Are you curious about how drill bits are numbered? Well, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’re going to dive into the fascinating world of drill bits and uncover the secrets behind their numbering system. So, if you’ve ever wondered why drill bits have those mysterious numbers on them, keep reading to satisfy your curiosity!
Have you ever noticed those numbers on drill bits and wondered what they mean? It’s not just random gibberish, I promise! In fact, the numbers on drill bits serve a specific purpose. They indicate the size of the drill bit and help you choose the right one for your project. But how exactly are these drill bits numbered? That’s what we’re here to find out!
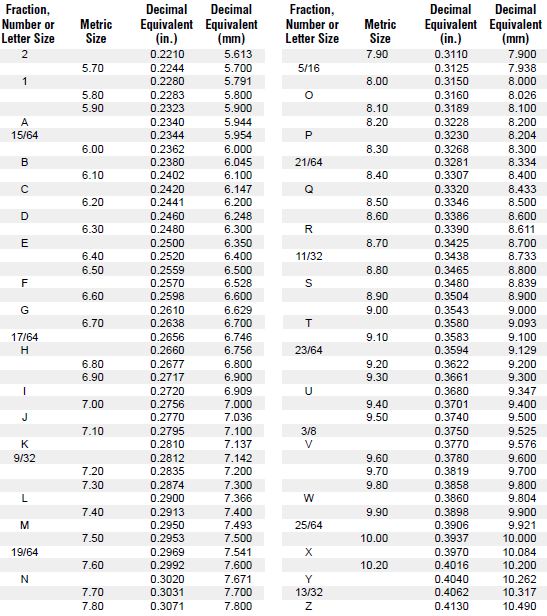
So, how are drill bits numbered? Good question! Drill bit sizes are typically indicated using a numerical system or a combination of letters and numbers. These numbers or letters represent the diameter of the bit. The most commonly used system is the fractional inch system, where a number like 1/16, 1/8, 3/16, and so on, corresponds to the bit’s diameter. But that’s not the only system out there! We’ll explore other numbering systems too, so get ready for a journey into the world of drill bits!

How Are Drill Bits Numbered? Exploring the Numbering System Behind Drill Bits
Drill bits are essential tools for any DIY enthusiast or professional contractor. They come in various sizes and types, allowing for different drilling applications. But have you ever wondered how drill bits are numbered? The numbering system behind drill bits may seem confusing at first, but once you understand it, choosing the right drill bit becomes a breeze. In this article, we will delve into the world of drill bit numbering and uncover the secrets behind their classification.
1. Understanding Fractional Inch Sizes
Drill bits are commonly labeled with fractional inch sizes, such as 1/8″, 1/4″, or 1/2″. These measurements refer to the diameter of the drill bit shaft. For example, a 1/8″ drill bit has a shaft diameter of 1/8 of an inch. The smaller the fraction, the thinner the drill bit. Fractional inch sizes are often used for general-purpose drilling tasks and are suitable for both wood and metal.
When using fractional inch sizes, it’s important to note that the increments between sizes can be quite small. For instance, the difference between a 1/16″ and a 3/32″ drill bit may seem minuscule, but it can have a significant impact on the accuracy of your drilling. It’s crucial to choose the right size for your specific project to achieve the desired results.
2. Decoding Numbered Gauge Sizes
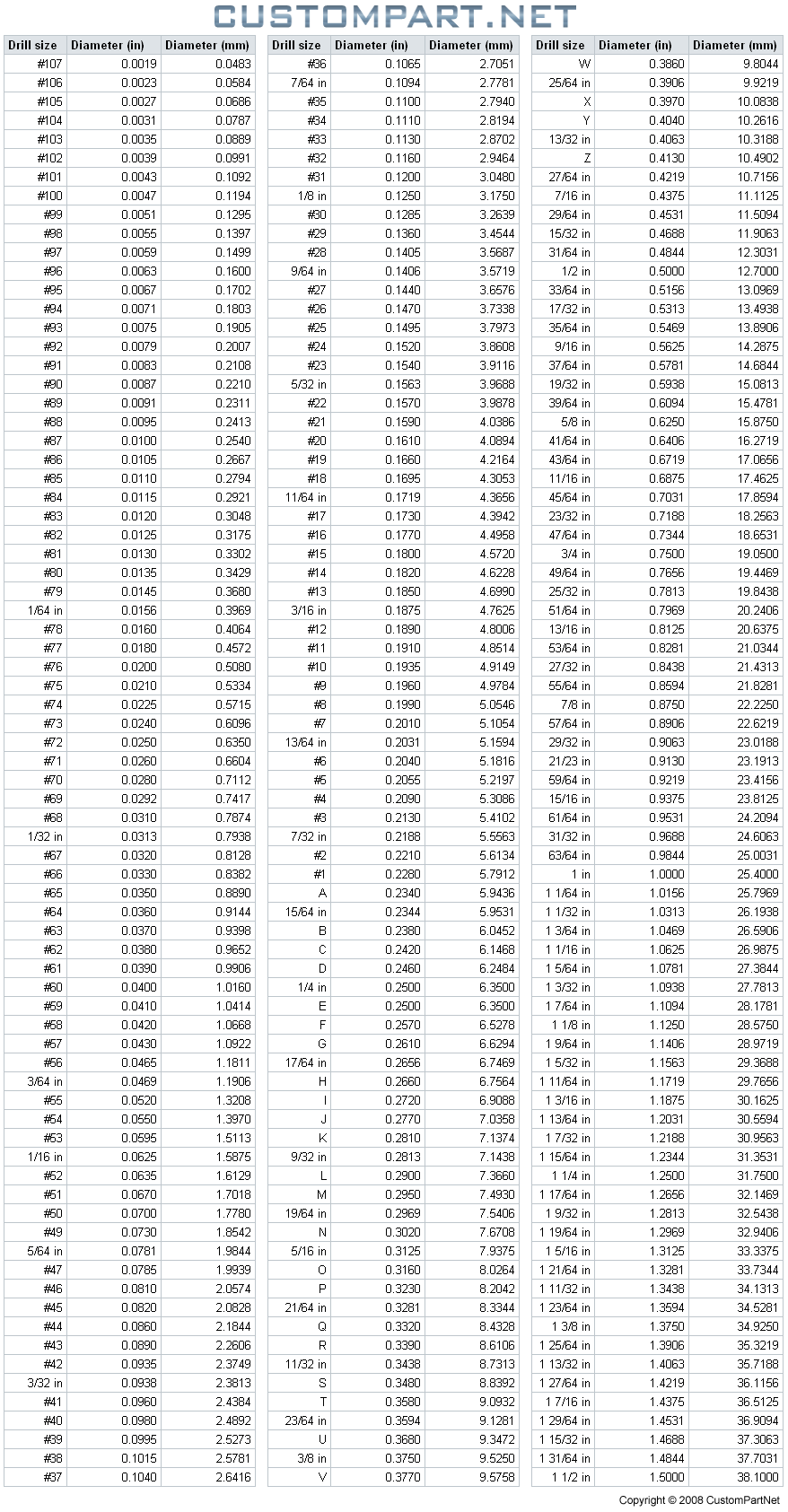
In addition to fractional inch sizes, drill bits are also classified using numbered gauge sizes. These gauge sizes are commonly used for measuring drill bits with smaller diameters, especially those used for precision work. Unlike fractional inch sizes, which have a range of options, numbered gauge sizes follow a specific sequence.
The numbering system for gauge sizes starts from the thinnest drill bit, which is numbered as 80. As the numbers increase, the drill bit diameter increases as well. For example, a drill bit numbered 60 is larger in diameter than a drill bit numbered 80. The sequence continues until it reaches the thickest drill bit, which is numbered 1. After that, the sizes switch to fractional inch measurements.
3. Exploring Metric Sizes
Drill bits are also available in metric sizes, which follow the International System of Units. Metric sizes use millimeters as the unit of measurement and are widely used in countries that have adopted the metric system. Unlike fractional inch and numbered gauge sizes, the metric sizing system offers a more precise and standardized way of selecting drill bits.
Metric sizes range from the smallest, which can be as thin as 0.2 mm, to larger sizes exceeding 50 mm. These drill bits are often used for specialized applications or when working with materials that require precise measurements. The metric sizing system provides greater accuracy and consistency, making it a popular choice in many industries.
4. Navigating Combination Drill Bit Sets
Combination drill bit sets offer a wide range of sizes and types to accommodate various drilling needs. These sets often include drill bits with both fractional inch and metric measurements, allowing users to work with different materials and achieve precise results. By having a combination set, you can tackle a wider range of projects without the need to purchase individual drill bits.
When selecting a combination drill bit set, consider the projects you frequently work on and the materials you commonly drill into. This will help you determine the specific sizes and types of drill bits you need. It’s also worth noting that some combination sets may feature additional drill bit types, such as spade or step drill bits, to further expand your capabilities.
5. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Drill Bit
Choosing the right drill bit goes beyond understanding their numbering system. There are several factors to consider to ensure you select the most suitable drill bit for your project. Here are a few key considerations:
Material:
Different materials require different types of drill bits. For example, masonry drill bits are designed for drilling into concrete or brick, while wood drill bits are specifically made for drilling into wood. Consider the material you will be working with to determine the appropriate drill bit type.
Application:
Consider the specific drilling application you will be undertaking. Are you drilling pilot holes, creating larger holes, or enlarging existing holes? Each application may require a different type and size of drill bit.
Speed and Power:
The drill speed and power you will be using also impact the choice of drill bit. Some materials may require slower speeds to prevent overheating or damage, while others may require more power to drive through tough surfaces. Ensure your drill and drill bit are compatible in terms of speed and power requirements.
Coating:
Certain drill bits come with coatings that enhance their durability, reduce friction, or improve heat resistance. Coated drill bits are often recommended for heavy-duty applications or when drilling into harder materials. Consider the coating options available and choose one that suits your specific needs.
In conclusion, understanding how drill bits are numbered is key to selecting the right tool for the job. Whether you’re using fractional inch sizes, numbered gauge sizes, or metric sizes, knowing the diameter and type of drill bit you need will ensure successful drilling outcomes. Additionally, considering factors such as material, application, speed, power, and coating will help you make an informed decision when choosing a drill bit. So next time you embark on a drilling project, remember to crack the code behind drill bit numbering and make the perfect choice.
Key Takeaways: How Are Drill Bits Numbered?
- Drill bits are numbered based on their size.
- The numbering system used for drill bits is not consistent across all countries.
- Common numbering systems include fractional, lettered, and numbered drills.
- Drill bit sizes are often represented by a combination of numbers and letters.
- Understanding drill bit numbering is important for selecting the right bit for the desired hole size.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to drill bits, understanding how they are numbered can be confusing. Here are some common questions and answers to help you unravel the mystery.
1. What do the numbers on drill bits mean?
The numbers on drill bits refer to their diameter. They represent the size of the hole that the bit will create. For example, a drill bit labeled as “1/8 inch” will create a hole with a diameter of 1/8 inch.
It’s important to note that drill bit sizes are typically given in fractional inches, although there are also metric measurements available. Understanding drill bit numbering will help you select the right bit for your project.
2. How are drill bit sizes numbered?
Drill bit sizes are numbered using a system called the “fractional inch” system. In this system, drill bits are labeled with a fraction that represents the bit’s diameter. The numerator of the fraction denotes the size of the bit, while the denominator indicates the number of 1/64-inch increments the size represents.
For example, a drill bit labeled as “3/16 inch” means that the bit has a diameter equivalent to 3/16 of an inch. Similarly, a bit labeled as “7/64 inch” has a diameter that is 7/64 of an inch.
3. Are there other systems for drill bit numbering?
Yes, apart from the fractional inch system, there are other systems used to number drill bits. One such system is the metric system, which uses millimeters to specify drill bit sizes. Metric drill bits are labeled with sizes like 3 mm, 6 mm, etc.
In addition, there is also the wire gauge system for numbering drill bits. This system is commonly used for smaller sized drill bits and assigns a number to each size. For example, a #7 drill bit has a different diameter than a #12 drill bit.
4. Can I convert drill bit sizes between different numbering systems?
Yes, it is possible to convert drill bit sizes between different numbering systems, although it may require some calculations. There are online conversion charts available that can help you convert drill bit sizes from fractional inches to metric or wire gauge, and vice versa.
Additionally, some drill bit sets come with bits labeled in multiple sizing systems, making it easier to work with different measurement systems for various projects.
5. Are drill bit sizes standardized across all manufacturers?
While there is some degree of standardization, it’s important to note that drill bit sizes can vary slightly between manufacturers. This is especially true for smaller sizes and specialty bits.
When precision is crucial, it’s recommended to double-check the sizing with the specific manufacturer or use a precision measuring tool to ensure a perfect fit for your project.
Summary
Drill bits are numbered based on their size and purpose. The size is indicated by a number or letter combination, while the purpose is represented by different types of bits. For example, twist bits are used for general drilling, while masonry bits are designed for concrete and stone. It’s important to use the right type and size of drill bit for the task at hand to ensure successful drilling.
When it comes to numbering, drill bits may follow different systems depending on the country. In the United States, fractional inch sizing is commonly used, while metric sizing is common in other parts of the world. Decimal inch sizing is another variation. By understanding these numbering systems, it becomes easier to choose the correct drill bit for your drilling needs. Remember to always check the packaging or consult a drill bit chart for guidance.