed for specific tools, and following these tips, you can ensure that your power tools operate at their optimal performance levels. Always prioritize safety and consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for accurate wattage requirements. Happy DIY-ing!
Choosing the Right Power Tools for Your Projects
When it comes to power tools, it’s crucial to choose ones that are well-suited for the projects you plan to tackle. Having the right tool not only makes the task easier but also ensures better results. Whether you’re a professional contractor or a passionate DIYer, here are three essential power tool categories and what to consider when selecting the right ones.
1. Drills and Drivers: Versatility and Power
Drills and drivers are a staple in any toolbox and offer versatility for a wide range of projects. When choosing a drill or driver, consider the following:
– Power source: Decide between corded drills, which offer consistent power but require a nearby outlet, or cordless drills that provide more freedom but may have limited battery life.
– Chuck size: The chuck size determines the maximum diameter of the drill bit or driver attachment. Consider the types of projects you’ll be working on and choose a chuck size accordingly.
– Torque settings: Look for a drill or driver with adjustable torque settings. This feature allows you to control the power output, essential for driving screws without stripping or damaging the material.
– Speed options: Opt for a tool with variable speed settings to achieve greater control over different materials. Lower speeds are suitable for driving screws, while higher speeds are better for drilling holes.
2. Saws for Precise Cuts
Saws are indispensable when it comes to woodworking and other projects that require precise cuts. Here’s what to consider when choosing a saw:
– Circular saw: Look for a model with adjustable cutting depth and bevel options. Some circular saws also feature built-in guides for more accurate cuts.
– Jigsaw: Consider the saw’s cutting capacity and orbital action settings. The ability to vary the blade’s action can enhance the saw’s performance on different materials.
– Miter saw: Evaluate the size of the miter saw based on the material dimensions you’ll be working with. Also, check for features like adjustable bevel and positive stops for common angles.
3. Sanders for a Smooth Finish
Sanders are essential for achieving a smooth, well-finished surface. When choosing a sander, keep these factors in mind:
– Power source: Sanders are available in corded and cordless options. Consider the tool’s usage and whether a constant power supply or portability is more important for your projects.
– Sanding pad size: Different sanding pads suit different projects. Larger pads cover more surface area, making them suitable for larger projects, while smaller pads offer more precision for intricate work.
– Variable speed control: Look for sanders with adjustable speed settings. This allows you to modify the speed based on the material and the desired finish.
– Dust collection: Sanders generate a significant amount of dust. Opt for models with built-in dust collection systems or the ability to connect to a vacuum for a cleaner working environment.
By considering these factors and understanding the specific requirements of your projects, you can choose power tools that will help you achieve outstanding results.
Power Tool Safety: Tips for Safe Operation
Operating power tools requires caution and adherence to safety measures to prevent accidents and injuries. Here are some essential tips for safely using power tools:
1. Read the Manual
Before using any power tool, thoroughly read the manufacturer’s manual. Familiarize yourself with the tool’s features, proper operation, maintenance, and safety precautions. Understanding the manufacturer’s instructions will help you safely operate the tool and prevent accidents.
2. Wear Appropriate Protective Gear
Always wear the necessary protective gear when using power tools. This includes safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris, ear protection to prevent hearing damage, and gloves to provide grip and reduce injury risks. Depending on the tool and the task, consider additional protective gear such as a dust mask or a face shield.
3. Use Tools in Proper Working Condition
Inspect your power tools before each use to ensure they are in good working condition. Check for any signs of damage, frayed cords, or loose parts. Do not use a tool if it appears faulty or if you suspect any issues. Regularly maintain and clean your tools to prolong their lifespan and ensure safe operation.
4. Secure Your Work Area
Maintain a clean and well-organized work area to minimize the risk of accidents. Remove any obstacles, debris, or tripping hazards from the area where you will be operating the power tool. If possible, secure your workpiece using clamps or other appropriate methods to ensure stability during operation.
5. Practice Proper Handling
Follow these handling tips to operate power tools safely:
– Hold the tool with both hands: Use a firm grip with both hands, keeping them away from the cutting or moving parts.
– Keep a proper stance: Maintain a stable footing and a balanced posture while operating the tool.
– Do not force the tool: Let the tool do the work at its own pace. Forcing a power tool can lead to loss of control and accidents.
– Disconnect power when not in use: When changing blades or bits, or during any maintenance, be sure to disconnect the tool from the power source to prevent accidental startup.
By following these safety tips and always prioritizing caution, you can reduce the risk of accidents and injuries when using power tools.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Power Tools
In addition to understanding how many watts you need to run power tools, it’s essential to choose the right power supply. Whether you’re working in a workshop or a remote location, selecting the appropriate power source ensures the smooth operation of your tools. Here are three common power supply options for power tools:
1. Outlets and Extension Cords
Using electrical outlets is the simplest and most convenient power supply option for many power tools. Ensure the outlet can handle the required wattage by checking its voltage and amperage rating. Additionally, choose the appropriate extension cord that matches the tool’s power requirements. Longer cords may have higher resistances, so opt for shorter cords whenever possible.
2. Generators
Generators provide a portable and independent power supply, making them ideal for construction sites, outdoor projects, and remote locations. When choosing a generator, consider the following factors:
– Wattage output: Ensure the generator has enough wattage to meet the requirements of your power tools. Consider the combined wattage of all the tools you may be using simultaneously.
– Fuel type: Generators can be powered by gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. Choose a fuel type that suits your needs, availability, and environmental considerations.
– Noise level: Some generators can be noisy, especially larger models. If noise is a concern, look for generators specifically designed for quiet operation.
3. Battery-Powered Tools
Battery-powered tools offer mobility and convenience. They are ideal for small projects or when access to power sources is limited. When choosing battery-powered tools, consider the following:
– Battery capacity: The battery capacity determines how long the tool can operate before needing a recharge. Consider the project duration and the tool’s runtime to ensure the battery can handle the workload.
– Battery compatibility: If you plan to invest in multiple battery-powered tools, opt for ones that use the same battery platform. This allows you to interchange batteries and maximize their utility.
– Charging options: Check for charging options for the batteries, such as fast chargers or dual battery ports. Quick charging capabilities can minimize downtime and keep your projects running smoothly.
By selecting the appropriate power supply for your power tools, you can ensure uninterrupted operation and efficient workflow. Consider your specific needs and the type of projects you’ll be working on to make the best choice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how many watts you need to run power tools is crucial for their efficient operation. Different power tools require varying wattages, depending on their type and intended use. By assessing the continuous power requirements of your tools, you can determine the suitable wattage needed.
When choosing power tools, consider their power source options, specific features, and compatibility with your projects. Always prioritize safety when operating power tools and follow proper handling and maintenance procedures.
Lastly, selecting the right power supply for your power tools is essential. Whether using outlets and extension cords, generators, or battery-powered tools, ensure that the power source can meet the required wattage and provide consistent and reliable operation.
By following these guidelines and considering the specific requirements of your projects and tools, you can confidently use power tools to complete your tasks efficiently and safely.
Key Takeaways: How Many Watts Do You Need to Run Power Tools?
1. Power tools require different wattage levels depending on their type. For example, an electric drill typically needs around 600-700 watts, while a circular saw might require 1,200-1,500 watts.
2. It’s important to check the power tool’s user manual or label for the specific wattage requirement.
3. If you plan to use multiple power tools simultaneously, add up their individual wattage requirements to ensure your power source can handle the load.
4. Consider the power tool’s efficiency and potential power spikes during usage. Oversizing the wattage of the power source can provide a safety margin.
5. In general, it’s best to have at least a 15-amp circuit and a power source with a wattage capacity higher than the total wattage of the power tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to running power tools, understanding how many watts you need is essential. Here are some commonly asked questions related to power tools and their wattage requirements.
1. How can I determine how many watts a power tool requires?
The wattage required by a power tool can usually be found on the tool itself or in the owner’s manual. This information is often listed as “power consumption” or “power input.” If you can’t find the wattage listed, you can also calculate it by multiplying the voltage (V) by the current (A) listed on the tool, using the formula: watts = volts x amps.
It’s important to note that the wattage listed for a power tool indicates its maximum power consumption. In reality, the tool may not always operate at its maximum wattage. Understanding the maximum wattage can help you determine if your power source can handle the tool’s power requirements.
2. Can I use a power tool with a wattage lower than what’s recommended?
Using a power tool with a lower wattage than what is recommended can have negative consequences, such as reduced performance or even damage to the tool. When a power tool doesn’t receive enough wattage, it may not function as intended and may overheat. This can lead to shortened tool lifespan and potential safety hazards.
Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure that the wattage of your power tool matches or exceeds the recommended wattage. This will help optimize performance, maintain tool longevity, and ensure personal safety during use.
3. What happens if I use a power tool with a higher wattage?
Using a power tool with a higher wattage than what is recommended is generally safe. However, it’s important to consider the power source’s capacity. If the power source (such as an outlet or generator) cannot handle the higher wattage, it may overload and trip a circuit breaker or blow a fuse.
Additionally, using a power tool with a higher wattage than necessary may lead to unnecessary energy consumption and increased operating costs. It is always best to use a power tool with the appropriate wattage for the job at hand.
4. Do cordless power tools have wattage requirements?
Cordless power tools do not have specific wattage requirements since they are battery-powered. However, they still have power ratings, often measured in volts (V) or amp-hours (Ah). These ratings indicate the power and capacity of the battery, which can affect the tool’s performance and runtime.
It’s important to pay attention to the battery specifications when choosing a cordless power tool. Higher voltage or higher amp-hour ratings generally indicate more power and longer runtime. However, it’s essential to strike a balance between power and portability, as higher ratings may result in heavier batteries.
5. Can I use a power tool with a wattage higher than my generator’s rating?
Using a power tool with a wattage higher than your generator’s rating can overload the generator and cause it to trip or fail. It’s crucial to ensure that the total wattage of the power tools you want to use does not exceed the generator’s rated wattage capacity.
To determine the compatibility between the tools and the generator, add up the wattage requirements of all the tools you plan to run simultaneously. Ensure that this total does not surpass the generator’s maximum wattage. This way, you can avoid overloading the generator and maintain efficient and safe power tool operation.
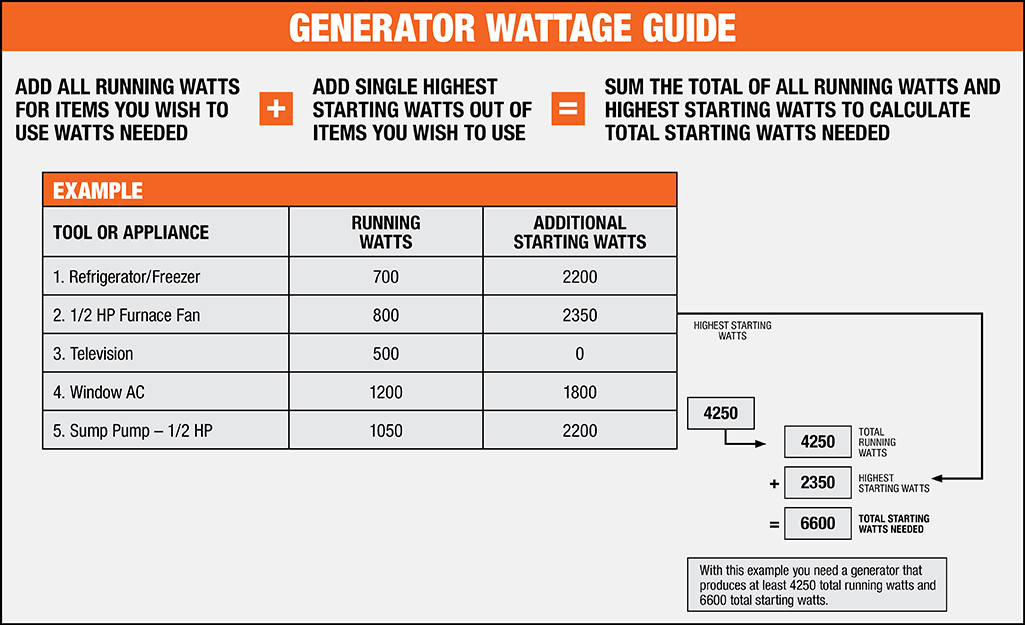
What size generator do I need for power tools compressor & more. Using volts x amps = watts formula.
Summary
Okay, let’s wrap it up! So, when it comes to running power tools, it’s important to know how many watts you need. Remember, each tool has its own wattage requirement. To find out how many watts your tool needs, check the manufacturer’s instructions or the tool’s label. Make sure your power source, like a generator or outlet, can provide enough watts to handle your tool. And don’t forget, it’s always better to have a power source that can handle more watts than your tool requires. This way, you won’t risk damaging your tools or causing any electrical problems. Play it safe and use the right amount of watts for your power tools!