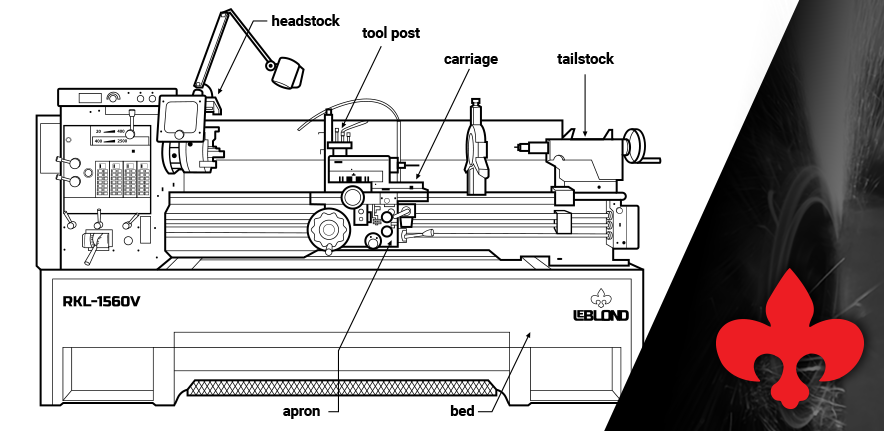
Are you curious about how a lathe machine works and what its main parts are? Well, you’re in the right place! In this article, we’re going to explore the fascinating world of lathe machines and break down their key components. So, buckle up and get ready to dive into the exciting world of machining!
You might be wondering, what exactly is a lathe machine? Simply put, a lathe machine is a powerful tool used in metalworking to shape and cut various materials with precision. It’s like a sculptor’s chisel, but for metal! Whether you’re creating intricate designs or turning long cylindrical pieces, a lathe machine gets the job done.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the main parts of a lathe machine. First up, we have the bed. Think of it as the sturdy backbone of the machine, providing stability and support for all the other components. Next, we have the headstock, where the main power source and spindle are located. This is where the magic happens, as the spindle rotates the workpiece and allows for precise cutting and shaping. Lastly, we have the carriage, which moves along the bed and holds the cutting tools. It’s like the lathe machine’s faithful sidekick, assisting in the machining process.
So, whether you’re a budding metalworker or simply a curious mind, understanding the main parts of a lathe machine is an exciting step into the world of machining. Now that we’ve laid the groundwork, let’s dive deeper into each component and explore their fascinating functions. Let the lathe machine adventure begin!
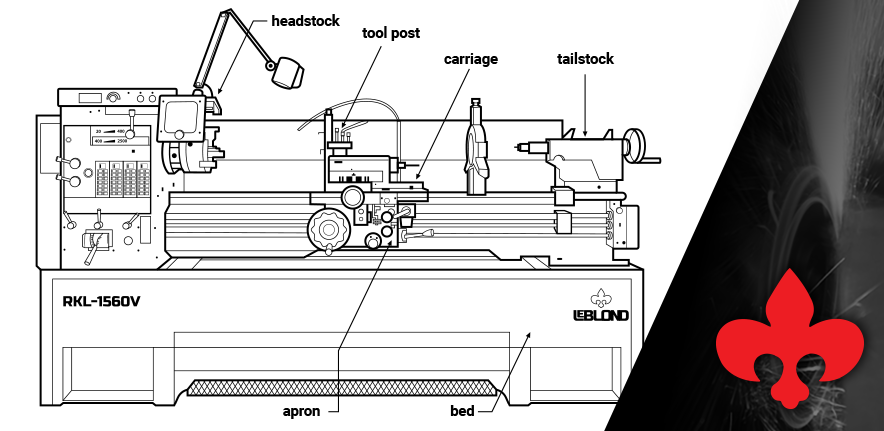
Exploring the Main Parts of a Lathe Machine
Lathe machines are powerful tools used in various industries, such as metalworking and woodworking, to shape and cut materials with precision. Understanding the main parts of a lathe machine is crucial for operating the machine effectively and ensuring optimal results. In this article, we will delve into the different components that make up a lathe machine and their functions, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential piece of equipment.
1. Bed
The bed is the foundation of a lathe machine, serving as a sturdy base upon which other components are mounted. It is typically made of cast iron, offering durability and stability. The bed provides support for the carriage and tailstock, maintaining their alignment and allowing for smooth movement along the machine’s length. It also houses key components such as the headstock and feed mechanism. A well-designed bed ensures minimal vibrations and enhances the accuracy of the machining process.
The length and width of the bed depend on the size of the lathe machine, with longer beds accommodating larger workpieces. To prevent wear and tear, the bed is often coated with a protective layer and equipped with features like T-slots for attaching fixtures and accessories. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the bed are essential to ensure its longevity and optimal performance.
2. Headstock
The headstock is a vital component of the lathe machine, located at the left end of the bed. It houses the main spindle, which rotates the workpiece, and other essential parts like gears, pulleys, and bearings. The spindle is driven by an electric motor, which can be adjusted to control the speed of the rotation. This versatility allows for a wide range of cutting speeds, enabling the machining of different materials and achieving desired finishes.
The headstock also contains a chuck, a device that securely clamps the workpiece and holds it in place during machining. Chucks come in various types, such as three-jaw chucks for holding cylindrical workpieces and four-jaw chucks for irregularly shaped objects. The headstock is often equipped with a spindle lock, which immobilizes the spindle for easy changing of chucks or other accessories. Proper lubrication and regular maintenance of the headstock ensure smooth operation and extend its lifespan.
3. Tailstock
The tailstock, also known as the live center, is positioned on the right end of the lathe machine’s bed and serves as a support for the opposite end of the workpiece. It consists of a movable spindle, which can be adjusted longitudinally to accommodate workpieces of varying lengths. The tailstock spindle is fitted with a live center, which rotates with the workpiece, reducing friction and supporting the material during machining.
The tailstock is equipped with a handwheel or lever for easy movement and locking of the spindle, allowing for precise positioning of the workpiece. It also often features a morse taper, a standardized fitting used for attaching tools or centers to the machine. A properly aligned tailstock ensures the accurate centering of the workpiece and prevents any deflection during the machining process.
4. Carriage
The carriage is the component that moves along the length of the lathe machine’s bed and holds various cutting and shaping tools. It consists of several parts, including the saddle, cross-slide, compound rest, apron, and tool post. The saddle is mounted on the bed and provides support for the other carriage components.
The cross-slide, situated on top of the saddle, allows for lateral movement of the tool in relation to the workpiece, enabling precise cuts and shaping. The compound rest, located on top of the cross-slide, provides an additional level of movement, allowing for angled cuts and intricate designs. The apron houses the gears and levers responsible for controlling the feed mechanism, which moves the carriage along the bed.
The tool post is an essential part of the carriage, holding the cutting tools securely and enabling their adjustment and positioning. It is typically mounted on top of the compound rest and can accommodate various types of tool holders. The carriage is crucial for controlling the depth, direction, and speed of the cutting process, determining the precision and quality of the machined workpiece.
5. Tool Holders
Tool holders are accessories that attach to the tool post and secure the cutting tools in place during machining. They come in various forms, including single-tool holders, turret tool holders, and quick-change tool holders. Single-tool holders are simple and allow for the attachment of a single cutting tool, while turret tool holders can hold multiple tools simultaneously, enabling faster tool changes. Quick-change tool holders are designed for efficient and rapid tool swapping, reducing downtime during operations.
Tool holders play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and accuracy of cutting tools. They provide a secure grip on the tools, minimizing vibrations and ensuring precise machining. Different cutting operations require specific tool types, such as turning tools, boring tools, and threading tools. Tool holders must be chosen accordingly to accommodate the specific cutting requirements and achieve optimal results.
6. Feed Mechanism
The feed mechanism in a lathe machine is responsible for moving the carriage along the bed, controlling the rate and direction of movement. It consists of gears, shafts, and levers that transfer power from the main spindle to the carriage. The feed mechanism offers both longitudinal and cross-feed movements, allowing for the machining of different shapes and contours on the workpiece.
The feed rate can be adjusted to achieve desired cutting speeds and depths, ensuring precision and accuracy. A properly functioning feed mechanism is crucial for achieving smooth and consistent cutting operations. Regular lubrication and maintenance of the feed mechanism are necessary to prevent excessive wear and extend its lifespan.
7. Chip Pan
The chip pan is a container located below the lathe machine that collects the chips and debris produced during the machining process. As the workpiece is cut and shaped, small metal or wood chips are generated and expelled from the cutting area. The chip pan prevents the chips from scattering and accumulating, keeping the workspace clean and reducing the risk of accidents or damage.
Regular cleaning and emptying of the chip pan are necessary to maintain a safe and efficient working environment. Excessive accumulation of chips can interfere with the machine’s operation and even cause damage to its components. Proper disposal of the collected chips is also essential for proper waste management and environmental sustainability.
Additional Considerations for Lathe Machine Parts
1. Lubrication and Maintenance
Proper lubrication and regular maintenance of the lathe machine parts are essential for optimal performance and longevity. Lubrication prevents friction and wear, ensuring smooth movement and reducing the risk of breakdowns. Each component, from the spindle to the feed mechanism, should be adequately lubricated according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Regular inspections and cleaning are also necessary to identify any potential issues or damage early on.
2. Safety Measures
Operating a lathe machine involves inherent risks, and implementing safety measures is crucial to protect operators and prevent accidents. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses and gloves, when working with the machine. Familiarize yourself with the machine’s safety features, such as emergency stop buttons and safety guards, and use them as required. Proper training and supervision are essential for safe and responsible lathe machine operation.
3. Upgrades and Accessories
Depending on your specific machining needs, there are numerous upgrades and accessories available for lathe machines. These include digital readouts (DROs) for precise measurements, coolant systems for heat and chip management, and tool-setting and tool-lowering devices for enhanced efficiency. Research the available options and consult with experts to determine which upgrades and accessories would benefit your machining operations.
In summary, understanding the main parts of a lathe machine is crucial for operating the machine effectively and achieving accurate and high-quality results. Components such as the bed, headstock, tailstock, carriage, tool holders, feed mechanism, and chip pan all play important roles in the machining process. Proper maintenance, adherence to safety guidelines, and considering additional accessories and upgrades can further enhance the capabilities and performance of a lathe machine. Whether you’re a professional machinist or an enthusiast, knowing your lathe machine inside and out is the key to success in the world of precision machining.
Key Takeaways: What are the Main Parts of a Lathe Machine?
- A lathe machine has a bed, which is the foundation that supports the other parts.
- The headstock is located at one end of the bed and holds the spindle.
- The tailstock is situated at the other end of the lathe and helps support and stabilize the workpiece.
- The carriage moves along the bed and houses the cutting tool, allowing it to move across the workpiece.
- The chuck is used to hold the workpiece securely in place while it rotates.
Frequently Asked Questions
Curious about the main components of a lathe machine? Look no further! Below are five engaging questions and answers to help you understand the main parts of a lathe machine:
1. What is the purpose of the headstock in a lathe machine?
The headstock is a critical part of a lathe machine. It houses the main spindle, which is responsible for holding the workpiece firmly in place. The headstock also contains the gearbox, allowing the operator to choose different speeds for the spindle rotation. This enables the lathe to work on different types of materials and create various shapes and sizes.
Essentially, the headstock acts as the powerhouse of the lathe machine, providing the necessary rotational force to carry out the machining operations accurately and efficiently.
2. What role does the tailstock play in a lathe machine?
The tailstock is another crucial component of a lathe machine. It helps support the workpiece and prevents it from vibrating or moving while machining operations are being carried out. The tailstock is generally adjustable, allowing the operator to extend or retract it as needed.
Furthermore, the tailstock often houses a live center or a dead center, depending on the type of lathe machine. These centers provide additional support to the workpiece, ensuring stability and precision during the machining process.
3. What are the main parts of the carriage in a lathe machine?
The carriage is responsible for holding and moving the cutting tool during machining operations. It consists of several important components, including the saddle, cross-slide, and compound rest.
The saddle is the base of the carriage and travels along the lathe bed, supporting the cross-slide and compound rest. The cross-slide moves perpendicular to the lathe bed and allows for precise cutting tool movement. The compound rest, on the other hand, enables the operator to make angled cuts by adjusting its position.
4. What is the function of the apron in a lathe machine?
The apron is an essential part of a lathe machine and is located at the front of the carriage. Its primary function is to house and control the various mechanisms that drive the carriage and enable different operations.
Within the apron, you’ll find components such as gears, clutches, and levers. These mechanisms are used to engage or disengage the carriage during threading, feed, or other operations, providing the necessary control for precise machining.
5. What are the main parts of the toolpost in a lathe machine?
The toolpost is an integral part of a lathe machine that holds the cutting tool securely in place. It allows for easy tool change and precise alignment, ensuring accurate and efficient machining.
The main components of the toolpost include the base or body, which is attached to the carriage, and the tool holder, where the cutting tool is mounted. Additionally, quick-change toolposts are also available, which allow for rapid tool changes without the need for realignment.
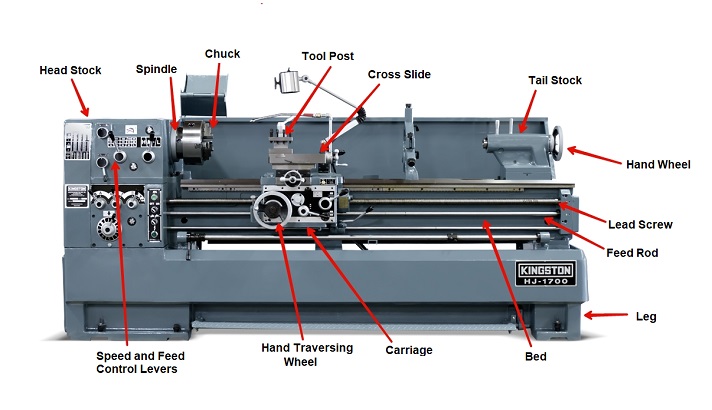
Summary
A lathe machine has three important parts: the bed, the headstock, and the tailstock.
The bed is the main foundation of the machine, providing support and stability. The headstock houses the main motor and controls the spindle, which holds the material being worked on. The tailstock secures the other end of the material and helps keep it in place. Together, these parts work harmoniously to shape and create various objects with precision and accuracy. Learning about these key parts can help you understand how a lathe machine functions and what it can do.